Use Camera to Get Point Cloud, Generate Target Object Model, and Configure Pick Point Manually
In this workflow, you can use the point cloud acquired by the camera to generate a point cloud model and create a target object.
|
Before selecting this workflow, ensure that the current project contains the “Capture Images from Camera” Step, and that the camera is connected or the virtual mode is enabled. |
On the homepage of the target object editor, click Select under the Get point cloud by camera workflow, and set the target object name to enter the configuration process. The overall configuration process is shown in the figure below.

-
Acquire the point cloud: Use the current project to acquire the point cloud. Then adjust the parameters and set the 3D ROI to generate a point cloud model.
-
Edit model: Edit the generated point cloud model, including the calibration of the object center point and configuration of the point cloud model, to ensure better performance of the subsequent 3D matching.
-
Set pick point: Set the pick point or add the pick point array on the edited point cloud model.
-
Set collision model (optional): Generate the collision model for collision detection during path planning.
The following sections provide detailed instructions on the configuration.
Acquire Point Cloud
After entering the configuration process, the point cloud should be acquired first to generate the point cloud model.
Set Project Information
Select the “Capture Images from Camera” Step in the current project to acquire the point cloud. Then click Acquire point cloud, and then the result can be viewed in the visualization area.
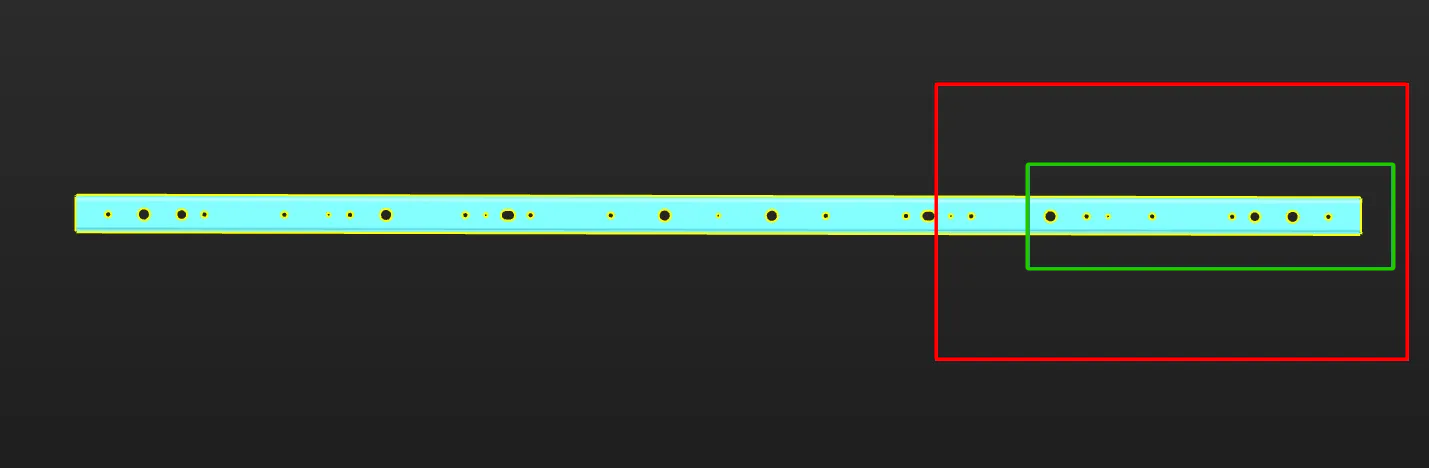
Note that when the camera’s field of view cannot cover the entire target object, priority should be given to ensuring that the key areas of the object are within the camera’s field of view.
The figure below shows an example of a long sheet metal part. Assuming that the region marked by the red frame on the right is the camera’s FOV, it is recommended to select the point cloud within the region marked by the green frame as the point cloud model for matching stability. Make sure that the region marked by the green frame is within the camera’s FOV when acquiring data. Specifically, the right edge part should be within the camera’s FOV.
Record Robot Flange Pose at Image-Capturing Point
If the camera is mounted in the EIH mode, you can click the Obtain current pose button to obtain the robot flange pose when capturing the point cloud. Please note:
-
The pose refers to the robot flange pose, not the TCP.
-
The pose corresponds to the robot flange pose at the image-capturing point.
