샘플 프로그램6: MM_S6_Viz_ErrorHandle
프로그램 소개
기능 설명 |
로봇이 Mech-Viz프로젝트 실행을 트리거한 후, 경로 계획 결과를 휙득하고 상태 코드에 따라 계획된 경로를 성공적으로 획득했는지 확인합니다. 성공적으로 계획 경로를 획득하면 로봇은 피킹 및 배치 작업을 실행합니다. 그렇지 않으면, 로봇은 실행이 종료됩니다. |
파일 경로 |
Mech-Vision 및 Mech-Viz의 설치 디렉토리로 이동하여 |
필요한 프로젝트 |
Mech-Vision와 Mech-Viz 프로젝트 |
사용 전제 조건 |
|
| 이 샘플 프로그램은 참고용으로 제공됩니다. 사용자는 실제 상황에 맞춰 이 내용을 바탕으로 수정해야 하며, 해당 프로그램을 그대로 사용하지 않도록 하십시오. |
프로그램 설명
다음에는 MM_S6_Viz_ErrorHandle 샘플 프로그램의 코드와 관련 설명입니다.
| MM_S2_Viz_Basic 샘플과 비하면, 이 샘플은 다양한 오류 상태 코드를 처리할 수 있는 기능만 추가되었습니다.(이 기능의 코드가 굵게 표시됨). 따라서, MM_S6_Viz_ErrorHandle의 MM_S2_Viz_Basic과 일치하는 부분은 다시 설명하지 않습니다. (일치하는 부분에 대한 정보는 MM_S2_Viz_Basic샘플 프로그램 설명을 참조하십시오). |
1: !-------------------------------- ;
2: !FUNCTION: trigger Mech-Viz ;
3: !project and get planned path, ;
4: !handle errors according to ;
5: !status codes (if no point cloud ;
6: !in ROI, retry several times ;
7: !before exit loop) ;
8: !Mech-Mind, 2023-12-25 ;
9: !-------------------------------- ;
10: ;
11: !set current uframe NO. to 0 ;
12: UFRAME_NUM=0 ;
13: !set current tool NO. to 1 ;
14: UTOOL_NUM=1 ;
15: !reset counter ;
16: R[99]=0 ;
17: !move to robot home position ;
18:J P[1] 100% FINE ;
19: !initialize communication ;
20: !parameters(initialization is ;
21: !required only once) ;
22: CALL MM_INIT_SKT('8','127.0.0.1',50000,5) ;
23: !move to image-capturing position ;
24:L P[2] 1000mm/sec FINE ;
25: LBL[1:vision] ;
26: !trigger Mech-Viz project ;
27: CALL MM_START_VIZ(2,10) ;
28: !get planned path, 1st argument ;
29: !(1) means getting pose in JPs ;
30: CALL MM_GET_VIZ(1,51,52,53) ;
31: !check whether planned path has ;
32: !been got from Mech-Viz ;
33: !successfully ;
34: IF R[53]<>2100,JMP LBL[99] ;
35: !save waypoints of the planned ;
36: !path to local variables one ;
37: !by one ;
38: CALL MM_GET_JPS(1,60,70,80) ;
39: CALL MM_GET_JPS(2,61,71,81) ;
40: CALL MM_GET_JPS(3,62,72,82) ;
41: !follow the planned path to pick ;
42: !move to approach waypoint ;
43: !of picking ;
44:J PR[60] 50% FINE ;
45: !move to picking waypoint ;
46:J PR[61] 10% FINE ;
47: !add object grasping logic here, ;
48: !such as "DO[1]=ON" ;
49: PAUSE ;
50: !move to departure waypoint ;
51: !of picking ;
52:J PR[62] 50% FINE ;
53: !move to intermediate waypoint ;
54: !of placing ;
55:J P[3] 50% CNT100 ;
56: !move to approach waypoint ;
57: !of placing ;
58:L P[4] 1000mm/sec FINE Tool_Offset,PR[2] ;
59: !move to placing waypoint ;
60:L P[4] 300mm/sec FINE ;
61: !add object releasing logic here, ;
62: !such as "DO[1]=OFF" ;
63: PAUSE ;
64: !move to departure waypoint ;
65: !of placing ;
66:L P[4] 1000mm/sec FINE Tool_Offset,PR[2] ;
67: !move back to robot home position ;
68:J P[1] 100% FINE ;
69: END ;
70: ;
71: LBL[99:vision error] ;
72: IF R[53]=2038,JMP LBL[2] ;
73: JMP LBL[999] ;
74: ;
75: LBL[2] ;
76: !no point cloud in ROI, add ;
77: !handling logic here ;
78: !self-adding then check retry ;
79: !counter ;
80: R[99]=R[99]+1 ;
81: !jump back to vision retry label ;
82: !if the number of retry times is ;
83: !less than 3 ;
84: IF R[99]<3,JMP LBL[1] ;
85: !reset counter and exit loop if ;
86: !the number of retry times has ;
87: !reached 3 ;
88: R[99]=0 ;
89: JMP LBL[999] ;
90: ;
91: LBL[999:other error] ;
92: !add other error handling logic ;
93: !here ;
94: PAUSE ;위 샘플 프로그램 코드에 해당하는 워크플로는 아래 그림에 표시되어 있습니다.
