ABB Standard Interface Commands
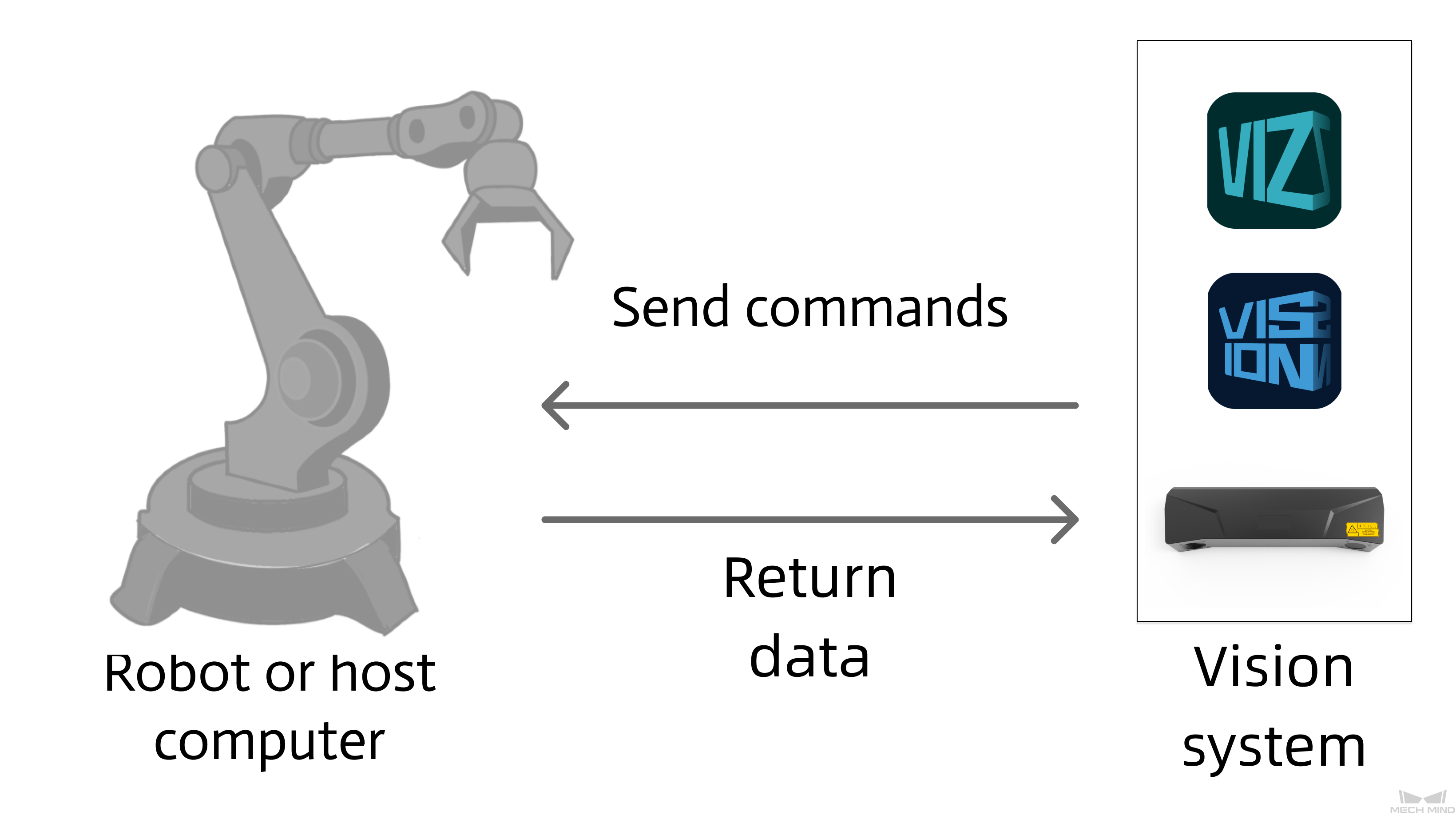
This section describes standard interface commands used in TCP communications between a ABB robot and Mech-Mind Vision System. The robot (the client) sends commands to Mech-Mind Vision System (the server), and Mech-Mind Vision System returns the processed data to the robot.
Command Overview
Precautions
-
When programming an ABB robot, pay attention to the following items:
-
Parameters in the parameter list of a command must be separated by commas (,).
-
Variable-type parameters of a command should use local variables and take effect only in the command.
-
Input and output parameters can be customized in commands.
-
Arguments in a command: The input arguments can be constants, global variables, or local variables. The output arguments can be global variables or local variables.
-
In Mech-Vision & Mech-Viz versions earlier than 1.8.0, each command encapsulates codes that establish and close the communication.
-
In Mech-Vision & Mech-Viz 1.8.0 and later versions, two individual commands are developed to establish and close the communication, preventing frequent disconnections and reconnections between the robot and the vision system.
-
-
Unit of data:
-
The unit of joint positions is degree (°).
-
A robot’s flange pose or TCP consists of the position and pose. The position is represented in XYZ coordinates and is measured in millimeters (mm); the pose is represented in Euler angles and is measured in degrees (°).
-
-
Vision point and waypoint:
-
Vision point: An object recognized by Mech-Vision. A vision point has information including the object pose, label, dimensions, and custom data.
-
Waypoint: Each point that the robot reaches when moving along the planned path. A waypoint has information including the robot pose, label, and motion type. Waypoints can be divided into two categories:
-
Vision Move waypoint: Waypoint corresponding to the Vision Move Step.
-
Non-Vision Move waypoints, which refer to the waypoints corresponding to Move-type Steps other than the Vision Move Step.
-
The robot can obtain up to 100 vision points or waypoints from the vision system. -
Initialize Communication
Command
This command sets the IP address of the IPC, port number, and timeout period for robot communication.
Calling Sequence
To establish the communication between the robot and the vision system, call Establish TCP Communication after this command.
Command Format
MM_Init_Socket IP_Address,Server_Port,Time_Out;Input Parameters
IP_Address
This parameter specifies the IP address of the IPC. The data type is string.
Server_Port
This parameter specifies the port number used by the IPC to establish the communication between the IPC and the robot. This port number must be consistent with the host port number that is specified for robot communication in the toolbar of Mech-Vision. The data type is num.
Time_Out
This parameter specifies the communication timeout period. Unit: seconds. The data type is num.
Establish TCP Communication
This command establishes the TCP communication between the robot and the vision system.
Calling Sequence
This command should be called after Initialize Communication.
Close TCP Communication
This command closes the TCP communication between the robot and the vision system.
Calling Sequence
After you receive the result of the Mech-Vision or Mech-Viz project, you can call this command to close the communication and store the result in variables. If the communication is not closed for a long time, an error that indicates that communication was abnormally closed may be returned for robot programs.
Run Mech-Vision Project
Command
This command triggers the Mech-Vision project to run. When the Mech-Vision project is running, the vision system triggers the camera to capture images and then process the returned images with algorithms to produce a series of vision points or waypoints.
|
Calling Sequence
-
You should set Step parameters before starting a Mech-Vision project. Therefore, call Switch Mech-Vision Parameter Recipe or Input Object Dimensions to Mech-Vision Project before calling Run Mech-Vision Project.
-
Vision system gets vision points and waypoints only after a Mech-Vision project runs. Therefore, call Run Mech-Vision Project before calling Get Vision Result, Get Planned Path in Mech-Vision, or Get Mech-Vision Custom Data.
Command Format
MM_Start_Vis Job,Pos_Num_Need,SendPos_Type,MM_J;Input Parameters
Job
Mech-Vision project ID. You can view the project ID of a The data type is num. Mech-Vision project in the Project List section of Mech-Vision. The project ID is the number before the project name.
Pos_Num_Need
This parameter specifies the expected number of vision points or waypoints to be obtained from the Mech-Vision project. The data type is num. Value range: 0 to the largest positive integer.
| If the Mech-Vision project has a Path Planning Step, this parameter indicates the expected number of waypoints. Otherwise, it indicates the expected number of vision points. |
-
0: Obtain all vision points or waypoints from the Mech-Vision project.
-
A positive integer: Obtain the specific number of vision points or waypoints from the Mech-Vision project.
-
If the total amount of vision points or waypoints output by the Mech-Vision project is smaller than the parameter value, this command will obtain the number of all vision points or waypoints.
-
If the total amount of vision points or waypoints output by the Mech-Vision project is larger than or equal to the parameter value, this command will obtain the number of vision points or waypoints as specified by this parameter.
-
|
SendPos_Type
This parameter specifies the way in which the real robot pose is sent to the Mech-Vision project. The data type is num. Valid values: 0, 1, 2, and 3. The following table describes the details.
| SendPos_Type | Description | Applicable scenario |
|---|---|---|
0 |
The command does not send the robot pose data to the Mech-Vision project. If the Path Planning Step is used in the Mech-Vision project, the start point of the planned path will be the Home point set in the path planning tool. |
This setting should be used if the camera is mounted in eye to hand mode and the project does not require images to be captured beforehand. |
1 |
The current joint positions and flange pose of the robot must be input to the Mech-Vision project. |
This setting should be used when the camera is mounted in eye in hand mode. This setting is recommended for most scenarios except those involving gantry robots. |
2 |
The robot flange pose must be input to the Mech-Vision project. |
This setting is recommended for scenarios involving gantry robots. |
3 |
This command sends custom joint positions to the Mech-Vision project. These joint positions will be sent to the Path Planning Step in the Mech-Vision project as the start point, where the robot will move from this start point to the first waypoint of the planned path. |
This setting should be used if the camera is mounted in eye to hand mode and the project requires images to be captured beforehand. |
|
MM_J
This parameter specifies the custom joint positions. The data type is jointtarget.
-
If SendPos_Type is set to 3, the joint positions will be sent to the Path Planning Step in the Mech-Vision project as the start point, where the robot moves from this start point to the first waypoint of the planned path.
-
If SendPos_Type is set to a parameter value other than 3, the joint positions are of no practical use but must be set.
Example
MM_Start_Vis 1,1,1,MM_J;In the preceding example, the Mech-Vision project whose ID is 1 is run, and one vision point is expected to be returned by the Mech-Vision project. At the same time, the robot sends the current joint position and flange pose data to the Mech-Vision project. In this example, MM_J has no practical use, but the joint positions must be set.
