Create Plane from Features
Description
Use this Step to create a plane from the geometric features such as point, line, plane, and circle.
Workflow
The process of configuring this Step is as follows:
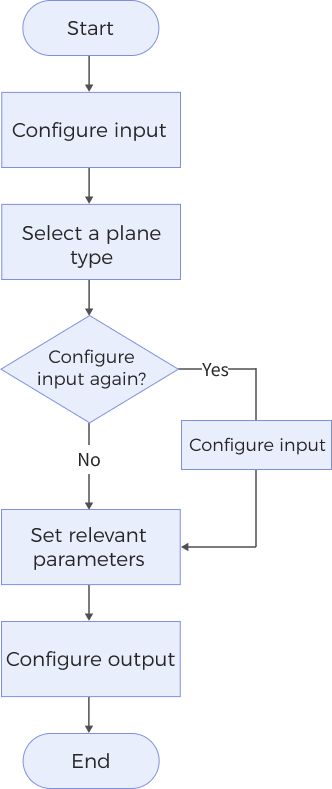
-
Configure the input. Connect the ports manually in the graphical programming workspace or select the input under Input in the parameter configuration panel.
-
In the Parameters section, select the Plane Type to determine how a plane is generated, and choose the corresponding input data in the Input section.
-
If there are additional parameters in the Parameters section, select and adjust them according to your actual needs.
-
Select the desired output items under Output. For an expandable output item, click ▶ and configure the Min and Max values to determine the acceptable range for the item.
Parameter Description
Plane Type
The method to create a plane.
For different types of planes, the geometric features input into the Step and the parameters that need to be adjusted will vary accordingly. The specific correspondences are as follows:
| Plane type | Geometric features to be input | Parameter adjustment |
|---|---|---|
Constant plane |
- |
You need to input the coordinates of a constant point and the normal vector of the plane to be created. After the Step is run, it outputs a plane passing through the point. |
Plane from point and normal |
Point, Line |
The given line is taken as the normal vector of the plane to be created. After the Step is run, it outputs a plane passing through the given point. No other parameters need to be adjusted. |
Plane from point and line |
Point, Line |
After the Step is run, it outputs a plane that passes through the given point and the given plane. No other parameters need to be adjusted. |
Plane from three points |
Point 1, Point 2, Point 3 |
After the Step is run, it outputs a plane that passes through the given three points. No other parameters need to be adjusted. |
Plane from circle |
Circle |
After the Step is run, it outputs a plane that passes through the given circle. No other parameters need to be adjusted. |
Parallel plane from point and plane |
Point, Plane |
After the Step is run, it outputs a plane that passes through the given point and is parallel to the given plane. No other parameters need to be adjusted. |
Perpendicular plane from points and plane |
Point 1, Point 2, Plane |
After the Step is run, it outputs a plane that passes through the given two points and is perpendicular to the given plane. No other parameters need to be adjusted. |
Perpendicular plane from line and plane |
Line, Plane |
After the Step is run, it outputs a plane that passes through the given line and is perpendicular to the given plane. No other parameters need to be adjusted. |
Midplane between two planes |
Plane 1, Plane 2 |
After the Step is run, it outputs a plane that bisects the given two planes. No other parameters need to be adjusted. |
Output Description
Select the output item(s) to add the output port(s) to the Step, and the corresponding data will be output after the Step is run. You can select the output according to the actual measurement requirements.
|
If you select an expandable output item, you should expand it by clicking ▶, and then set the Min and Max values to determine the acceptable range. If the output value falls within the acceptable range, the measurement item is judged as passing (OK), or else it is judged as failing (NG). |
| Output item | Description |
|---|---|
Rotation Angle about X-axis |
The rotation angle of the plane refer to the angles by which the plane’s normal vector rotates sequentially around the Y-axis and then the X-axis. Rotating the normal vector (0, 0, 1) first around the Y-axis and then around the X-axis will result in the created plane’s normal vector. |
Rotation Angle about Y-axis |
|
Z Offset |
The Z value of the intersection of the created plane and Z-axis. |
Normal X |
The X value of the normal to the created plane. |
Normal Y |
The Y value of the normal to the created plane. |
Normal Z |
The Z value of the normal to the created plane. |
Distance |
The distance from the origin to the plane. |
Created Plane |
The plane created on the basis of the selected plane type, which can be used as an input for other Steps. |
Troubleshooting
|
CV-W8302
Error: Unable to create a unique plane since the point is on the line.
Solution: Ensure the input point is not on the input line.
CV-W8303
Error: Unable to create a unique plane since the three points are collinear.
Solution: Ensure the input three points are not collinear.
CV-W8304
Error: The input two points are the same point.
Solution: Ensure the input two points are two different points.
CV-W8305
Error: Unable to create a unique plane.
Possible causes:
-
The plane type is set to “Perpendicular plane from points and plane,” and the line connecting the two points is perpendicular to the input plane. As a result, there are multiple planes that pass through the line connecting the two points and are perpendicular to the input plane.
-
The plane type is set to “Perpendicular plane from line and plane,” and the input line is perpendicular to the input plane. As a result, there are multiple planes that pass through the input line and are perpendicular to the input plane.
Solutions:
-
When the plane type is set to “Perpendicular plane from points and plane,” ensure the line connecting the two points is not perpendicular to the input plane.
-
When the plane type is set to “Perpendicular plane from line and plane,” ensure the input line is not perpendicular to the input plane.