-
Carefully check the values to avoid errors.
Preprocess Parameters
To remove interference points and speed up processing in subsequent Steps, you can perform preprocessing on the point cloud. For detailed explanations of the parameters, refer to Preprocessing Parameters.
|
If the “3D Target Object Recognition” Step is used in the project, you can enable Use parameters of Step “3D Target Object Recognition”, and then the parameter values in the “3D Target Object Recognition” Step will be synchronized. This improves the accuracy of 3D matching. |
Set ROI and Background
To quickly remove irrelevant point clouds in the scene and extract the target object point cloud, you can set an ROI and remove the background.
If you need to remove the background by capturing the image of the background, you must move the target object out of the camera’s view after acquiring the point cloud. Then click Capture and remove background, and the tool will automatically capture an image of the background and remove the point cloud of the background.
Now the point cloud acquisition is completed. You can click Next to start editing the generated point cloud model.
Edit Point Cloud Model
The generated point cloud model should be edited for better performance in the subsequent 3D matching.
Edit Point Cloud
When generating a point cloud model by acquiring the point cloud of a target object with the camera, make sure that the point cloud acquired by the camera accurately reproduces the features of the target object and removes any interfering parts from the point cloud. Refer to Edit Point Cloud for detailed instructions on removing the interference points.
The figure below shows the point cloud model of a gearbox housing. The background point cloud below the housing and the cohesive point cloud (in orange) on the side should be removed.

Calibrate Object Center Point
After an object center point is automatically calculated, you can calibrate it based on the actual target object in use. Select a calculation method under Calibrate center point by application, and click Start calculating to calibrate the object center point.
| Method | Description | Operation | Application Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
Re-calculate by using original center point |
The default calculation method. Calculate the object center point according to the features of the target object and the original object center point. |
Select Re-calculate by using original center point, and click the Start calculating button. |
In general, this method can be used to calculate the center point of all target objects. |
Calibrate to center of symmetry |
Calculate the object center point according to the target object’s symmetry.
|
Select Calibrate to center of symmetry and click the Start calculating button. |
This method can be used to calculate the object center point when filtering matching results by target object symmetry. |
Calibrate to center of feature |
Calculate the object center point according to the selected Feature type and the set 3D ROI. |
|
Target objects with obvious geometric features
|
Configure Point Cloud Model
To better use the point cloud model in the subsequent 3D matching and enhance matching accuracy, the tool provides the following two options for configuring the point cloud model. You can enable the Configure point cloud model feature as needed.
Calculate Poses to Filter Matching Result
Once Calculate poses to filter matching result is enabled, more matching attempts will be made based on the settings to obtain matching results with higher confidence. However, more matching attempts will lead to longer processing time.
Two methods are available: Auto-calculate unlikely poses and Configure symmetry manually. In general, Auto-calculate unlikely poses is recommended. See the following for details.
| Method | Description | Operation |
|---|---|---|
Auto-calculate unlikely poses |
Poses that may cause false matches will be calculated automatically. During the calculation process, a set of candidate poses is automatically generated based on equivalent or ambiguous poses that may arise due to the target object’s rotational symmetry about the Z-axis. In subsequent matches, poses that successfully match these poses will be considered unqualified and filtered out. |
Note that the calculation results will not be automatically updated when the point cloud model is modified. If there are any modifications, please click "Calculate unlikely poses" again to update the results. |
Configure symmetry manually |
Calculate potentially mismatched poses based on the manually set parameters such as the Order of symmetry and Angle range. In subsequent matches, poses that successfully match these poses will be considered unqualified and filtered out. |
Select the symmetry axis by referring to Rotational Symmetry of Target Objects, and then set the Order of symmetry and Angle range. |
|
After the symmetry is set manually, the symmetry setting of the target object takes effect in the Coarse Matching, Fine Matching, and Extra Fine Matching (if enabled) processes in the 3D Matching Step. |
|
When this feature is enabled, you should configure the relevant parameters in the subsequent matching Steps to activate the feature. See the following for details.
|
Set Weight Template
During target object recognition, setting a weight template highlights key features of the target object, improving the accuracy of matching results. The weight template is typically used to distinguish target object orientation. The procedures to set a weight template are as follows.
|
A weight template can only be set when the Point cloud display settings is set to Display surface point cloud only. |
-
Click Edit template.