Get Vision Result
Command
This command obtains vision result, namely, a series of vision points, from Mech-Vision. The object pose of the vision point (namely, the output of the poses port of the Output Step) will be automatically converted to the robot’s TCP by the vision system. The process is as follows.
| If the first input port of the Output Step is Object Center Points, the Output Step will convert the object center points into the corresponding pick points. Therefore, the object poses obtained by running this command are actually poses of pick points, instead of poses of object center points. |
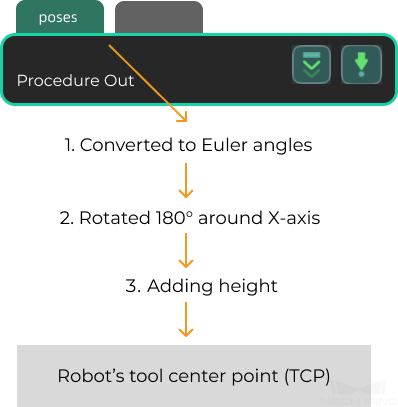
-
Convert the object pose from a quaternion to Euler angles.
-
Rotate the object’s pose around the X-axis by 180° to orient its Z-axis downward.
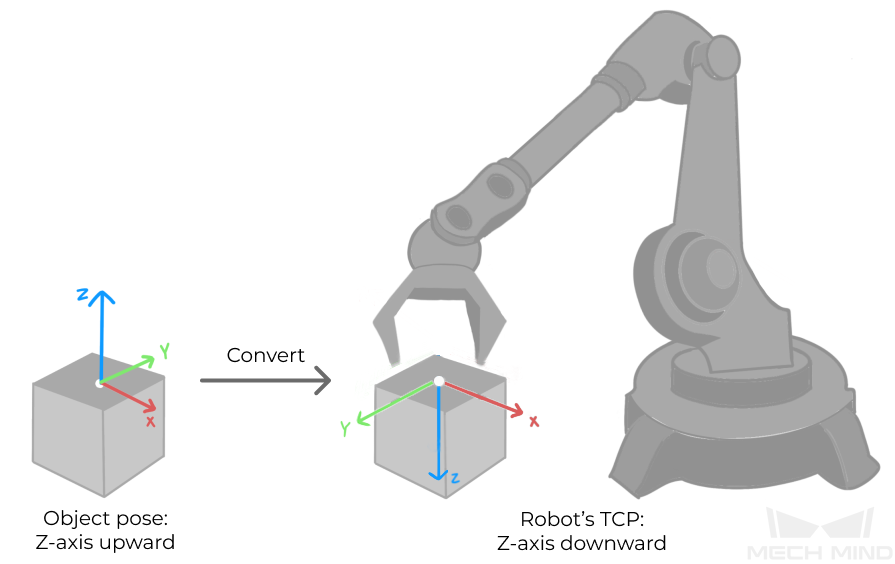
Calling Sequence
This command should be called after Run Mech-Vision Project. After you call this command, call Store Vision Result or Planned Path (TCP) to access pose data.
Command Format
MM_Get_VisData Job,Pos_Num,MM_Status;Input Parameters
Job
Mech-Vision project ID. You can view the project ID of a The data type is num. Mech-Vision project in the Project List section of Mech-Vision. The project ID is the number before the project name.
Output Parameters
Pos_Num
This parameter stores the number of vision points returned by Mech-Vision. The data type is num.
MM_Status
This parameter stores the status code of this command. The data type is num. If the command is successfully executed, the status code is 1100. If a command fails to be run, a specific error code is returned. For details, see Status Codes and Troubleshooting.
|
By default, after the robot sends this command, the vision system returns the result in 10 seconds. If the vision system fails to return any result in 10 seconds, a timeout error code is returned. To modify the default timeout period as needed, go to Robot and Communication > in the toolbar of Mech-Vision. 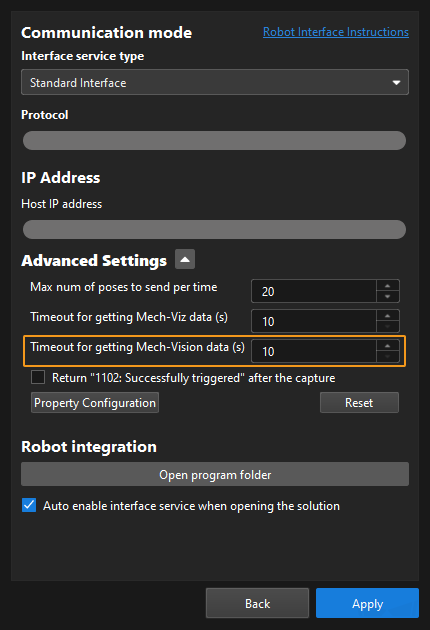
|
Store Vision Result or Planned Path (TCP)
Command
This command stores the TCP, label, and tool ID of the vision point or waypoint in the variables.
Command Format
MM_Get_Pose Serial,MM_P,MM_Label,MM_ToolId;Input Parameters
Serial
This parameter specifies the index of the vision point or waypoint. The TCP, label, and tool ID of the vision point or waypoint that corresponds to the index are stored in the variables. The data type is num. Indexes start with 1.
Output Parameters
MM_P
This parameter stores the TCP of the vision point or waypoint that corresponds to the index. The data type is robtarget.
MM_Label
This parameter stores the label of the vision point or waypoint that corresponds to the index. The data type is num.
MM_ToolId
This parameter stores the tool ID of the vision point or waypoint that corresponds to the index. The data type is num.
Store Planned Path (joint positions)
Command
This command stores the joint positions, label, and tool ID of the waypoint in the variables.
Command Format
MM_Get_Jps Serial,MM_J,MM_Label,MM_ToolId;Input Parameters
Serial
This parameter specifies the index of the waypoint. The joint positions, label, and tool ID of the waypoint that corresponds to the index are stored in the variables. The data type is num. Indexes start with 1.
Output Parameters
MM_J
This parameter stores the joint positions of the waypoint that corresponds to the index. The data type is jointtarget.
MM_Label
This parameter stores the label of the waypoint that corresponds to the index. The data type is num.
MM_ToolId
This parameter stores the tool ID of the waypoint that corresponds to the index. The data type is num.
Switch Mech-Vision Parameter Recipe
Command
This command triggers Mech-Vision to switch the parameter recipe used by the project. The image below shows how to manually switch the parameter recipe for a Mech-Vision project. For details about parameter recipes, see the parameter recipe guide.
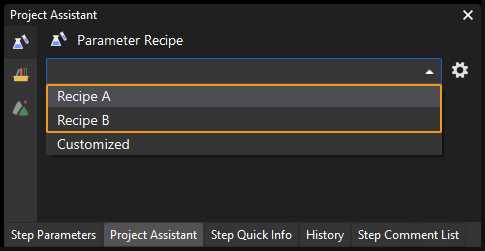
Calling Sequence
This command should be called before Run Mech-Vision Project.
Command Format
MM_Switch_Model Job,Model_Number;Input Parameters
Job
Mech-Vision project ID. You can view the project ID of a The data type is num. Mech-Vision project in the Project List section of Mech-Vision. The project ID is the number before the project name.
Model_Number
This parameter specifies the parameter recipe ID in the Mech-Vision project. The data type is num. For information about how to view the parameter recipe ID, see View the Parameter Recipe ID.
Get Planned Path in Mech-Vision
Command
This command obtains the path planned by the Mech-Vision project as a series of waypoints. The path is planned by the path planning tool, which you may enter by clicking Config wizard as shown in the image below. For details about Path Planning, see Path Planning.
| Set the Port Type parameter of the Output Step in Mech-Vision to Predefined (robot path). |
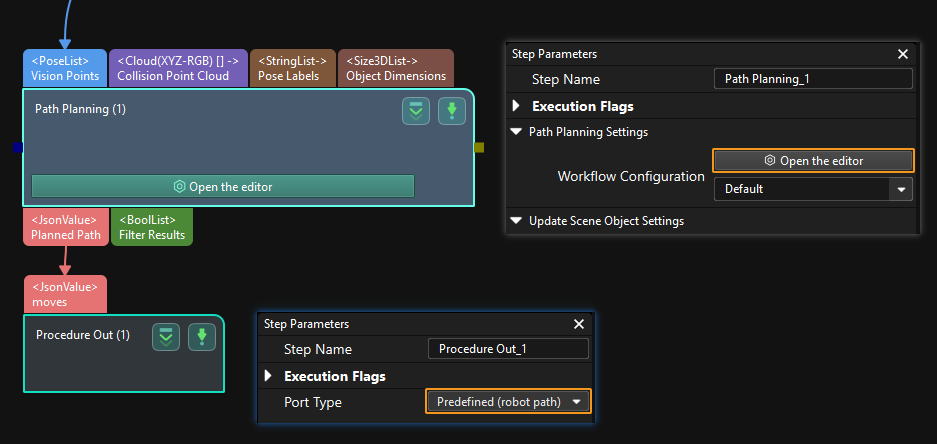
Calling Sequence
This command should be called after Run Mech-Vision Project. After you call this command, call Store Vision Result or Planned Path (TCP) or Store Planned Path (joint positions) to access pose data.
Command Format
MM_Get_VisPath Job,Jps_Pos,Pos_Num,VisPos_Num,MM_Status;Input Parameters
Job
Mech-Vision project ID. You can view the project ID of a The data type is num. Mech-Vision project in the Project List section of Mech-Vision. The project ID is the number before the project name.
Jps_Pos
This parameter specifies the type of waypoint poses to be obtained. The data type is num. can be set to 1 or 2.
-
1: joint positions. After you run this command, run Store Planned Path (joint positions) to access joint position data.
-
2: tool poses. After you run this command, run Store Vision Result or Planned Path (TCP) to access tool pose data.
Output Parameters
Pos_Num
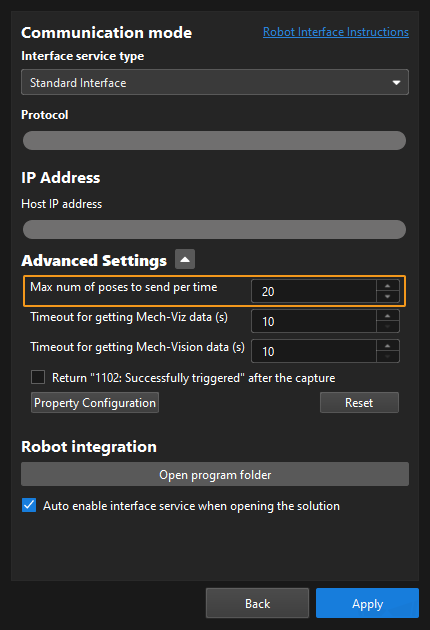
This parameter stores the number of waypoints returned by the vision system. The data type is num. By default, the vision system can send 20 waypoints at most. As such, the maximum default value of this parameter is 20. To modify the default maximum number of poses to obtain each time as needed, go to Robot and Communication > in the toolbar of Mech-Vision. The upper limit is 30.

