Process Surface by Filter
Description
This Step is used to preprocess the surface data with a specific filter to obtain better surface data.
Workflow
The process of configuring this Step is as follows:
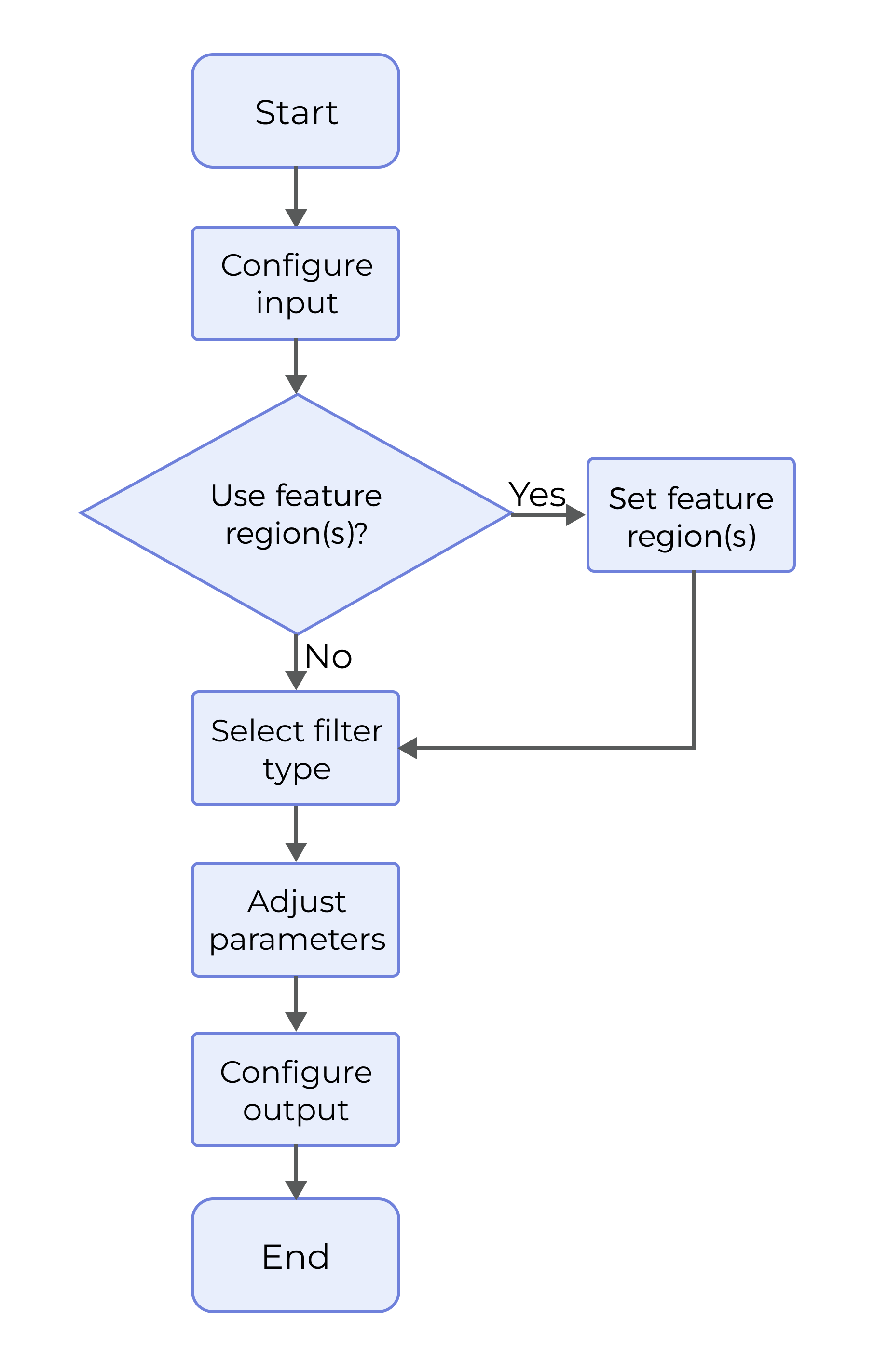
-
Configure the input. Connect the ports manually or select the input(s) under Input in the parameter configuration panel.
-
Determine whether to use the feature region, select the Filter Type, and set the filter parameters.
-
Select the output item Surface Data (selected by default).
