Correction Principles
During the production process, the long-term operation of the vision system may cause the camera to experience thermal drift due to temperature changes. This affects the stability of target object recognition and leads to accuracy drift in the vision system, which requires correction. This section describes the basic principles of drift correction for the vision system.
What is Camera Thermal Drift?
Camera thermal drift happens when the camera’s performance changes because of temperature changes. These temperature changes cause the camera’s internal parts—like its optical components, electronics, and mechanical structures—to expand and contract. This affects how the camera captures images. Possible changes include focal length shifts, increased image distortion, pixel position shifts, and other effects, all of which can impact the camera’s accuracy and the stability of target object recognition.
How to Correct Accuracy Drift in Vision System?
The drift correction feature Mech-Mind provided compensates for accuracy drift in the vision system by monitoring changes in the calibration sphere poses.
On the premise that the robot’s repeatability is normal and the camera and calibration sphere are securely mounted, periodic collection of the calibration sphere poses can reveal accuracy drift in the vision system if changes in the poses are detected. If target object recognition is performed with an accuracy drift, incorrect target object poses will be obtained, impacting the subsequent picking task.
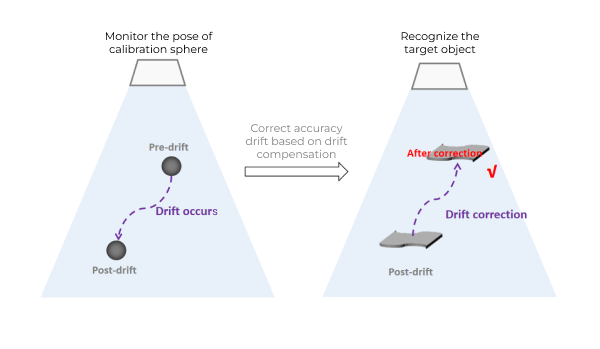
By using fluctuations in the calibration sphere poses to gauge the extent of accuracy drift in the vision system, the drift can be corrected, ensuring accurate target object recognition and stable picking by the robot.
As shown in the figure below, the left figure shows the calibration sphere pose collected before and after the accuracy drift, which are used to generate the drift correction data. The right figure shows the effect of accuracy drift being corrected using the drift correction feature.