| Before you call Get Planned Path in Mech-Vision, set Pos_Num_Need of Run Mech-Vision Project to 0 to reduce the number of Get Planned Path in Mech-Vision calls. If Pos_Num_Need of Run Mech-Vision Project is set to 1, only one waypoint is obtained each time you call Get Planned Path in Mech-Vision. You need to call Command 105 several times to obtain all waypoints. |
VisPos_Num
The sequence number of the Vision Move waypoint (the waypoint corresponding to the Vision Move step of the path planning tool) in the path. The data type is num. If the waypoint does not exist in the path, the petameter value is 0.
If the planned path consists of the following waypoints in sequence: Fixed-Point Move_1, Fixed-Point Move_2, Vision Move, and Fixed-Point Move_3, the sequence number of the Vision Move waypoint is 3.
MM_Status
This parameter stores the status code of this command. The data type is num. If the command is successfully executed, the 1103 status code is returned. If a command fails to be run, a specific error code is returned. For details, see Status Codes and Troubleshooting.
|
By default, after the robot sends this command, the vision system returns the result in 10 seconds. If the vision system fails to return any result in 10 seconds, a timeout error code is returned. To modify the default timeout period as needed, go to Robot and Communication > in the toolbar of Mech-Vision. 
|
Example
MM_Get_VisPath 2,2,PosNum,Vis_Index,StatusCode;In the preceding example, the planned path of the Mech-Vision project No.2 is returned, the waypoints of the path are stored in the TCP format, the number of waypoints is stored in PosNum, the sequence number of the Vision Move waypoint in the planned path is stored in Vis_Index, and the command execution status code is stored in StatusCode.
Trigger Mech-Vision Project and Get Result
Command
This command triggers the following operations in sequence: set the parameter recipe to be used by the Mech-Vision project (which is skipped if the project doesn’t have a parameter recipe), trigger the Mech-Vision project to run, and obtain vision result (i.e., vision points, waypoints, or custom data) from the vision system. This command combines the Switch Mech-Vision Parameter Recipe, Run Mech-Vision Project, Get Vision Result, Get Planned Path in Mech-Vision, and Get Mech-Vision Custom Data commands.
| At most 20 poses can be obtained by calling this command. To obtain more than 20 poses, don’t use this command. Use the Switch Mech-Vision Parameter Recipe, Run Mech-Vision Project, Get Vision Result, Get Planned Path in Mech-Vision, or Get Mech-Vision Custom Data command instead. |
Command Format
MM_Lite_Vis Job,Model_Number,Recv_Data_Type,MM_Status,\MM_J,\Pos_Num,\VisPos_Num;Input Parameters
Job
Mech-Vision project ID. You can view the project ID of a The data type is num. Mech-Vision project in the Project List section of Mech-Vision. The project ID is the number before the project name.
Model_Number
This parameter specifies the parameter recipe ID in the Mech-Vision project. The data type is num. For information about how to view the parameter recipe ID, see View the Parameter Recipe ID.
Recv_Data_Type
This parameter specifies the data type returned by the vision system. Value range: 1 to 4.
-
1: The vision system returns vision points (without custom data). Then, you must call Store Vision Result or Planned Path (TCP) to store vision point pose data in variables.
-
2: The vision system returns vision points (together with custom data). Then, you must call Get Mech-Vision Custom Data to store custom data of vision points in variables.
-
3: The vision system returns waypoints in the form of joint positions. Then, you must call Store Planned Path (joint positions) to store waypoints in the form of joint positions in variables.
-
4: The vision system returns waypoints in the form of TCP. Then, you must call Store Vision Result or Planned Path (TCP) to store waypoints in the form of TCP in specified variables.
Output Parameters
MM_Status
This parameter stores the status code of this command. The data type is num. If the command is successfully executed, the status code is 1100 or 1103. If a command fails to be run, a specific error code is returned. For details, see Status Codes and Troubleshooting.
Pos_Num (Optional)
This parameter stores the number of vision points or waypoints that are returned by the vision system. The data type is num.
VisPos_Num (Optional)
This parameter is valid only when the value of Recv_Data_Type is 3 or 4. This parameter stores the position of the first Vision Move waypoint in the entire planned path.
For example, if the planned path consists of: "Fixed-Point Move_1", "Fixed-Point Move_2", "Vision Move", "Fixed-Point Move_3", the position of the Vision Move is 3. If the path does not contain Vision Move, the value of this parameter is 0.
Example
MM_Lite_Vis 1,2,1,StatusCode,\Pos_Num:=PoseNum;In the preceding example, Mech-Vision uses the parameter recipe whose ID is 2 to run the Mech-Vision project whose ID is 1 to obtain vision points. The vision point quantity is stored in PoseNum, and command execution status code is stored in StatusCode.
Get Mech-Vision Custom Data
Command
This command obtains data from the custom port(s) of the Output Step in Mech-Vision. One command call saves all port data of the Output Step to robot memory.
Select the Output Step, set Port Type to Custom, and then click Open the editor to go to the custom port configuration window. The Customized Keys section of the window displays custom port names, such as customeData1 and customeData2 as shown in the following figure.
|
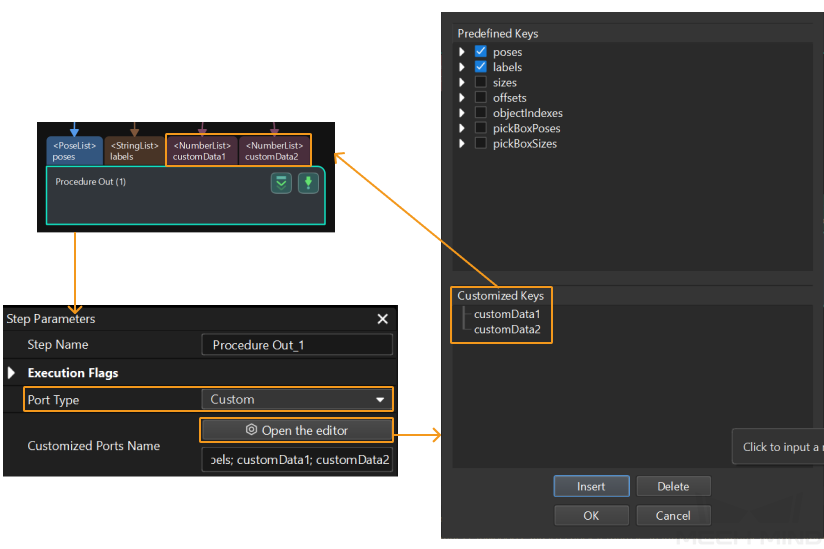
Calling Sequence
This command should be called after Run Mech-Vision Project. After you call this command, call Store Mech-Vision Custom Data to access custom data.
Command Format
MM_Get_DyData Job,Pos_Num,MM_Status;Input Parameters
Job
Mech-Vision project ID. You can view the project ID of a The data type is num. Mech-Vision project in the Project List section of Mech-Vision. The project ID is the number before the project name.
Output Parameters
Pos_Num
This parameter stores the number of vision points returned by Mech-Vision. The data type is num.
MM_Status
This parameter stores the status code of this command. The data type is num. If the command is successfully executed, the status code is 1100. If a command fails to be run, a specific error code is returned. For details, see Status Codes and Troubleshooting.
Store Mech-Vision Custom Data
Calling Sequence
This command should be called after Get Mech-Vision Custom Data.
Command Format
MM_Get_DyPose Serial,MM_P,MM_Label;Input Parameters
Serial
This parameter specifies the index of the vision point. The custom data of the vision point that corresponds to the index is stored in the variable. The data type is num. Indexes start with 1.
Output Parameters
MM_P
This parameter stores the TCP of the vision point that corresponds to the index. The data type is robtarget.
MM_Label
This parameter stores the label of the vision point that corresponds to the index. If no label ports are specified in Mech-Vision, 0 is used. The data type is num.
MM_UserData
This parameter stores the custom data of the vision point that corresponds to the specified index. The parameter is a predefined global array variable. The data type is num.
Get Gripper DO List
Command
This command obtains the control signal list for the multi-section vacuum gripper from the Mech-Vision or Mech-Viz project. The robot applies the DO signals obtained by Set Gripper DO List as the tool.
Before using this command, you must perform the following configurations in Mech-Vision or Mech-Viz.
-
Configure the Mech-Vision project
-
In the Path Planning Step, click Config wizard. In Global configuration, enable Box depalletizing.
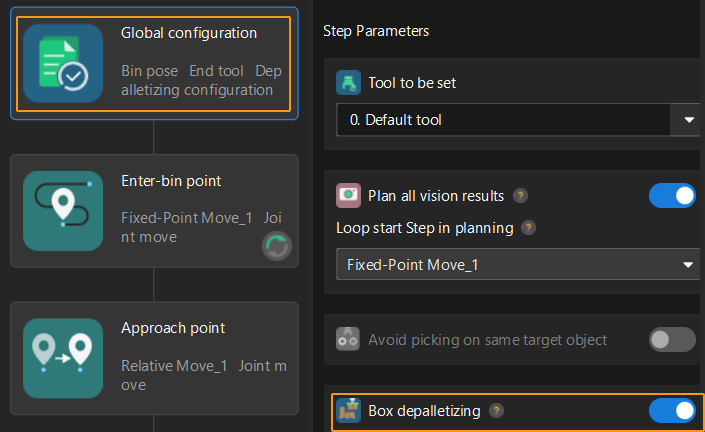
-
In the Path Planning Step, click Config wizard, and then double-click the name of the robot tool. In the pop-up window, select Depalletizing vacuum gripper for Tool type, click Configure depalletizing vacuum gripper, and then configure DO signals according to needs.