Parameter Description
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Show Advanced Filters |
Once this parameter is selected, both common filters and advanced filters will become available in the drop-down list of Filter Type. |
Use Feature Region |
Use feature region(s) to define the region where surface preprocessing will be performed. If no feature region is used, the Step will process all surface data. If a feature region or feature regions are used, set the following parameters:
|
Filter Type |
Decides the filter to use for surface data processing. Value list: The available filters are listed below. For more details, refer to Filters.
|
Output Description
The output of this Step is processed surface data that can be used as input into other Steps.
Filters
Common Filters
Gap filling
Fills the missing data within a specified window size by the selected gap-filling type.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Gap Filling Type |
Decides the method for filling the gaps.
|
Image for Gap Filling |
Used to specify the type of image for gap filling. Value list: Depth map, intensity image, depth map and intensity image |
Filter in X Direction |
Used to determine whether to filter the surface data in the X-direction. |
X-Direction Window Size |
The window size for X-direction filtering. Default value: 3 px. |
Filter in Y Direction |
Used to determine whether to filter the surface data in the Y-direction. |
Y-Direction Window Size |
The window size for Y-direction filtering. Default value: 3 px. |
Mean
Replaces the value of each pixel with the mean of the pixel and its neighbors, thereby smoothing the image and reducing random noise.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Filter in X Direction |
Used to determine whether to filter the surface data in the X-direction. |
X-Direction Window Size |
The window size for X-direction filtering. Default value: 3 px. |
Filter in Y Direction |
Used to determine whether to filter the surface data in the Y-direction. |
Y-Direction Window Size |
The window size for Y-direction filtering. Default value: 3 px. |
Median
Replaces the value of each pixel with the median of the pixel and its neighbors to effectively reduce noise in the image, especially salt and pepper noise (typically appearing as random black and white points).
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Filter in X Direction |
Used to determine whether to filter the surface data in the X-direction. |
X-Direction Window Size |
The window size for X-direction filtering. Default value: 3 px. |
Filter in Y Direction |
Used to determine whether to filter the surface data in the Y-direction. |
Y-Direction Window Size |
The window size for Y-direction filtering. Default value: 3 px. |
Decimation
Reduces image resolution by discarding certain pixels from the raw image.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Filter in X Direction |
Used to determine whether to filter the surface data in the X-direction. |
X-Direction Window Size |
The window size for X-direction filtering. Default value: 3 px. |
Filter in Y Direction |
Used to determine whether to filter the surface data in the Y-direction. |
Y-Direction Window Size |
The window size for Y-direction filtering. Default value: 3 px. |
Crop
Extracts data from specified regions of the image. If no feature regions are specified, the entire image is the cropping target.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Output as Single Image |
By default, this option is selected, indicating that the original positions of the cropped areas will be retained and merged into a single output image. When it is unselected, a separate image for each cropped area will be output. |
Advanced Filters
Dilation
Fills small holes in an image to make the image more complete.
Note that dilation may also expand noise in the image. When performing dilation on images, you should set a proper kernel size and symmetry to ensure that the operation can achieve the desired result.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Use Intensity Image |
When unselected, the Step processes the depth map; when selected, the Step processes the intensity image. |
Keep Original Pixel Value |
When selected, this parameter ensures that the original pixel values in non-edge areas of the image remain unchanged during the dilation operation. It is unselected by default. |
Kernel Size |
Used to determine the kernel size during dilation. Default value: 3 px. |
Symmetry |
Used to determine the direction of the dilation operation.
|
Erosion
Removes small objects or noise in the image to make the image clearer.
Note that the erosion operation may lead to loss of image details. When performing erosion on images, you should set a proper kernel size and symmetry to ensure that the operation can achieve the desired result.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Use Intensity Image |
When unselected, the Step processes the depth map; when selected, the Step processes the intensity image. |
Keep Original Pixel Value |
When selected, this parameter ensures that the original pixel values in non-edge areas of the image remain unchanged during the erosion operation. It is unselected by default. |
Kernel Size |
Used to determine the kernel size during erosion. Default value: 3 px. |
Symmetry |
Used to determine the direction of the erosion operation.
