Example Program 15: MM_S15_Viz_GetDoList
Program Introduction
Description |
After obtaining the picking path and DO signals, the robot can perform picking and placing by moving to the picking waypoint and setting the DO signals in a loop. This example program is used in depalletizing scenarios, and the tool used by the robot is a multi-section vacuum gripper. |
File path |
You can navigate to the installation directory of Mech-Vision and Mech-Viz and find the file by using the |
Project |
Mech-Vision project and Mech-Viz project (the tool is a depalletizing vacuum gripper) |
Prerequisites |
|
| This example program is provided for reference only. Before using the program, please modify the program according to the actual scenario. |
Program Description
This part describes the MM_S15_Viz_GetDoList example program.
| Compared with the MM_S2_Viz_Basic example program, this example program contains only the following modification (the code of this modification is bolded). As such, only the modification is described in the following section. For information about the parts of MM_S15_Viz_GetDoList that are consistent with those of MM_S2_Viz_Basic, see Example Program 2: MM_S2_Viz_Basic. |
NOP
'--------------------------------
'FUNCTION: trigger Mech-Viz
'project, then get planned path
'and gripper control signal using
'command 210
'Mech-Mind, 2023-12-25
'--------------------------------
'clear I50 to I69
CLEAR I050 20
'initialize p variables
SUB P071 P071
SUB P072 P072
SUB P073 P073
'move to robot home position
MOVJ C00000 VJ=50.00
'initialize communication
'parameters (initialization is
'required only once)
CALL JOB:MM_INIT_SOCKET ARGF"192.168.170.22;50000;1"
'move to image-capturing position
MOVJ C00001 VJ=50.00 PL=0
'open socket connection
CALL JOB:MM_OPEN_SOCKET
'trigger Mech-Viz project
CALL JOB:MM_START_VIZ ARGF"2;30"
'get planned path
CALL JOB:MM_GET_PLANDATA ARGF"0;3;51;52;53"
'check whether planned path has
'been got from Mech-Viz
'successfully
IFTHENEXP I053<>2100
'add error handling logic here
'according to different error
'codes
'e.g.: I053=2038 means no
'point cloud in ROI
PAUSE
ENDIF
'get gripper control signal list
CALL JOB:MM_GET_DOLIST ARGF"0;0"
'close socket connection
CALL JOB:MM_CLOSE_SOCKET
'save waypoints of the planned
'path to local variables one
'by one
CALL JOB:MM_GET_PLANPOSE ARGF"1;71;61;31"
CALL JOB:MM_GET_PLANPOSE ARGF"2;72;71;31"
CALL JOB:MM_GET_PLANPOSE ARGF"3;73;81;31"
'follow the planned path to pick
'move to approach waypoint of
'picking
MOVJ P071 VJ=50.00 PL=0
'move to picking waypoint
MOVJ P072 VJ=10.00 PL=0
'set gripper control signal when
'current waypoint is picking
'waypoint
CALL JOB:MM_SET_DOLIST ARGF"0"
PAUSE
'move to departure waypoint of
'picking
MOVJ P073 VJ=50.00 PL=0
'move to intermediate waypoint of
'placing
MOVJ C00002 VJ=50.00
'move to approach waypoint of
'placing
MOVL C00003 V=166.6 PL=0
'move to placing waypoint
MOVL C00004 V=50.0 PL=0
'add object releasing logic here,
'such as DOUT OT#(1) OFF
PAUSE
'move to departure waypoint of
'placing
MOVL C00005 V=166.6 PL=0
'move back to robot home position
MOVJ C00006 VJ=50.00
ENDThe workflow corresponding to the above example program code is shown in the figure below.