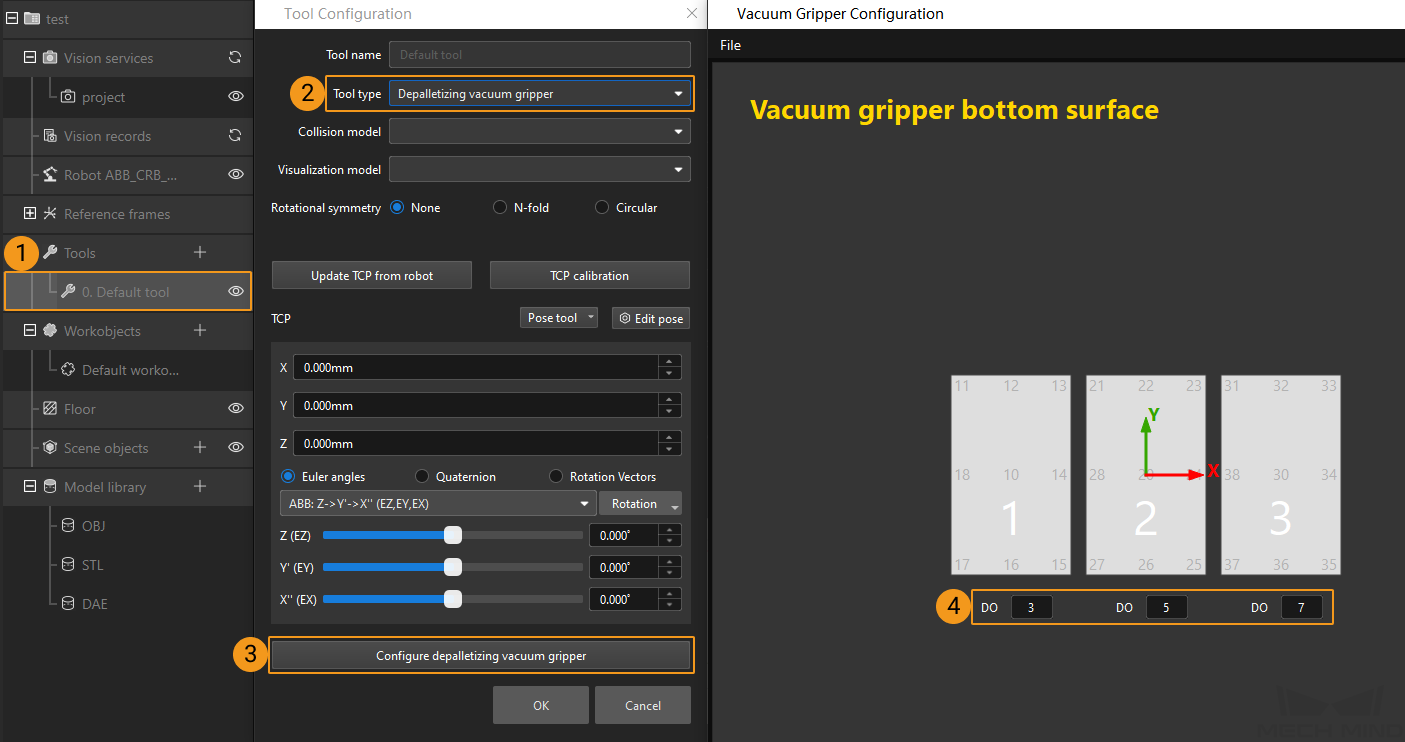
-
-
Configure the Mech-Viz project
-
In the Vision Move Step of Mech-Viz, set Select Picking Method to Box depalletizing.

-
In Mech-Viz, double-click the tool name, select Depalletizing vacuum gripper for Tool type, click Configure depalletizing vacuum gripper, and then configure the DO signal values according to needs.
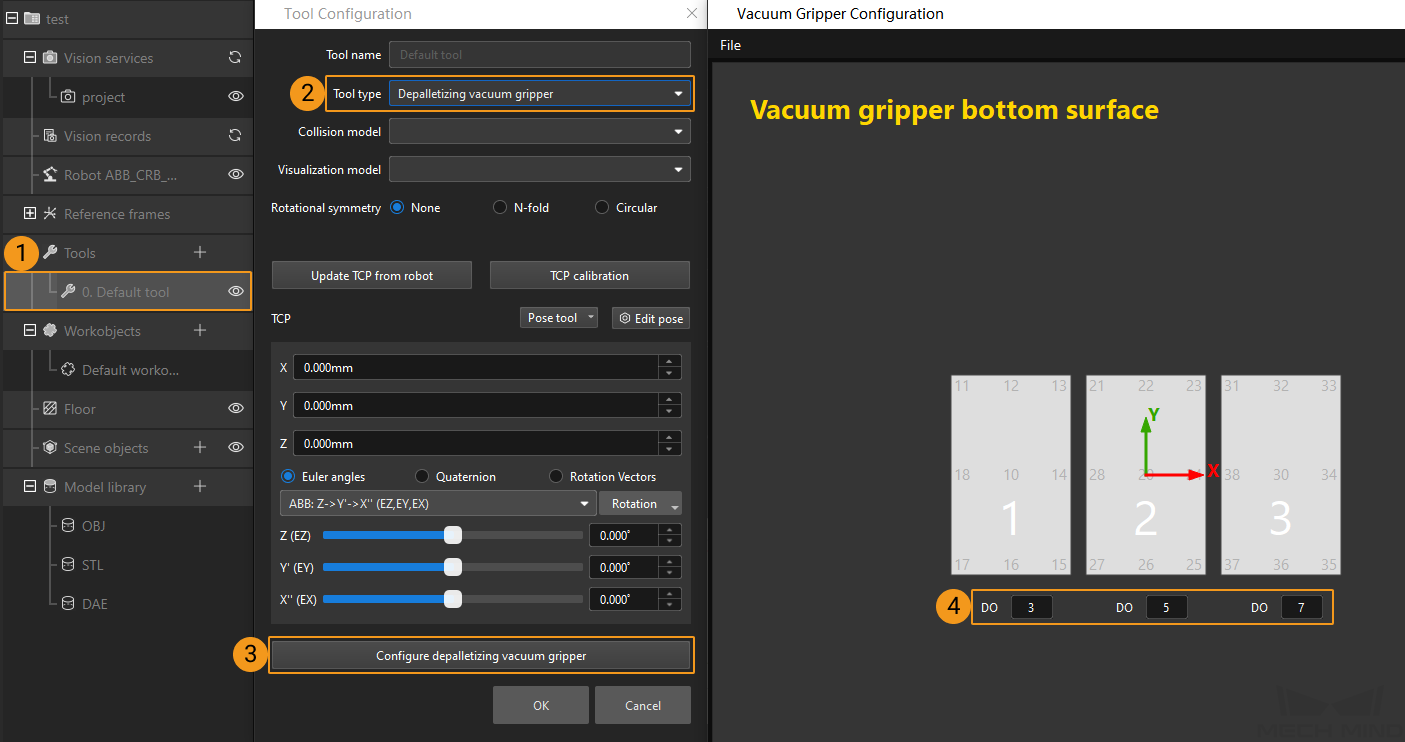
-
Calling Sequence
-
This command must be called before the Get Planned Path in Mech-Vision, Get Planned Path in Mech-Viz, or Get Vision Move Data or Custom Data command. This means that the robot must obtain the motion path and then obtain gripper DO signals of the Vision Move waypoint.
-
This command should be called before Set Gripper DO List.
Command Format
MM_Get_DoList Resource,BlockNum;Input Parameters
Resource
This parameter specifies the source of the DO signal list. The data type is num. Value range: 0 to the largest positive integer.
-
0: Get DO signal list from Mech-Viz.
-
A positive integer: Get DO signal list from Mech-Vision. The positive integer is the Mech-Vision project ID.
BlockNum
This parameter specifies the number of gripper sections that are specified in the gripper configuration tool. For example, the number of gripper sections in the above image is 3.
The DO signals returned by this command vary based on the deployed project.
-
Gripper DO signals planned by the Mech-Vision project
-
Under Global Configuration of the path planning tool, if Plan all vision results is disabled, this command returns 64 gripper DO signals that are planned in this round. Valid DO signals are non-negative integers ranging from 0 to 999. Invalid DO signals are -1, which serves as a placeholder.
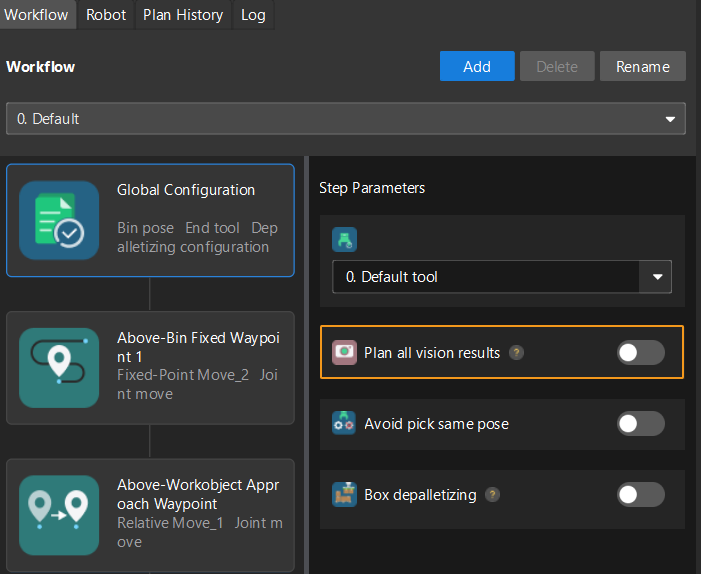
For example, valid DO signals in the table below are 1, 3, 5, and 6, which means that the robot will set the values of these DO signals to ON.
1st
2nd
3rd
4th
5th
6th
7th
8th
…
63rd
64th
1
3
5
6
-1
-1
-1
-1
…
-1
-1
-
Under Global Configuration of the path planning tool, if Plan all vision results is enabled, Mech-Vision can perform multiple rounds of planning based on the same vision result. The 64 gripper DO signals returned by this command are obtained during all rounds of planning. In this case, you can use the number of vacuum gripper sections to differentiate the gripper DO signals obtained during each round of planning.
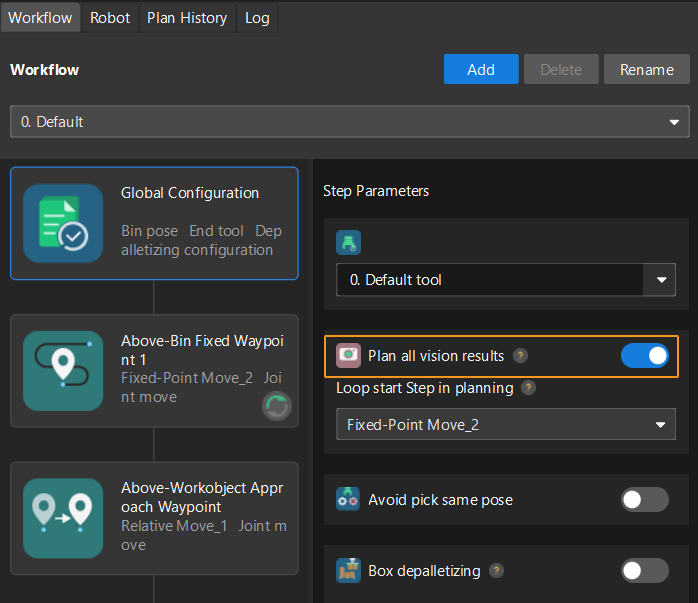
For example, if the number of vacuum gripper sections is 4 and the command returns 64 DO signals in total, each 4 DO signals are multi-section vacuum gripper signals obtained during each round of planning.
First round of planning
Second round of planning
…
16th round of planning
1st
2nd
3rd
4th
5th
6th
7th
8th
…
61st
62nd
63rd
64th
1
3
4
-1
1
4
-1
-1
…
-1
-1
-1
-1
-
-
Gripper DO signals planned by the Mech-Viz project
-
If Reuse Vision Result is not selected for the Vision Move Step, this command returns 64 gripper DO signals that are planned during this round. Valid DO signals are non-negative integers ranging from 0 to 999. Invalid DO signals are -1, which serves as a placeholder.