|
Opening
Removes the small noise in the image while preserving the edges and main features of objects. Opening is essentially erosion followed by dilation.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Use Intensity Image |
When unselected, the Step processes the depth map; when selected, the Step processes the intensity image. |
Keep Original Pixel Value |
When selected, this parameter ensures that the original pixel values in non-edge areas of the image remain unchanged during the opening operation. It is unselected by default. |
Kernel Size |
Used to determine the kernel size for opening. Default value: 3 px. |
Closing
Fills small holes and smooths object edges, effectively addressing the problem of rough edges caused by noise. Closing is essentially dilation followed by erosion.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Use Intensity Image |
When unselected, the Step processes the depth map; when selected, the Step processes the intensity image. |
Keep Original Pixel Value |
When selected, this parameter ensures that the original pixel values in non-edge areas of the image remain unchanged during the closing operation. It is unselected by default. |
Kernel Size |
This parameter is used to set the kernel size for closing. Default value: 3 px. |
Morphological Gradient
Morphological gradient is an operation in image morphological processing that highlights the edges in an image by calculating the difference between dilation and erosion.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Use Intensity Image |
When unselected, the Step processes the depth map; when selected, the Step processes the intensity image. |
Keep Original Pixel Value |
When selected, this parameter ensures that the original pixel values in non-edge areas of the image remain unchanged during the morphological gradient operation. It is unselected by default. |
Kernel Size |
Used to determine the kernel size during the gradient operation. Default value: 3 px. |
Gaussian
Effectively removes certain noise from the image to smooth the image while preserving edges and details as much as possible. It is commonly used for image smoothing, noise reduction, and preprocessing before edge detection.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Use Intensity Image |
When unselected, the Step processes the depth map; when selected, the Step processes the intensity image. |
Kernel Size |
This parameter is used to set the kernel size for Gaussian filtering. Default value: 3 px. |
Sobel
Used for edge detection, which can produce smooth edges and generally works best when the edges in the image have strong directional features.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Use Intensity Image |
When unselected, the Step processes the depth map; when selected, the Step processes the intensity image. |
Kernel Size |
This parameter is used to set the kernel size during edge detection. Default value: 3 px. |
Symmetry |
This parameter is used to set the applied method for edge detection.
|
Min Threshold |
Upon filtering, points with depth values greater than this threshold will be considered edge points. |
Max Threshold |
Used to limit the depth values of the filtered points to this threshold or lower. |
Min Intensity Threshold |
Upon filtering, points with intensity values greater than this threshold will be considered edge points. |
Max Intensity Threshold |
Used to limit the intensity values of the filtered points to this threshold or lower. |
Laplacian
Used for edge detection, which can produce sharp and fine edges and typically works best when the image has minimal noise.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Use Intensity Image |
When unselected, the Step processes the depth map; when selected, the Step processes the intensity image. |
Kernel Size |
Used to determine the kernel size during edge detection. Default value: 3 px. |
Min Threshold |
Upon filtering, points with depth values greater than this threshold will be considered edge points. |
Max Threshold |
Used to limit the depth values of the filtered points to this threshold or lower. |
Min Intensity Threshold |
Upon filtering, points with intensity values greater than this threshold will be considered edge points. |
Max Intensity Threshold |
Used to limit the intensity values of the filtered points to this threshold or lower. |
Negative
Inverts the value of each pixel in an image to produce a visually inverted color effect.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Use Intensity Image |
When unselected, the Step processes the depth map; when selected, the Step processes the intensity image. |
Include Null Points |
Null points do not contain any depth information. This parameter is used to determine whether to include null points in the processed image. When it is selected, set Null Filling Value of Depth. |
Null Filling Value of Depth |
Set the depth value for filling null points. It is visible only when Include Null Points is selected. |
Equalization
Enhances the contrast of an image.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Use Intensity Image |
When unselected, the Step processes the depth map; when selected, the Step processes the intensity image. |
Min Threshold |
The depth values of points will be normalized to the range of Min Threshold to Max Threshold. |
Max Threshold |
The depth values of points will be normalized to the range of Min Threshold to Max Threshold. |
Min Intensity Threshold |
The intensity values of points will be normalized to the range of Min Intensity Threshold to Max Intensity Threshold. |
Max Intensity Threshold |
The intensity values of points will be normalized to the range of Min Intensity Threshold to Max Intensity Threshold. |
Binarization
Resets the depth or intensity value of each point in an image according to the specified height or intensity threshold.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Use Intensity Image |
When unselected, the Step processes the depth map; when selected, the Step processes the intensity image. |
Min Threshold |
When the depth value of a data point is less than or equal to the set Depth Threshold, the depth value of the point will be reset to the value of Min Threshold. |
Max Threshold |
When the depth value of a data point is above the set Depth Threshold, the depth value of the point will be reset to the value of Max Threshold. |
Depth Threshold |
The threshold used to binarize the depth map. |
Min Intensity Threshold |
When the intensity value of a data point is less than or equal to the set Intensity Threshold, the intensity value of the point will be reset to the value of Min Intensity Threshold. |
Max Intensity Threshold |
When the intensity value of a data point is above the set Intensity Threshold, the intensity value of the point will be reset to the value of Max Intensity Threshold. |
Intensity Threshold |
The threshold used to binarize the intensity image. |
Percentile
Removes data points outside of the specified percentile range.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Use Intensity Image |
When unselected, the Step processes the depth map; when selected, the Step processes the intensity image. |
Low Threshold Percentile |
|
High Threshold Percentile |
|
Relative Threshold
Removes data points that fall outside of the specified depth or intensity range, where the depth or intensity threshold can be a relative value.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Use Intensity Image |
When it is unselected, the Step processes the depth map, and you need to set the Low Threshold and High Threshold. When it is selected, the Step processes the intensity image, and you need to set the Min Intensity Threshold and Max Intensity Threshold. |
Low Threshold |
Data points with a depth value between Low Threshold and High Threshold are retained. |
High Threshold |
Data points with a depth value between Low Threshold and High Threshold are retained. |
Min Intensity Threshold |
Set Min Intensity Threshold and Max Intensity Threshold to define the intensity value range of data points. Data points within the range keep their intensity values, while data points outside of the range have their intensity values reset to 1. |
Max Intensity Threshold |
Set Min Intensity Threshold and Max Intensity Threshold to define the intensity value range of data points. Data points within the range keep their intensity values, while data points outside of the range have their intensity values reset to 1. |
Use Reference Feature Region |
When this parameter is selected, you need to set one or multiple reference feature regions. The average depth or intensity value of data points defined by the reference feature region(s) serves as a reference value, and the specified depth or intensity value range should be set on this basis.