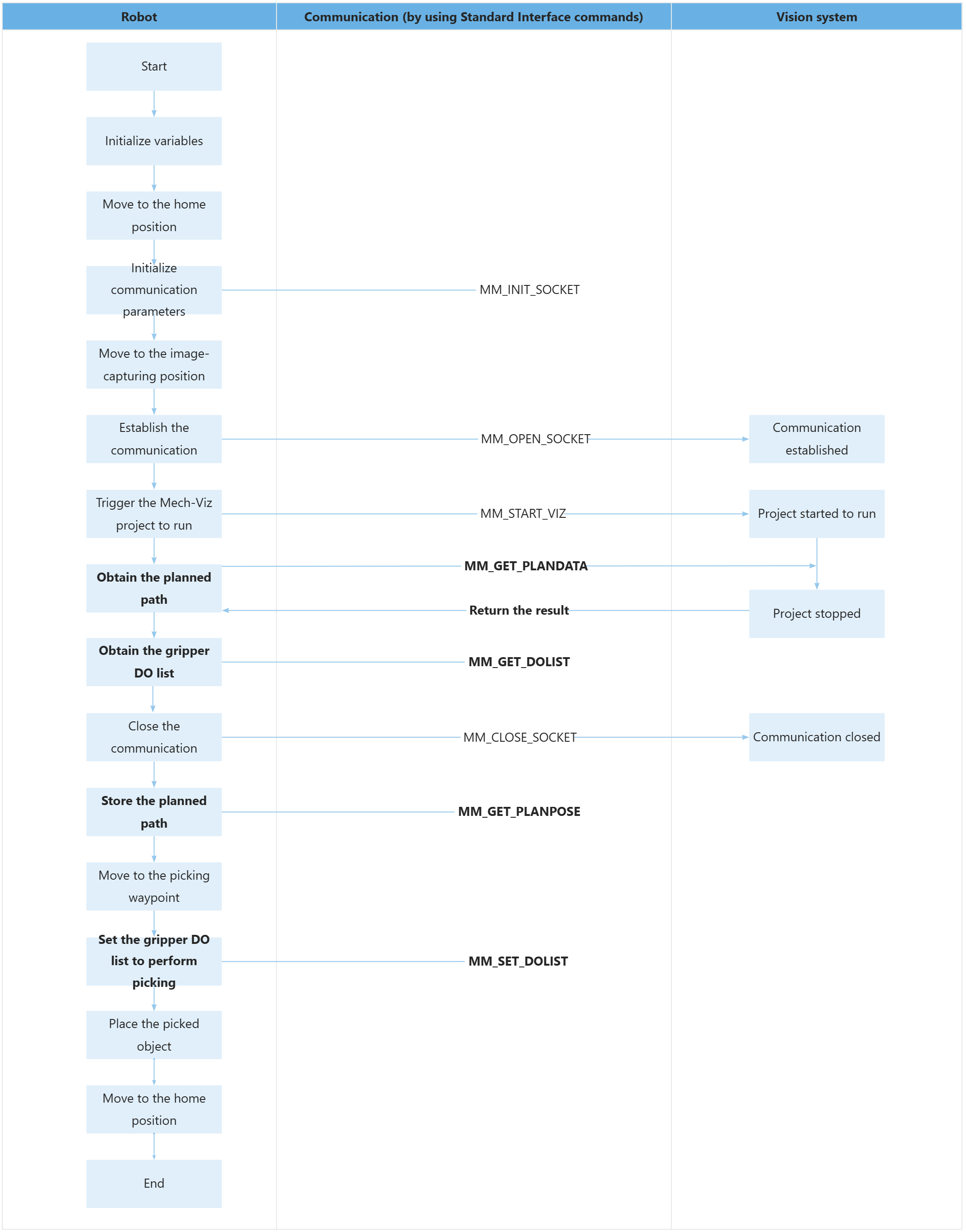
The table below describes the bolded code. You can click the hyperlink to the command name to view its detailed description.
| Feature | Code and description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Obtain the planned path |
|
||
Obtain the gripper DO list |
|
||
Store the planned path |
The entire statement “CALL JOB:MM_GET_PLANPOSE ARGF"1;71;61;31"” indicates that the pose, motion type, tool ID, velocity, Vision Move data, and custom data of the first waypoint are stored in the specified variables.
|
||
Move to the picking waypoint to perform picking |
The above statement indicates that the robot moves to the picking waypoint (P072) and then runs the MM_SET_DOLIST command to set gripper DO signals to perform picking. |