-
In the visualization area, hold and press the right mouse button to select a part of the features on the target object. The selected part, i.e., the weight template, will be assigned more weight in the matching process.
By holding Shift and the right mouse button together, you can set multiple weighted areas in a single point cloud model.
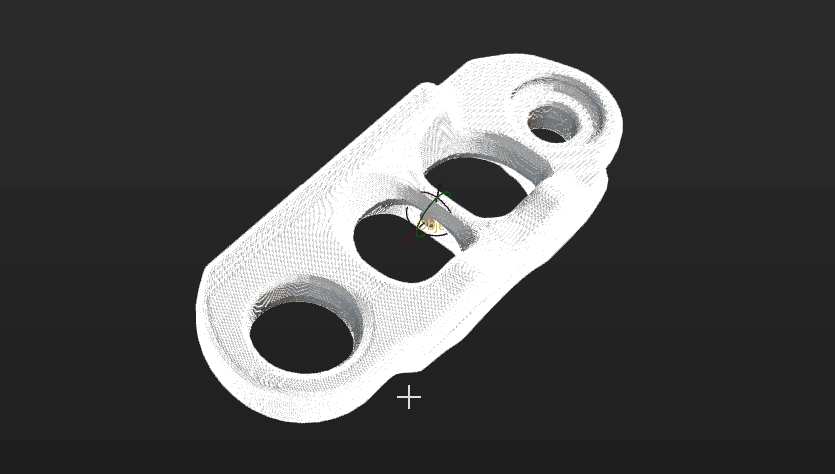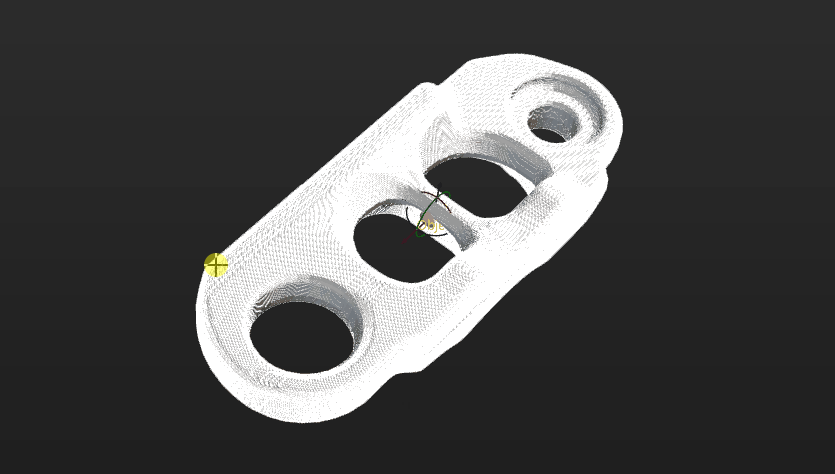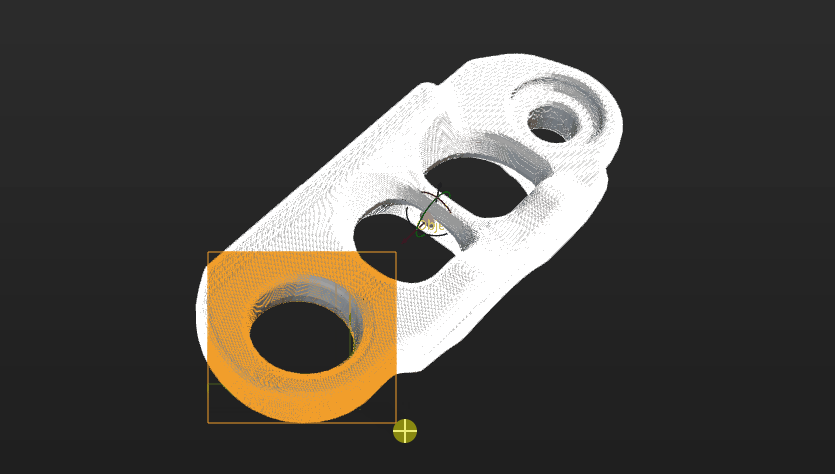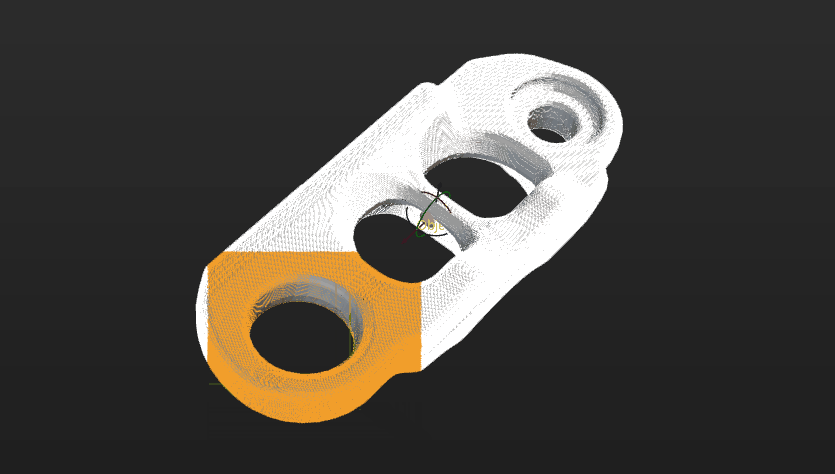
-
Click Apply to complete setting the weight template.
