Process Profile by Filter
Description
This Step is used to process the profile by a filter to obtain a better profile. The optional filters include Gaussian, median, mean, decimation, and gap filling.
Workflow
The process of configuring this Step is as follows:
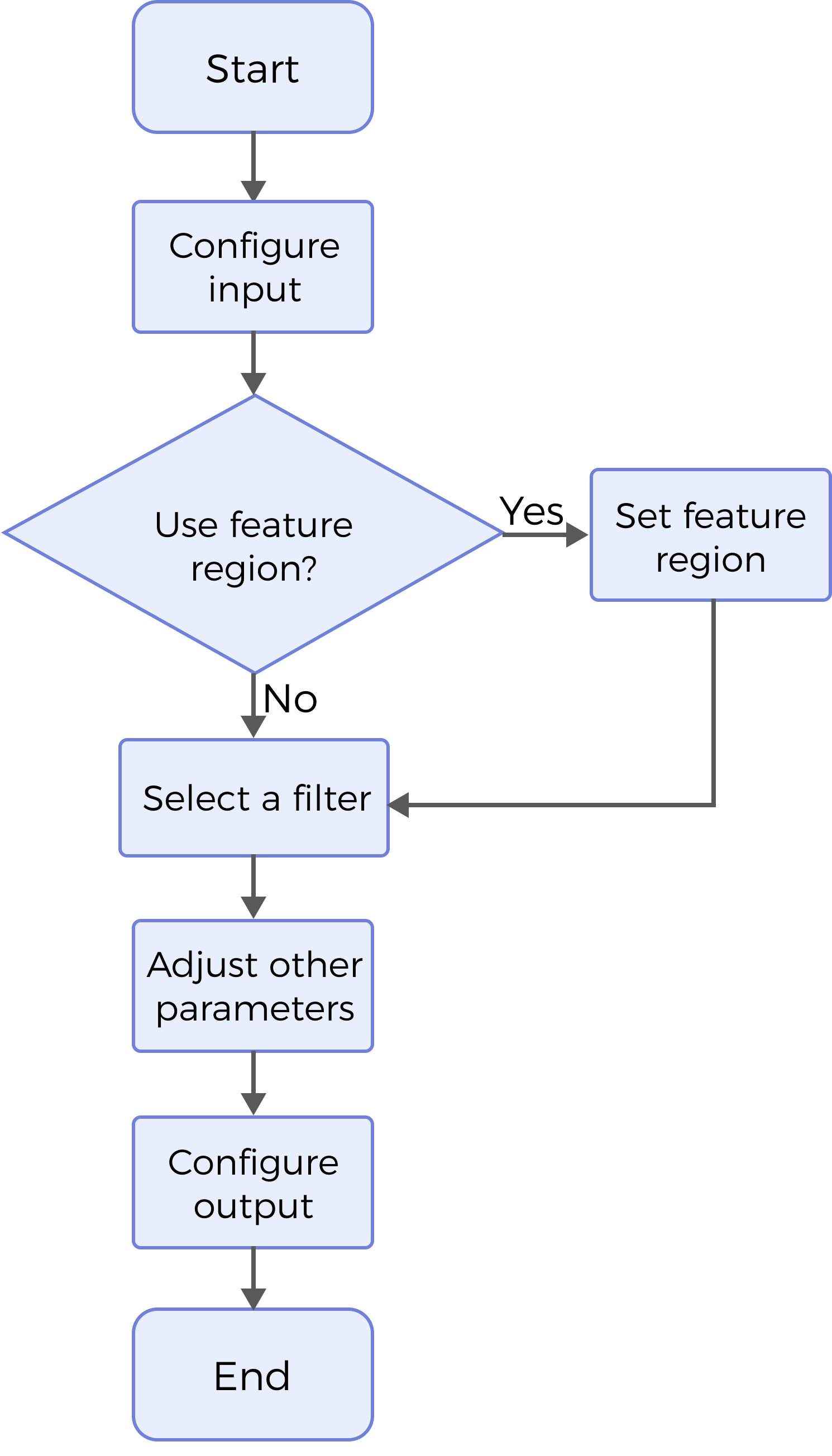
-
Configure the input. Connect the ports manually in the graphical programming workspace or select the input(s) under Input in the parameter configuration panel.
-
Determine whether to use a feature region. For more information, refer to Use Feature Region.
-
Select the filter type and set the corresponding parameters. For more information on the available filters, refer to Filter Type.
-
Select the output item Profile (selected by default).
Parameter Description
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Use Feature Region |
Use feature region(s) to define the region where profile preprocessing will be performed. Once this parameter is selected, only data within the feature region(s) will be processed. |
Feature Region |
Visible only when the Use Feature Region parameter is selected. For more information on how to set and adjust the feature region, see Feature Region. |
Filter Type |
The filter for profile preprocessing. Options: Mean, Gaussian, Median, Gap Filling, Decimation. For the detailed information on filters, please refer to Filter Type. |
Filter Type
| Filter Type | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Mean |
The mean filter can smooth the image by calculating the neighbors of pixels in the image and replacing the pixel values in the original image with the calculated average. When selecting this option, the following parameters need to be set:
|
||
Gaussian |
Gaussian filtering is used to remove the noise in the profile, smoothing the profile without losing major details. When selecting this option, the following parameters need to be set:
|
||
Median |
Median filtering is used to smooth and sharpen the profile by removing unwanted fluctuations and outliers. When selecting this option, the following parameters need to be set:
|
||
Gap Filling |
With the maximum or minimum Z values of the nearest neighbors or linear interpolation between neighboring values, this filter fills in missing data in the specified window. When selecting this option, the following parameters need to be set:
|
||
Decimation |
Decimation reduces the size or resolution of the image. During decimation, some pixels in the raw image will be discarded or merged to generate a small-sized image. When selecting this option, the following parameters need to be set:
|
Output Description
The output of this Step is a processed profile that can be used as input to other Steps.
Troubleshooting
|
CV-W6001
Error: The sigma value is outside of the valid range.
Possible cause: The parameter value is less than 0.
Solution: Make sure the parameter value is greater than or equal to 0.
CV-W6002
Error: The X-direction window size is outside of the valid range.
Possible cause: The parameter value is less than 3.
Solution: Reset the X-direction window size of the filter to ensure that it is greater than or equal to 3.