Translational Relaxation
This chapter introduces the translational relaxation.
Introduction
When some objects are picked, the picking pose of the tool is allowed to be translated along the X-axis or Y-axis of the pick point, which is the translational relaxation. By setting the translational relaxation, the robot can utilize such tolerance flexibly to avoid problems such as collisions.
Attempt Range and Step
The relaxation range is the maximum allowable distance between the picking pose and the vision pose (a in the figure below is the relaxation range).
The step specifies the distance interval between two picking attempts (b in the figure below represents the step).
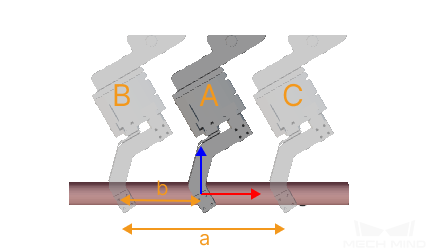
“A” represents the picking pose when the tool is at the pick point, while “B” and “C” represent the pose when the tool picks at the margin of the relaxation range.
Number of Attempts
The number of attempts is calculated automatically from the attempt range and step.
Assuming that the step is 5 mm and the attempt range is ±10 mm, then the number of attempts in one direction is 10/5 = 2, which is 2 attempts at the 5 mm and 10 mm positions. The total number of attempts = 1 + 2*2 = 5 (-10, -5, 0, 5, 10).