|
For the configured weight template to take effect in the subsequent matching, go to the “Model Settings” parameter of the “3D Matching” Step, and select the model with properly set weight template. Then, go to “Pose Filtering” and enable Consider Weight in Result Verification. The “Consider Weight in Result Verification” parameter will appear after the “Parameter Tuning Level” is set to Expert. |
Now the editing of the point cloud model is completed. You can click Next to set the pick point for the point cloud model.
Set Pick Point
Adjust Pick Point
By default, the pick point list displays the added pick points, defined in the reference frame with the object center point as the origin. Changing the object center point will affect the pick points. You can adjust the default pick points or add new pick points.
-
Adjust default pick points
If the automatically generated pick point does not meet the application requirements, you can customize the values in “Pick point settings” or manually drag the pick point in the visualization area.
-
Add new pick points
If the target object has multiple pick points, click the Add button to add new pick points.
Taking square tubes as an example, the magnetic gripper can pick from the sides, ends, and edges. Therefore, you can add pick points at these positions.

After adding pick points, you can drag the pick points in the pick point list to adjust the priority. The points higher in the list will be considered first during actual picking.
Set Pick Point Array
When the target object is symmetrical, you can set the pick point array based on the object center point according to actual requirements. Setting the pick point array can prevent the robot’s end tool from unnecessary rotations during picking. This increases the success rate of path planning and reduces the time required for path planning, allowing the robot to move more smoothly and swiftly. The procedures for setting are as follows.
-
Under “Pick point settings,” click Generate next to Pick point array.
-
Refer to Rotational Symmetry of Target Objects to select the axis of symmetry, and then set the Order of symmetry and Angle range.
-
(Optional) Make vision result contain pick point arrays.
If disabled, Mech-Viz or the path planning tool will generate pick point arrays based on the settings in the target object editor and plan the path according to the pick points in the array. If enabled, Mech-Vision will output pick point arrays based on the settings in the target object editor, and Mech-Viz or the path planning tool will use the pick points in the array to plan the path.
-
If you hope pick point arrays can be generated and outputted before path planning, you should enable the option.
-
If you hope pick point arrays can be generated after path planning, you should disable the option.
In real situations, you can decide to enable or not to enable this option based on project requirements and the system performance. For instance, when the pick point array contains many points, it is generally recommended to enable this option to filter out invalid pick points before path planning and output optimized pick point arrays, so as to avoid excessively long path planning times and improve overall efficiency.
-
Taking a round tube as an example, the settings of the pick point array are as follows.