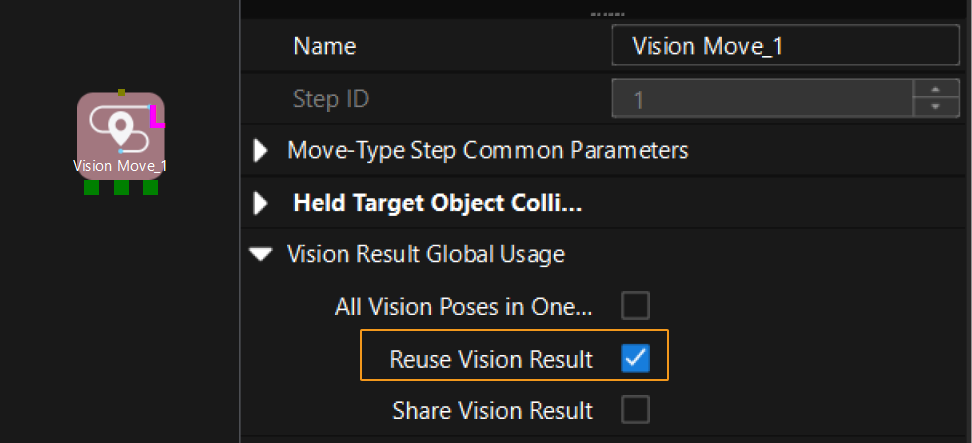
For example, valid DO signals in the table below are 1, 3, 5, and 6, which means that the robot will set the values of these DO signals to ON.
1st
2nd
3rd
4th
5th
6th
7th
8th
…
63rd
64th
1
3
5
6
-1
-1
-1
-1
…
-1
-1
-
If Reuse Vision Result is selected for the Vision Move Step and the Vision Move Step is used in a loop, Mech-Viz can perform multiple rounds of planning based on the same vision result. The 64 gripper DO signals returned by this command are obtained during all rounds of planning. In this case, you can use the number of vacuum gripper sections to differentiate the gripper DO signals obtained during each round of planning.
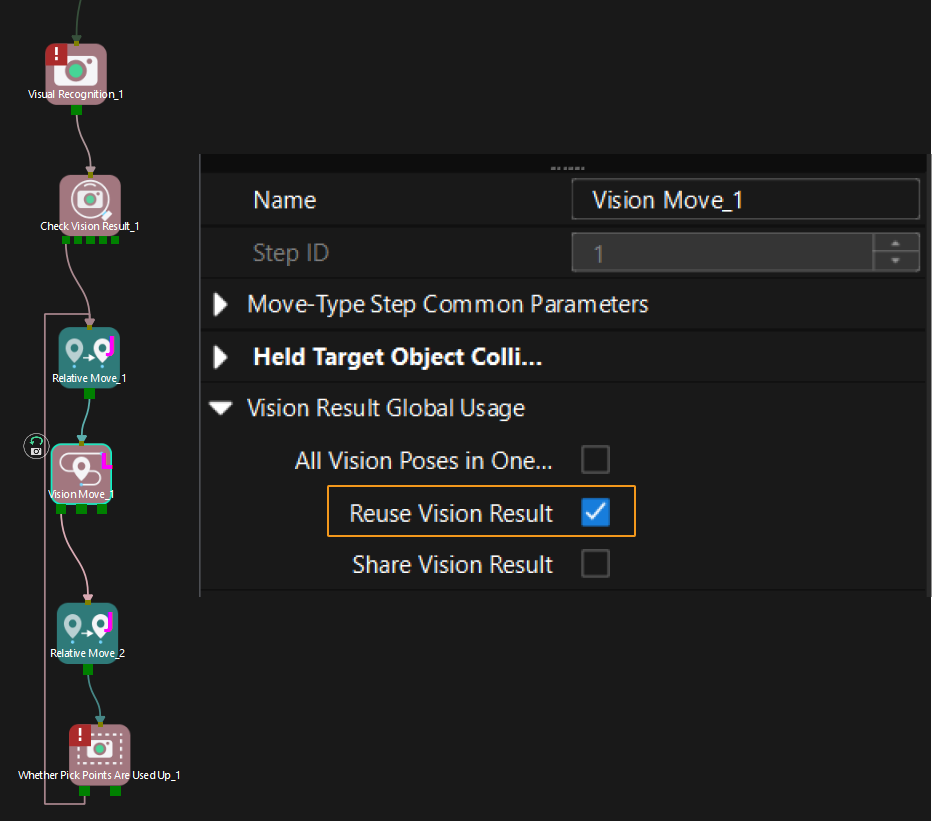
For example, if the number of vacuum gripper sections is 4 and the command returns 64 DO signals in total, each 4 DO signals are multi-section vacuum gripper signals obtained during each round of planning.
First round of planning
Second round of planning
…
16th round of planning
1st
2nd
3rd
4th
5th
6th
7th
8th
…
61st
62nd
63rd
64th
1
3
4
-1
1
4
-1
-1
…
-1
-1
-1
-1
-
Set Gripper DO List
Command
This command sets obtained DO signals to GO signals. It supports a maximum of four GO signal groups. Each GO signal group is 16-bit. If you need to set multiple groups of GO signals, call this command multiple times.
Calling Sequence
This command should be called after Get Gripper DO List.
Command Format
MM_Set_DoList Loop_Index,Serial,Go16;Input Parameters
Loop_Index
This parameter specifies the round of planning for which gripper DO signals are set.
Serial
This parameter specifies the signal group index. The following table describes how signal group indexes correspond to DO signals. The data type is num. Value range: 1 to 4.
Signal group index |
DO signal range |
1 |
0~15 |
2 |
16~31 |
3 |
32~47 |
4 |
48~63 |
Go16
This parameter indicates the signal group name, which can be used to set DO signals. You can define the signal group name based on the actual number of DO signals. The data type is signalgo.
Run Mech-Viz Project
Command
This command triggers the Mech-Viz project to run. Mech-Viz plans the robot’s motion path based on the vision result output by Mech-Vision.
| Right-click the project name in the project resource panel in Mech-Viz and select Autoload Project. |
Calling Sequence
You should set Step parameters before starting a Mech-Viz project. Therefore, call Read Mech-Viz Step Parameter or Set Mech-Viz Step Parameter before calling Run Mech-Viz Project.
Command Format
MM_Start_Viz SendPos_Type,MM_J;Input Parameters
SendPos_Type
This parameter specifies the way in which the real robot pose is sent to the Mech-Viz project. Valid values: 0, 1, and 2. The following table describes the details. The data type is num.
| Robot pose type | Description | Applicable scenario |
|---|---|---|
0 |
This command does not need to send the robot pose to the Mech-Viz project. The simulated robot in the Mech-Viz project will move from the set home position to the first waypoint. |
This setting is recommended when the camera is mounted in eye to hand mode. |
1 |
In this command, the robot sends its current joint positions and flange pose to the Mech-Viz project. The simulated robot in Mech-Viz moves from the input joint positions to the first waypoint. |
This setting is recommended when the camera is mounted in eye in hand mode. |
2 |
In this command, the robot sends the joint positions of a teach point (the custom joint positions, instead of the current joint positions) to the Mech-Viz project. The Mech-Viz project uses the input joint positions to plan the next path in advance while the robot is not in the camera capture region, as shown in the following figure. The simulated robot in Mech-Viz moves from the input joint positions to the first waypoint. |
This setting is recommended when the camera is mounted in eye to hand mode. |
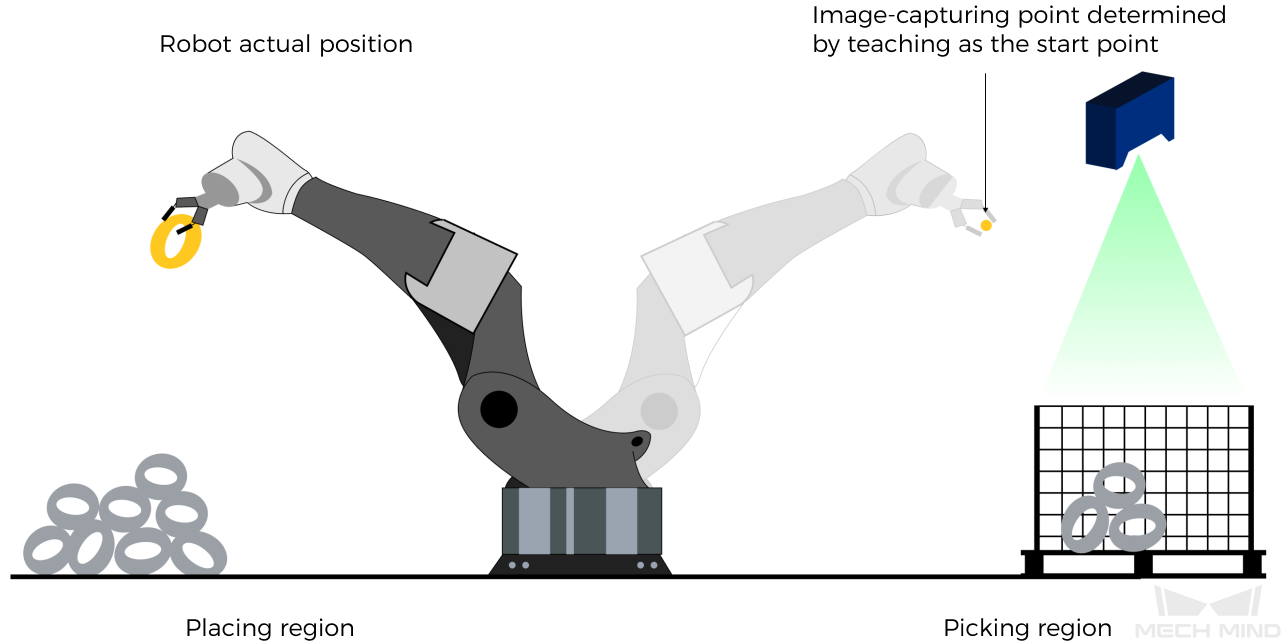
Why robot pose type 2 is recommended when the camera is mounted in eye to hand mode?
In eye to hand mode, the camera can perform image capturing for the next round of path planning before the robot returns to the image capture region and picking region, thus shortening the cycle time. The image below demonstrates how a robot works in the placing region.
If SendPos_Type is set to 1, the robot will send the current pose to Mech-Viz. It is possible that the real robot moves to other positions before reaching the first waypoint. However, the simulated robot moves directly to the first waypoint of the Mech-Viz project from the pose sent by the robot. Consequently, there may be a mismatch between the paths of the real robot and simulated robot. This mismatch can potentially lead to unpredicted safety hazards, especially if collision is detected in the path of the simulated robot.