|
Dynamic Thresholding
Used to binarize the depth map or intensity image.
| Parameter | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Use Intensity Image |
When unselected, the Step processes the depth map; when selected, the Step processes the intensity image. |
||
Image Filter |
Used to select a filter for image preprocessing.
You can adjust the Kernel Size parameter to set the neighborhood size used during filtering. Default value: Mean filter |
||
Kernel Size |
The kernel size for the selected filter, i.e., the neighborhood size used during filtering. Default value: 3 px |
||
Depth Value Offset / Intensity Value Offset |
Used to apply a uniform offset to all pixel values after filtering. The effect of this offset depends on the selected Thresholding Type. |
||
Max Threshold |
Used to limit the pixel values to this threshold or lower. Default value: 10.000 mm
|
||
Thresholding Type |
Determines the method for binarizing the image. Let P be the original pixel value, P' the filtered value of the pixel corresponding to P, and offset the set depth value or intensity value offset. The processing logic of each type can be described as follows:
|
Adaptive Thresholding
Used to binarize the intensity image.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Threshold Calculation Method |
Used to specify a method for calculating the threshold for each pixel in the image.
|
Kernel Size |
The neighborhood size used during threshold calculation. Default value: 21 px |
Thresholding Type |
Determines the method for binarizing the image.
|
Constant |
The constant used for threshold calculation. Refer to the Threshold Calculation Method parameter to learn how the constant affects the results. |
Troubleshooting
|
CV-W2001
Error: The selected filter type is invalid.
Possible cause: The selected filter type was not Negative, Equalization, or Binarization.
Solution: Make sure the selected filter type is Negative, Equalization, or Binarization.
CV-W2301
Error: The “Kernel Size” value of the selected filter should exceed 0.
Possible cause: The “Kernel Size” value is less than or equal to 0.
Solution: Make sure the parameter value is greater than 0.
CV-W2302
Error: The selected filter type is invalid.
Possible cause: The selected filter type was not Gaussian, Sobel, or Laplacian.
Solution: Make sure the selected filter type is Gaussian, Sobel, or Laplacian.
CV-W2401
Error: The X-direction window size or Y-direction window size should exceed 0.
Possible cause: The parameter value is less than or equal to 0.
Solution: Make sure the parameter value is greater than 0.
CV-W2402
Error: The selected gap filling type is invalid.
Possible cause: The selected gap filling type is invalid.
Solution: Select the gap filling type again from the drop-down list.
CV-W2403
Error: The set “Image for Gap Filling” is invalid.
Solution: Select a valid image type for gap filling from the drop-down list.
CV-W2501
Error: The selected filter type is invalid.
Possible cause: The selected filter type was not Dilation, Erosion, Opening, Closing, or Morphological gradient.
Solution: Make sure the selected filter type is Dilation, Erosion, Opening, Closing, or Morphological gradient.
CV-W2502
Error: The “Kernel Size” value of the selected filter should exceed 0.
Possible cause: The parameter value is less than or equal to 0.
Solution: Make sure the parameter value is greater than 0.
CV-W2601
Error: The X-direction window size or Y-direction window size should exceed 0.
Possible cause: The parameter value is less than or equal to 0.
Solution: Make sure the parameter value is greater than 0.