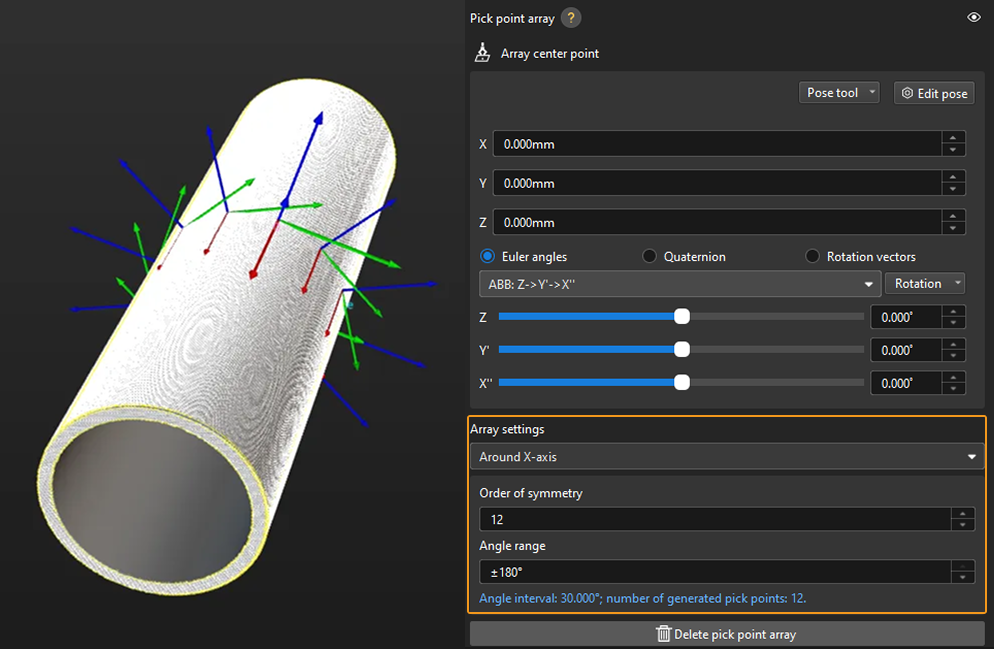
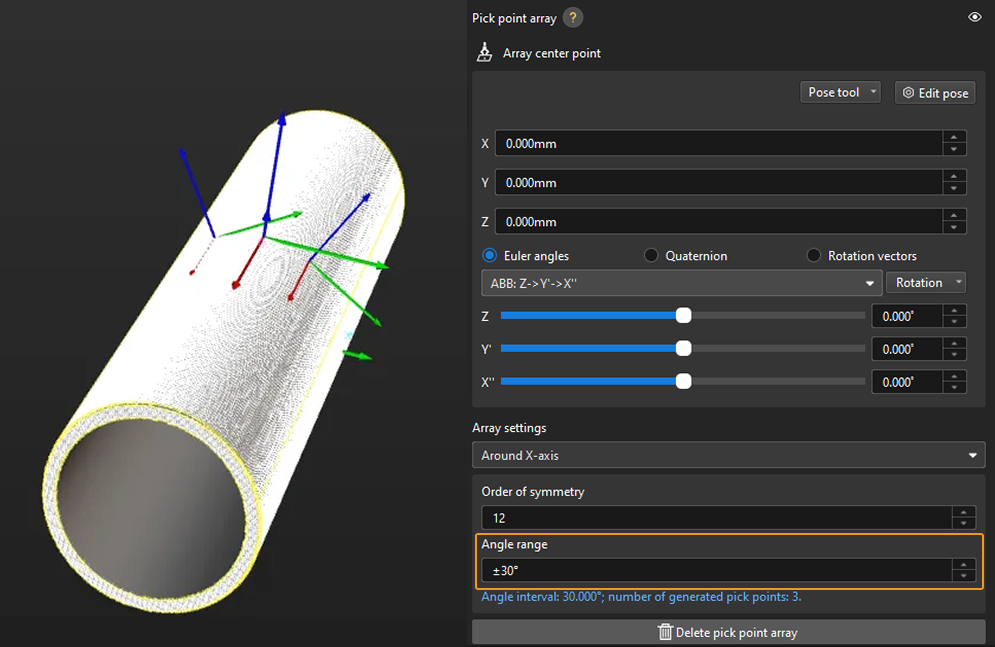
In practice, pick points with a downward Z-axis are often invalid and will affect path planning. Therefore, you should narrow down the Angle range. It is generally recommended to keep the range within ±90°. For example, when configuring a pick point array for randomly placed round tubes, the angle range value is set to ±30° in the figure below.
Add Picking Configuration
Preview Picking Effect
If a tool has been configured in the path planning tool or Mech-Viz, you can enable it in the target object editor to preview the positional relationship between the pick point and the tool during actual picking. This helps determine whether the pick point settings are appropriate. The detailed instructions are as follows.