On the other hand, if SendPos_Type is set to 2, the robot will send the image-capturing pose set by teach to Mech-Viz. Thus, the real robot can trigger the next round of path planning in Mech-Viz when the real robot is in the image-capturing region and the cycle time can be shortened.
In conclusion, robot pose type should be set to 2 for projects in eye to hand mode.
MM_J
This parameter specifies the custom joint positions. The data type is jointtarget.
-
If SendPos_Type is set to 2, the joint positions will be sent to the Mech-Viz project as the start point, where the robot moves from this start point to the first waypoint of the planned path.
-
If SendPos_Type is set to a parameter value other than 2, the joint positions are of no practical use but must be set.
Set Exit Port for Branch by Msg Step in Mech-Viz
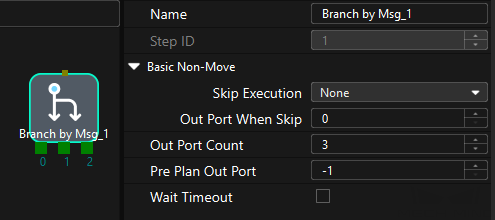
Command
This command sets the exit port for the Branch by Msg Step. When the next Step is a Branch by Msg Step, the Mech-Viz project will wait for this command to specify the exit port.
Calling Sequence
This command should be called after Run Mech-Viz Project.
Command Format
MM_Set_Branch Branch_Num,Export_Num;Input Parameters
Branch_Num
This parameter specifies the Step ID of the Branch by Msg Step. The data type is num. The value is a positive integer. The Step ID is displayed in the Step parameter panel. For example, the Step ID of the Step in the image above is 1.
Export_Num
This parameter specifies the exit port ID of the Branch by Msg Step. The data type is num. The value is a positive integer. When the parameter value is set to N, the Mech-Viz project exits from the port with an ID of N-1 of the Branch by Msg Step.
Set Current Index in Mech-Viz
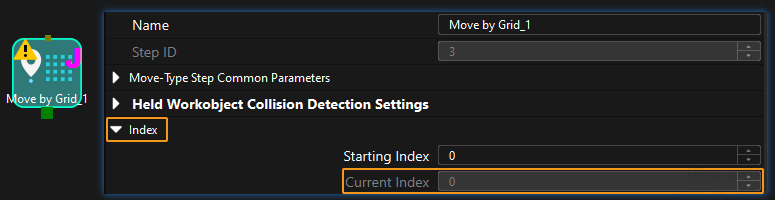
Command
This command sets the value of the Current Index parameter of index-type Steps. Steps that include the Index section include Move by Grid, Move by List, Custom Pallet Pattern, and Predefined Pallet Pattern.
Calling Sequence
Index-type Steps are often preceded by a Branch by Msg Step. The robot should call commands in this order: Run Mech-Viz Project, Set Current Index in Mech-Viz, and Set Exit Port for Branch by Msg Step in Mech-Viz. This is to ensure that Mech-Viz has enough time to set the Current Index value.
Command Format
MM_Set_Index Skill_Num,Index_Num;Input Parameters
Skill_Num
This parameter specifies the Step ID of the Index-type Step. The data type is num. The value is a positive integer. The Step ID is displayed in the Step parameter panel. For example, the Step ID of the Step in the image above is 3.
Index_Num
This parameter specifies the current index for a Index-type Step. The data type is num. The value is a positive integer. When this parameter value is set to N, the current index of the corresponding Step is N-1.
Get Planned Path in Mech-Viz
Command
This command obtains the path planned by the Mech-Viz project as a series of waypoints.
|
Waypoint: Each point that the robot reaches when moving along the planned path. A waypoint has information including the robot pose, label, and motion type. Waypoints can be divided into two categories:
|
Calling Sequence
This command should be called after Run Mech-Viz Project. After you call this command, call Store Vision Result or Planned Path (TCP) or Store Planned Path (joint positions) to access pose data.
Command Format
MM_Get_VizData Jps_Pos,Pos_Num,VisPos_Num,MM_Status;Input Parameters
Jps_Pos
This parameter specifies the type of waypoint poses to be obtained. The data type is num. can be set to 1 or 2.
-
1: joint positions. After you run this command, run Store Planned Path (joint positions) to access joint position data.
-
2: tool poses. After you run this command, run Store Vision Result or Planned Path (TCP) to access tool pose data.
Output Parameters
Pos_Num
This parameter stores the number of waypoints that are returned by the vision system. By default, the vision system sends no more than 20 waypoints at a time. Therefore, the maximum default value of this parameter is 20. To modify the default maximum number of poses to obtain each time as needed, go to Robot and Communication > in the toolbar of Mech-Vision. The upper limit is 30.

VisPos_Num
The sequence number of the Vision Move waypoint (i.e., the waypoint corresponding to the Vision Move step in the Mech-Viz project) in the path. The data type is num. If the waypoint does not exist in the path, the petameter value is 0.
If the planned path consists of the following waypoints in sequence: Fixed-Point Move_1, Fixed-Point Move_2, Vision Move, and Fixed-Point Move_3, the sequence number of the Vision Move waypoint is 3.
MM_Status
This parameter stores the status code of this command. The data type is num. If the command is successfully executed, the status code is 2100. If a command fails to be run, a specific error code is returned. For details, see Status Codes and Troubleshooting.
|
By default, after the robot sends this command, the vision system returns the result in 10 seconds. If the vision system fails to return any result in 10 seconds, a timeout error code is returned. To modify the default timeout period as needed, go to Robot and Communication > in the toolbar of Mech-Vision. 
|
Example
MM_Get_VizData 2,PosNum,VisIndex,StatusCode;In the preceding example, the planned path of the Mech-Viz project is obtained, the pose type of the waypoints is TCP, the number of waypoints is stored in PosNum, the sequence number of the Vision Move waypoint in the planned path is stored in VisIndex, and the status code of the command is stored in StatusCode.
Trigger Mech-Viz Project and Get Planned Path
Command
This command triggers the following operations in sequence: start the Mech-Viz project, set the exit port for the Branch by Msg Step (which is skipped if the project doesn’t have a parameter recipe), and return the path planned by the Mech-Viz project. This command is equivalent to the combination of the Run Mech-Viz Project, Set Exit Port for Branch by Msg Step in Mech-Viz, and Get Planned Path in Mech-Viz commands.
|
Command Format
MM_Lite_Viz Branch_Num,Export_Num,Recv_Data_Type,MM_Status,\Pos_Num,\VisPos_Num;Input Parameters
Branch_Num
This parameter specifies the ID of the Branch by Msg Step. The data type is num. Value range: 0 to the largest positive integer. A value of 0 indicates that no Branch by Msg Steps are used in the Mech-Viz project. The Step ID is displayed in the parameters of the Step.
Export_Num
This parameter specifies the exit port ID of the Branch by Msg Step. The data type is num. The value is a positive integer. When the parameter value is set to N, the Mech-Viz project exits from the port with an ID of N-1 of the Branch by Msg Step.
Recv_Data_Type
This parameter specifies the type of waypoint poses to be obtained. The data type is num. can be set to 1 or 2.
-
1: joint positions. After you run this command, run Store Planned Path (joint positions) to access joint position data.
-
2: tool poses. After you run this command, run Store Vision Result or Planned Path (TCP) to access tool pose data.
Output Parameters
MM_Status
This parameter stores the status code of this command. The data type is num. If the command is successfully executed, the status code is 2100. If a command fails to be run, a specific error code is returned. For details, see Status Codes and Troubleshooting.
Pos_Num (Optional)
This parameter stores the number of waypoints that are returned by the vision system. The data type is num.
VisPos_Num (Optional)
The sequence number of the Vision Move waypoint (i.e., the waypoint corresponding to the Vision Move step in the Mech-Viz project) in the path. The data type is num. If the waypoint does not exist in the path, the petameter value is 0.
If the planned path consists of the following waypoints in sequence: Fixed-Point Move_1, Fixed-Point Move_2, Vision Move, and Fixed-Point Move_3, the sequence number of the Vision Move waypoint is 3.
Example
MM_Lite_Viz 1,2,1,StatusCode,\Pos_Num:=PoseNum;In the preceding example, the Mech-Viz project exits from the port with an ID of 1 of the Branch by Msg Step whose ID is 1 and outputs waypoints. The number of waypoints obtained from the Mech-Viz project is stored in PoseNum, and the status code of this command is stored in StatusCode.
Get Vision Move Data or Custom Data
Command
This command obtains Vision Move data from the Mech-Vision project, or the Vision Move data or custom data from the Mech-Viz project. One command call stores all data in robot memory.
|
-
Mech-Vision projects: Vision Move data refers to data output by the Vision Move Step in the path planning tool, which you may enter from the Path Planning Step. Vision Move data includes labels of picked target objects, number of picked target objects, number of target objects to be picked this time, edge or corner ID of vacuum gripper, TCP offset, orientation of target object group, orientation of target object, and dimensions of target object group.
-
Mech-Viz projects:
-
Vision Move data refers to data output by the Vision Move Step in Mech-Viz, including the labels of picked target objects, number of picked target objects, number of target objects to be picked this time, edge or corner ID of vacuum gripper, TCP offset, orientation of target object group, orientation of target object, and dimensions of target object group.
-
Custom data refers to data output by the custom port(s) of the Output Step in Mech-Vision and then forwarded by Mech-Viz.
Select the Output Step, set Port Type to Custom, and then click Open the editor to go to the custom port configuration window. The Customized Keys section of the window displays custom port names, such as customeData1 and customeData2 as shown in the following figure.
-
Data output from Predefined Keys, such as poses, labels, sizes, offsets, is not custom data.
-
You must set Port Type of the Output Step to Custom and select the poses port in the Predefined Keys section in Mech-Vision.

-
-
Calling Sequence
This command should be called after Run Mech-Vision Project or Run Mech-Viz Project. After you call this command, call Store Vision Move Data or Custom Data to access Vision Move data or custom data.
Command Format
MM_get_plandata Resource,Jps_Pos,Pos_Num,VisPos_Num,MM_Status;Input Parameters
Resource
This parameter specifies the source of Vision Move planned data. The data type is num. Value range: 0 to the largest positive integer.
-
0: Get Vision Move data from Mech-Viz.
-
A positive integer: Get Vision Move data from Mech-Vision. The positive integer is the Mech-Vision project ID.
Jps_Pos
This parameter specifies the expected returned data format. The data type is num.
-
If Resource is set to 0, the valid value range of Jps_Pos is 1 to 4.
Parameter value of Jps_Pos
Description of expected returned data (Each field is explained below. If the Mech-Vision project does not have a custom port, no elements of custom data are returned.)