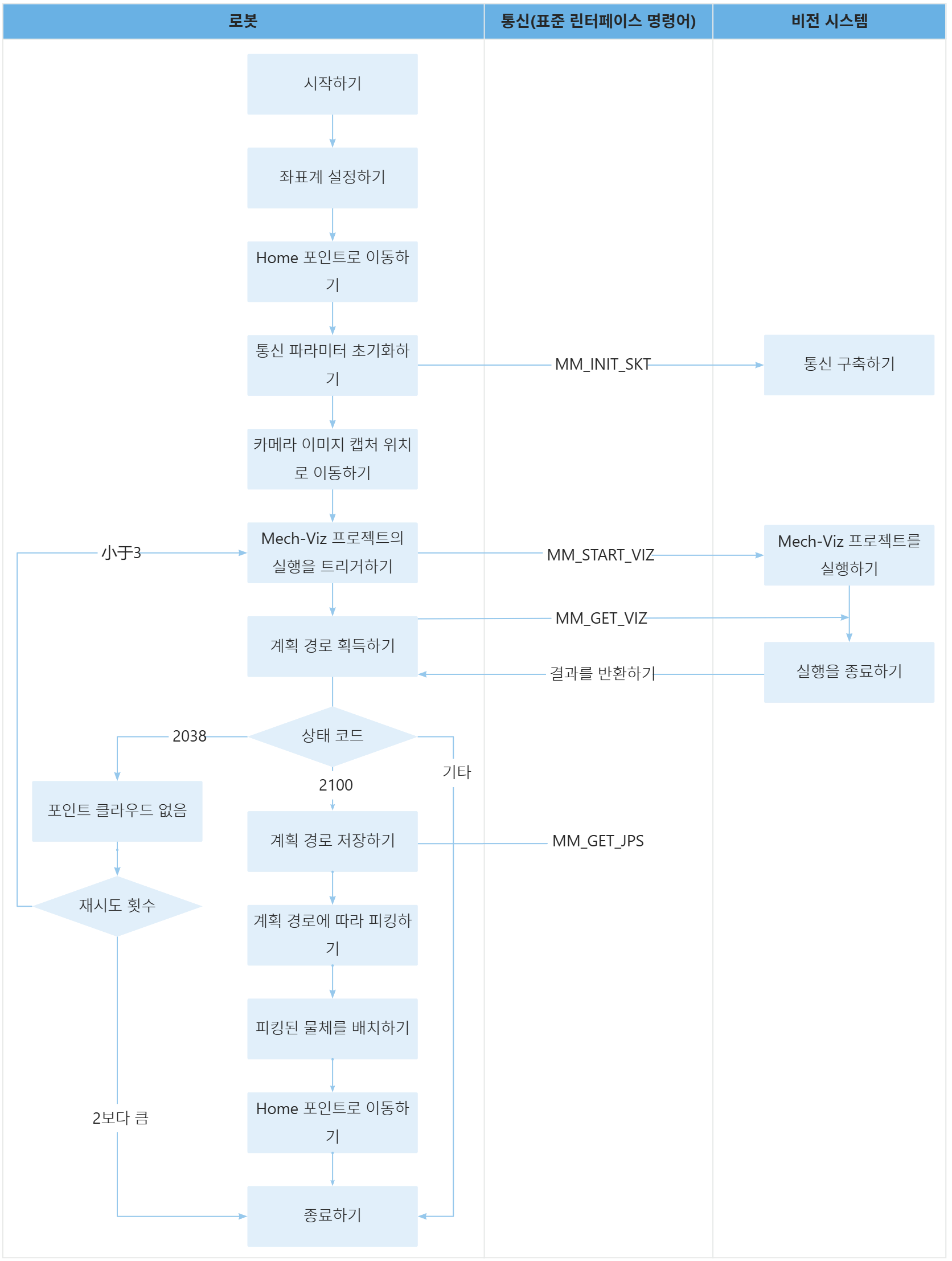
아래 표는 다양한 오류 상태 코드 처리의 설명입니다.
| 워크플로 | 코드와 설명 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
다양한 상태 코드를 처리하기 |
로봇이 MM_GET_VIZ명령어를 실행한 후, 수신된 상태 코드를 R[53] 레지스터 저장할 것입니다. 사용자는 구체적인 상태 코드에 따라 해당 처리를 할 수 있습니다. 이 샘플의 처리 논리를 참조하십시오.
|