-
Path Planning Tool
-
Mech-Viz
-
Add an end tool.
Add an end tool and set the TCP in the path planning tool.
-
Preview and enable the tool.
Once the end tool is added, the tool information will be automatically updated in the tool list within the target object editor. You can select a tool from the tool list based on your actual needs and preview the positional relationship between the pick point and the tool in the visualization area during actual picking (as shown in the figure below).
If the tool is modified in the path planning tool, please save the changes in the path planning tool to update the tool list in the target object editor. In addition, enabling the corresponding tool for the pick point in the target object editor is a prerequisite for successful path planning. 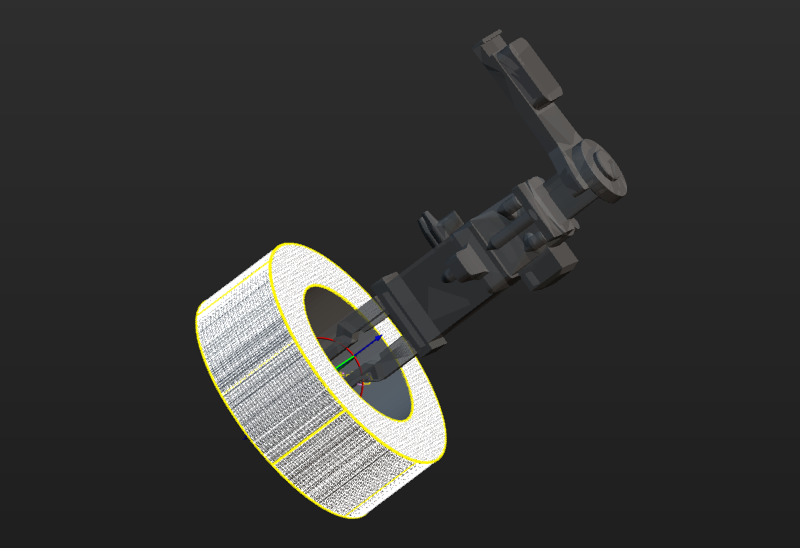
-
Ensure the Mech-Viz project is within the current solution.
To ensure that the end tool information in Mech-Viz can be updated in the target object editor, refer to Export Project to Solution to move the Mech-Viz project to the current solution.
-
Add an end tool.
Add an end tool and set the TCP in Mech-Viz.
-
Preview and enable the tool.
Once the end tool is added, the tool information will be automatically updated in the tool list within the target object editor. You can select a tool from the tool list based on your actual needs and preview the positional relationship between the pick point and the tool in the visualization area during actual picking (as shown in the figure below).
If you have modified the tool configurations in Mech-Viz, save the changes in Mech-Viz to update the tool list in the target object editor. In addition, enabling the corresponding tool for the pick point in the target object editor is a prerequisite for successful simulation in Mech-Viz. 
Configure Translational and Rotational Relaxation for Tools
In practice, to ensure the tool can still pick the target object after translating or rotating along a certain axis of the pick point, you can configure the translational relaxation and rotational relaxation for the tool in the target object editor.
Take the round tube as an example, the tool can be translated along the X-axis of the pick point while picking.