Waypoint type
Returned data
1
Non-Vision Move waypoint
Pose (JPs), motion type, tool ID, velocity
Vision Move waypoint
Pose (joint positions), motion type, tool ID, velocity, element 1 in custom data, … element N in custom data
2
Non-Vision Move waypoint
Pose (TCP), motion type, tool ID, velocity
Vision Move waypoint
Pose (TCP), motion type, tool ID, velocity, element 1 in custom data, … element N in custom data
3
Non-Vision Move waypoint
Pose (JPs), motion type, tool ID, velocity
Vision Move waypoint
Pose (joint positions), motion type, tool ID, velocity, Mech-Viz Vision Move data, element 1 in custom data, … element N in custom data
4
Non-Vision Move waypoint
Pose (TCP), motion type, tool ID, velocity
Vision Move waypoint
Pose (TCP), motion type, tool ID, velocity, Mech-Viz Vision Move data, element 1 in custom data, … element N in custom data
-
If Resource is set to a positive integer, Jps_Pos can be set to 1 to 2.
Parameter value of Jps_Pos
Description of expected returned data (Each field is explained below.)
Waypoint type
Returned data
1
Non-Vision Move waypoint
Pose (JPs), motion type, tool ID, velocity
Vision Move waypoint
Pose (joint positions), motion type, tool ID, velocity, Mech-Vision Vision Move data
2
Non-Vision Move waypoint
Pose (TCP), motion type, tool ID, velocity
Vision Move waypoint
Pose (TCP), motion type, tool ID, velocity, Mech-Vision Vision Move data
Pose
The pose of a waypoint can be joint positions (measured in degrees) or TCP (measured in millimeters for three-dimensional coordinates and in degrees for Euler angles) of the robot.
Motion type
The motion type of the robot. Valid values: 1 and 2.
-
1: Joint motion (MOVEJ)
-
2: Linear motion (MOVEL)
Tool ID
The ID of the tool to be used at this waypoint. A value of -1 means that no tool is used at this waypoint.
Velocity
The meaning of velocity varies based on the project type.
-
For Mech-Vision projects, velocity indicates the Simulation Speed value in the path planning tool, in the form of percentage.
-
For Mech-Viz projects, velocity, represented in percentage, indicates the velocity set for a motion-type Step multiplied by the global velocity set in Mech-Viz.
Vision Move data
Data output by the Vision Move Step in Mech-Vision or Mech-Viz, including labels of picked target objects, number of picked target objects, number of target objects to be picked this time, edge or corner ID of vacuum gripper, TCP offset, orientation of target object group, orientation of target object, and dimensions of target object group.
| Name | Description | Number of elements |
|---|---|---|
Labels of picked target objects |
A label consists of 10 integers. The default value is ten 0s. |
10 |
Number of picked target objects |
The total number of picked target objects. |
1 |
Number of target objects to be picked this time |
The number of target objects to be picked this time. |
1 |
Edge or corner ID of vacuum gripper |
The ID of the edge or corner used to pick target objects this time. |
1 |
TCP offset |
The XYZ offset between the center of the target object group and the tool pose center. |
3 |
Orientation of target object group |
The relative position between the target object group and the length of the vacuum gripper. The value is 0 or 1, where 0 stands for parallel and 1 for vertical. |
1 |
Orientation of target object |
The relative position between the length of a target object and that of the vacuum gripper. The value is 0 or 1, where 0 stands for parallel and 1 for vertical. |
1 |
Dimensions of target object group |
The length, width, and height of the target object group to be picked this time. |
3 |
Elements in custom data
The data of all custom ports of a single vision point. For example, data output from ports of the Output Step is presented in the following table. The elements in custom data of the first vision point are [0, 0, 1] and [0, 0]; and the elements in custom data of the second vision point are [1, 0, 0] and [1, 1].
Port name |
poses |
labels |
customData1 |
customData2 |
Output data |
[ [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0] ] |
[ "0", "1" ] |
[ [0, 0, 1], [1, 0, 0] ] |
[ [0, 0], [1, 1] ] |
First vision point |
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0] |
0 |
[0, 0, 1] |
[0, 0] |
Second vision point |
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0] |
1 |
[1, 0, 0] |
[1, 1] |
Output Parameters
Pos_Num
This parameter stores the number of waypoints that are returned by the vision system. The data type is num.
VisPos_Num
This parameter indicates the sequence number of the Vision Move waypoint (i.e., the waypoint corresponding to the “Vision Move” Step) in the planned path. The data type is num. If the path does not contain a “Vision Move” waypoint, the value of this parameter is 0.
For example, if the planned path consists of the following waypoints: "Fixed-Point Move_1", "Fixed-Point Move_2", "Vision Move", "Fixed-Point Move_3", the sequence number of the Vision Move waypoint is 3.
MM_Status
This parameter stores the status code of this command. The data type is num. If the command successfully obtained Vision Move data of the Mech-Vision project, the status code is 1103. If the command successfully obtained the Vision Move data or custom data from the Mech-Viz project, the status code is 2100. If a command fails to be run, a specific error code is returned. For details, see Status Codes and Troubleshooting.
Example
MM_get_plandata 0,4,PosNum,VisIndex,StatusCode;In the preceding example, the Vision Move data or custom data is obtained from the Mech-Viz project. The number of waypoints is stored in PoseNum, the sequence number of the Vision Move waypoint in the path is stored in VisIndex, and the status code of the command is stored in StatusCode.
Store Vision Move Data or Custom Data
Command
After calling the Get Vision Move Data or Custom Data command, this command is used to save the waypoint data to specified variables.
Calling Sequence
This command should be called after Get Vision Move Data or Custom Data.
Command Format
Select different commands based on the Jps_Pos value in the Get Vision Move Data or Custom Data command.
MM_Get_PlanPose Serial,Jps_Pos,MM_P,MM_MoveType,MM_ToolNum,MM_Speed; (when the value of Jps_Pos is 2 or 4)
MM_Get_PlanJps Serial,Jps_Pos,MM_J,MM_MoveType,MM_ToolNum,MM_Speed; ( when the value of Jps_Pos is 1 or 3)Input Parameters
Serial
This parameter specifies the index of the waypoint. The data of the waypoint that corresponds to the index are stored in the variables. The data type is num. Indexes start with 1.
Jps_Pos
This parameter must be set to the same as the Jps_Pos value in the Get Vision Move Data or Custom Data command. The data type is num.
Output Parameters
MM_P
This parameter stores the TCP data of the waypoint that corresponds to the index. This parameter is used in MM_Get_PlanPose. The data type is robtarget.
MM_J
This parameter stores the joint positions of the waypoint that corresponds to the index. This parameter is used in MM_Get_PlanJps. The data type is jointtarget.
MM_MoveType
This parameter stores the motion type of the waypoint that corresponds to the index. The data type is num. A value of 1 indicates joint motion, and a value of 2 indicates linear motion.
MM_ToolNum
This parameter stores the tool ID of the waypoint that corresponds to the index. The data type is num. If the tool ID is -1, no tool is used.
MM_ToolId
This parameter stores the velocity of the waypoint that corresponds to the index. The data type is num.
MM_UserData
This parameter stores the custom data of the waypoint that corresponds to the index. The parameter is a predefined global array variable. The data type is num.
MM_Plan_Results
This parameter stores the Vision Move data of the waypoint that corresponds to the index. The parameter is a predefined global array variable. The data type is num.
The following table describes the MM_Plan_Results array variable.
| Value | Description | Variable |
|---|---|---|
Labels of picked target objects |
A label consists of 10 integers. The default value is ten 0s. |
MM_Plan_Results{1} ~ MM_Plan_Results{10} |
Number of picked target objects |
The total number of picked target objects. |
MM_Plan_Results{11} |
Number of target objects to be picked this time |
The number of target objects to be picked this time. |
MM_Plan_Results{12} |
Edge or corner ID of vacuum gripper |
The ID of the edge or corner used to pick target objects this time. |
MM_Plan_Results{13} |
TCP offset |
The XYZ offset between the center of the target object group and the tool pose center. |
MM_Plan_Results{14} ~ MM_Plan_Results{16} |
Orientation of target object group |
The relative position between the target object group and the length of the vacuum gripper. The value is 0 or 1, where 0 stands for parallel and 1 for vertical. |
MM_Plan_Results{17} |
Orientation of target object |
The relative position between the length of a target object and that of the vacuum gripper. The value is 0 or 1, where 0 stands for parallel and 1 for vertical. |
MM_Plan_Results{18} |
Dimensions of target object group |
The length, width, and height of the target object group to be picked this time. |
MM_Plan_Results{19} ~ MM_Plan_Results{21} |
Example
-
Example 1:
MM_Get_PlanPose 2,4,TcpPose,MoveType,ToolNum,Speed;In the preceding example, the TCP, motion type, tool ID, and velocity of the second waypoint are stored in TcpPose, MoveType, ToolNum, and Speed respectively. If the waypoint is not a Vision Move waypoint, no Vision Move data is returned; if the waypoint is a Vision Move waypoint, the corresponding Vision Move data is stored in the MM_Plan_Results global array and the corresponding custom data is stored in the MM_UserData global array.
-
Example 2:
MM_Get_PlanJps 1,3,JpsPose,MoveType,ToolNum,Speed;In the preceding example, the joint positions, motion type, tool ID, and velocity of the first waypoint are stored in JpsPose, MoveType, ToolNum, and Speed respectively. If the waypoint is not a Vision Move waypoint, no Vision Move data is returned; if the waypoint is a Vision Move waypoint, the corresponding Vision Move data is stored in the MM_Plan_Results global array and the corresponding custom data is stored in the MM_UserData global array.
Read Mech-Viz Step Parameter
Calling Sequence
This command should be called before Run Mech-Viz Project.
Command Format
MM_Get_Property Get_Id,MM_Status,MM_Viz_Prop;Input Parameters
Get_Id
This parameter corresponds to the Config ID field defined in the property_config file. The data type is num.
|
From the toolbar of Mech-Vision, go to . Click Property Configuration to open the property_config file. 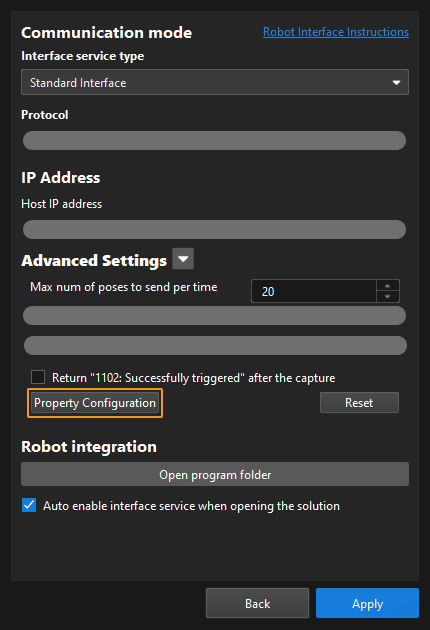
|
Before calling this function, you should define a Config ID and its corresponding Step ID and parameter key name in the following format in the property_config file.
read, Config ID, Step ID, parameter key name
read |
Indicates that this line is used to read the parameter value of a Step. |
Config ID |
Specifies a unique ID, which is a positive integer. One Config ID corresponds to only one parameter value of a Step. To read multiple parameter values, you should set different Config IDs. |
Step ID |
The Step ID of the Step whose parameter is to be read. |
parameter key name |
Specifies the key name of the parameter whose value the robot requires to read. |
|
|
The property_config file can have multiple read commands. The Config ID in these commands must be different. |
Output Parameters
MM_Status
This parameter stores the status code of this command. The data type is num. If the command is successfully executed, the status code is 2109. If a command fails to be run, a specific error code is returned. For details, see Status Codes and Troubleshooting.
MM_Viz_Prop
This parameter stores the parameter value of the Step. The data type is num.
Example
In the line below, 5 is the Config ID; 3 is the Step ID; and xCount is the parameter key name. Add this line to the property_config file.
read,5,3,xCountWhen the robot sends the command below, the robot receives the value of the parameter whose key name is xCount.
MM_Get_Property 5,StatusCode,Viz_Prop;In the preceding example, the value of the xCount parameter of the Step with an ID of 3 of the Mech-Viz project is stored in Viz_Prop, and the status code of the command is stored in StatusCode.
Set Mech-Viz Step Parameter
Calling Sequence
This command should be called before Run Mech-Viz Project.
Command Format
MM_Set_Property Set_Id,MM_Status;Input Parameters
Set_Id
This parameter corresponds to the Config ID field defined in the property_config file. The data type is num.
|
From the toolbar of Mech-Vision, go to . Click Property Configuration to open the property_config file. 
|
Before sending this command, you should define a Config ID and its corresponding Step ID, parameter key name and parameter value in the following format in the property_config file.
write, Config ID, Step ID, parameter key name, parameter value
write |
Indicates that this line is used to set the parameter value of a Step. |
Config ID |
Specifies an ID, which is a positive integer and can be used repeatedly. |
Step ID |
Specifies the Step whose parameter value the robot requires to read. |
parameter key name |
Specifies the key name of the parameter whose value the robot requires to set. |
parameter value |
Specifies the value that the robot sets for the parameter. |
|
Output Parameters
MM_Status
This parameter stores the status code of this command. The data type is num. If the command is successfully executed, the status code is 2108. If a command fails to be run, a specific error code is returned. For details, see Status Codes and Troubleshooting.
Example
In the line below, 1 is the Config ID and 3 is the Step ID. xOffset, yOffset and zOffset are parameter key names; and 10, 20 and 30 are their respective values. Add this line to the property_config file.
write,1,3,xOffset,10
write,1,3,yOffset,20
write,1,3,zOffset,30When the robot sends the command below, Mech-Viz sets the values of the parameters whose key names are xOffset, yOffset and zOffset respectively to 10, 20 and 30.
MM_Set_Property 1,StatusCode;The preceding example sets the values of the parameters whose key names are xOffset, yOffset and zOffset respectively to 10, 20 and 30, and stores the status code of the command in StatusCode.
Input Object Dimensions to Mech-Vision Project
Command
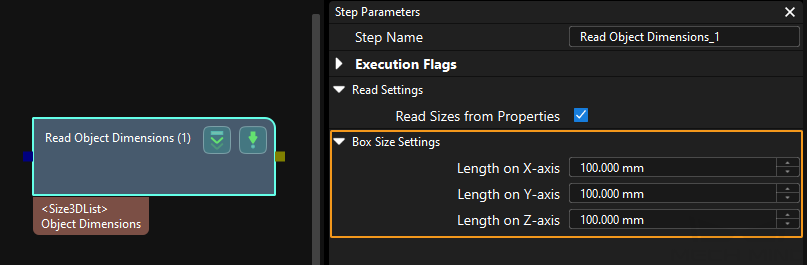
This command dynamically inputs object dimensions into the Mech-Vision project. The object dimensions are the values of the Box Size Settings parameters in the Read Object Dimensions Step.
| When you use this command, only one Read Object Dimensions Step is allowed in the Mech-Vision project. Otherwise, the vision system will return an error. |
Calling Sequence
This command should be called before Run Mech-Vision Project.
Command Format
MM_Set_BoxSize Job,Length,Width,Height;Input Parameters
Job
Mech-Vision project ID. You can view the project ID of a The data type is num. Mech-Vision project in the Project List section of Mech-Vision. The project ID is the number before the project name.
Length, Width, and Height
The preceding three parameters sequentially input the length, width, and height of the object to the Mech-Vision project. The length, width, and height are measured in millimeters (mm). These values are read by the Read Object Dimensions Step and set for the parameters Length on X-axis, Length on Y-axis and Length on Z-axis. The data type is num.
Get Message from Notify Step
Command
When the Mech-Vision project or Mech-Viz project is executing the Notify Step, the vision system returns the message predefined in the Notify Step.
Before sending this command, complete the following settings for the Notify Step:
-
For a Notify Step in the Mech-Vision project:
-
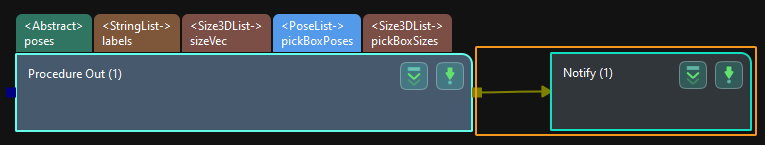
Connect the Notify Step to the right side of another Step. The Output Step is used in the example in the image below.
-
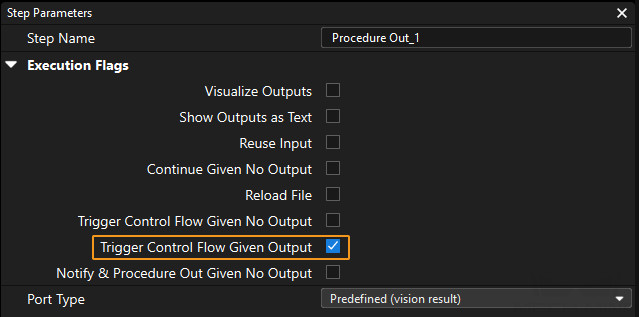
Select Trigger Control Flow Given Output in the parameter panel of the Output Step.
-
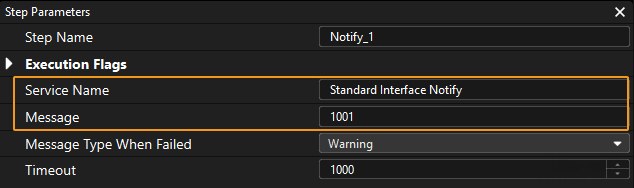
In the parameter panel of the Notify Step, enter Standard Interface Notify (a required value) for Service Name. Enter a positive integer for Message, for example, 1001.
-
-
For a Notify Step in the Mech-Viz project:
-
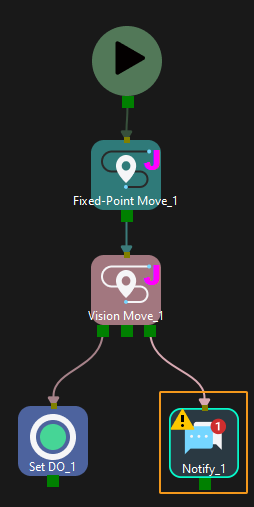
Connect the Notify Step to a proper Step in the workflow.
-
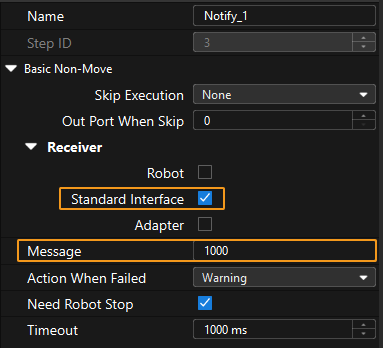
In the parameter panel of the Notify Step, select Standard Interface. Enter a positive integer for Message, for example, 1000.
-
Calling Sequence
This command should be called right after Run Mech-Vision Project or Run Mech-Viz Project.
Command Format
MM_Get_Notify Msg;Output Parameters
Msg
This parameter stores the message from the Notify Step. Only positive integer messages are supported at the moment. The data type is num.
| When the Notify Step is executed in the Mech-Vision or Mech-Viz project, the message remains in the buffer of the vision system for only three second. Therefore, you should consider the timing of calling this command to ensure successful message retrieval. |
Calibration
Command
This command is used for robot hand-eye calibration (extrinsic parameter calibration). This command must be used together with the Camera Calibration setting to complete automatic calibration. You can find Camera Calibration in the toolbar of Mech-Vision. For more information, see ABB RobotWare 6 Automatic Calibration.
Command Format
MM_Calib Move_Type,Pos_Jps,Wait_time\Ext;Input Parameters
Move_Type
This parameter specifies the motion type of the robot. Valid values: 1 and 2.
-
1: Linear motion (MOVEL)
-
2: Joint motion (MOVEJ)
Pos_Jps
This parameter specifies the type of calibration point poses to be obtained. Valid values: 1 and 2.
-
1: TCP
-
2: Joint positions
Wait_time
This parameter specifies the time the robot waits to avoid shaking after it moves to the calibration point. The default value is 2 (s). The data type is num.
Ext (optional)
This parameter specifies the external axis data. Unit: millimeters. If a 7th axis exists and is controlled by the robot on site, this parameter must be set.
Example
-
Example 1:
MM_Calib 2,1,2;In the preceding example, the pose data of the calibration point is represented in TCP. The robot moves to the calibration point based on the joint positions of the robot and then waits for 2 seconds.
-
Example 2:
MM_Calib 2,1,2\EXT:=Axis7;In the preceding example, the pose data of the calibration point is represented in TCP. The robot moves to the calibration point based on the joint positions of the robot and then waits for 2 seconds. The 7th-axis value is Axis7.
Stop Mech-Viz Project
Calling Sequence
This command should be called after Run Mech-Viz Project.
Command Format
MM_Stop_Viz MM_Status;Output Parameters
MM_Status
This parameter stores the status code of this command. The data type is num. If the command is successfully executed, the status code is 2104. If a command fails to be run, a specific error code is returned. For details, see Status Codes and Troubleshooting.
Get Project Status
Command Format
MM_Get_Status MM_Status;Output Parameters
MM_Status
This parameter stores the status code of this command. The data type is num. If the command is successfully executed, a status code of 1101 is returned to indicate that the Mech-Vision project is ready. If a command fails to be run, a specific error code is returned. For details, see Status Codes and Troubleshooting.