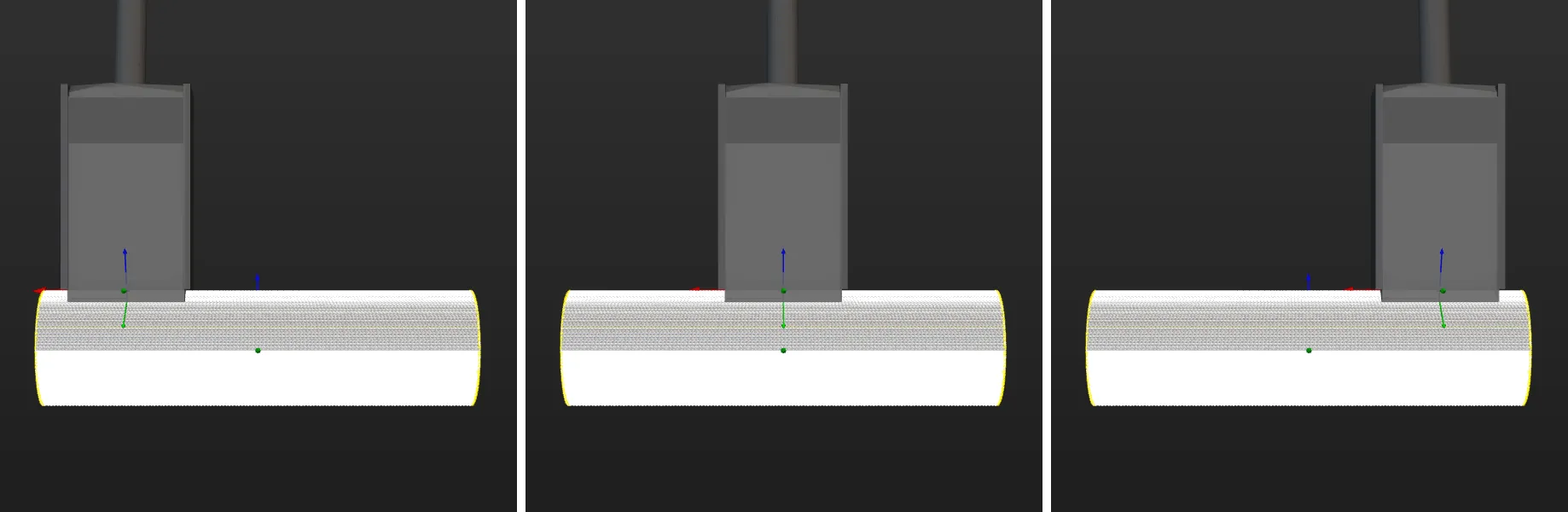
The corresponding configuration is shown below.
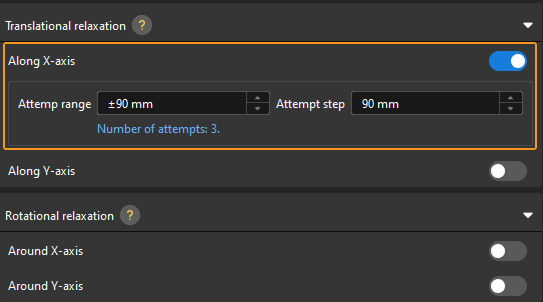
Set the Pick Point Selection Strategy
Minimum tool rotation will be used by default, and you can select a pick point selection strategy based on the actual requirements.
-
Minimum tool rotation: When this strategy is selected, the pick point that results in the smallest rotation of the tool’s Z-axis during the entire pick-and-place process will be selected with the highest priority. This strategy can prevent the tool from rotating in vain after picking the target object and avoid dropping the picked target object.
-
Minimum difference between tool and vision pose: When this strategy is selected, the pick point with the smallest angle difference from the target object pose will be selected with the highest priority.
-
Minimum collision between tool and point cloud: When this strategy is selected, the pick point that causes the least collision between the tool and the target object point clouds will be selected with the highest priority.
Click Save to save the configurations for the target object. To set the collision model, click Next.
Set Collision Model (Optional)
Set Collision Model
The collision model is a 3D virtual object used in collision detection for path planning. The tool automatically recommends the collision model generating mode based on the current configuration workflow. The recommended mode for this case is Use STL model to generate point cloud cube. This tool will generate point cloud cubes based on the selected STL model for collision detection. The collision model generated in this method features high accuracy, while the collision detection speed is lower.
-
Select the STL model.
Click Select STL model and then select the STL model used to generate the point cloud cube.
-
Align models.
Aligning the collision model with the point cloud model of the target object ensures effective collision detection. You can click Auto-align point cloud model and collision model or manually adjust the pose of the collision model to achieve the alignment with the point cloud model of the target object.
Configure Symmetry of Held Target Object
Rotational symmetry is the property of the target object that allows it to coincide with itself after rotating a certain angle around its axis of symmetry. When the “Waypoint type” is “Target object pose,” configuring the rotational symmetry can prevent the robot’s tool from unnecessary rotations while handling the target object. This increases the success rate of path planning and reduces the time required for path planning, allowing the robot to move more smoothly and swiftly.
Select the symmetry axis by referring to Rotational Symmetry of Target Objects, and then set the Order of symmetry and Angle range.
Now, the collision model settings are completed. Click Save to save the target object to Solution folder\resource\workobject_library. Then the target object can be used in subsequent 3D matching Steps.
