Example Program 17: MM_S17_Vis_ParseLabel
Program Introduction
Description |
The robot triggers the Mech-Vision project to run to obtain the vision result, parses the labels, and then adopts a handling method based on the label to perform picking and placing. |
||
File path |
You can navigate to the installation directory of Mech-Vision and Mech-Viz and find the file by using the
|
||
Project |
Mech-Vision project (data needs to exist in the labels port of the Output Step) |
||
Prerequisites |
|
| This example program is provided for reference only. Before using the program, please modify the program according to the actual scenario. |
Program Description
This part describes the MM_S17_Vis_ParseLabel example program.
| The only difference between the MM_S17_Vis_ParseLabel example program and the MM_S1_Vis_Basic example program is that MM_S17_Vis_ParseLabel can parse labels (the code of this feature is bolded). As such, only the feature of parsing labels is described in the following section. For information about the parts of MM_S17_Vis_ParseLabel that are consistent with those of MM_S1_Vis_Basic, see Example Program 1: MM_S1_Vis_Basic. |
MODULE MM_S17_Vis_ParseLabel
!----------------------------------------------------------
! FUNCTION: trigger Mech-Vision project and get vision result,
! then parse the label info
! Mech-Mind, 2023-12-25
!----------------------------------------------------------
!define local num variables
LOCAL VAR num pose_num:=0;
LOCAL VAR num status:=0;
LOCAL VAR num label:=0;
LOCAL VAR num label_1:=0;
LOCAL VAR num label_2:=0;
LOCAL VAR num toolid:=0;
!define local joint&pose variables
LOCAL CONST jointtarget home:=[[0,0,0,0,90,0],[9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9]];
LOCAL CONST jointtarget snap_jps:=[[0,0,0,0,90,0],[9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9]];
LOCAL PERS robtarget camera_capture:=[[302.00,0.00,558.00],[0,0,-1,0],[0,0,0,0],[9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9]];
LOCAL PERS robtarget pick_waypoint:=[[302.00,0.00,558.00],[0,0,-1,0],[0,0,0,0],[9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9]];
LOCAL PERS robtarget pickpoint:=[[500,100,300],[0.00226227,-0.99991,-0.00439596,0.0124994],[0,0,0,0],[9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9]];
LOCAL PERS robtarget drop_waypoint:=[[302.00,0.00,558.00],[0,0,-1,0],[0,0,0,0],[9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9]];
LOCAL PERS robtarget drop:=[[302.00,0.00,558.00],[0,0,-1,0],[0,0,0,0],[9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9,9E+9]];
!define local tooldata variables
LOCAL PERS tooldata gripper1:=[TRUE,[[0,0,0],[1,0,0,0]],[0.001,[0,0,0.001],[1,0,0,0],0,0,0]];
PROC Sample_17()
!set the acceleration parameters
AccSet 50, 50;
!set the velocity parameters
VelSet 50, 1000;
!move to robot home position
MoveAbsJ home\NoEOffs,v3000,fine,gripper1;
!initialize communication parameters (initialization is required only once)
MM_Init_Socket "127.0.0.1",50000,300;
!move to image-capturing position
MoveL camera_capture,v1000,fine,gripper1;
!open socket connection
MM_Open_Socket;
!trigger NO.1 Mech-Vision project
MM_Start_Vis 1,0,2,snap_jps;
!get vision result from NO.1 Mech-Vision project
MM_Get_VisData 1,pose_num,status;
!check whether vision result has been got successfully
IF status<>1100 THEN
!add error handling logic here according to different error codes
!e.g.: status=1003 means no point cloud in ROI
!e.g.: status=1002 means no vision result
Stop;
ENDIF
!close socket connection
MM_Close_Socket;
!save first vision point data to local variables
MM_Get_Pose 1,pickpoint,label,toolid;
!parse label info received from Mech-Vision, eg. "label=56" will decompose into 5 and 6
label_1:=label DIV 10; !label_1=5
label_2:=label MOD 10; !label_2=6
!add handling logic according to decomposed label value
IF label_1=5 THEN
!add handling logic a
Stop;
ELSE
!add handling logic b
Stop;
ENDIF
!move to intermediate waypoint of picking
MoveJ pick_waypoint,v1000,z50,gripper1;
!move to approach waypoint of picking
MoveL RelTool(pickpoint,0,0,-100),v1000,fine,gripper1;
!move to picking waypoint
MoveL pickpoint,v300,fine,gripper1;
!add object grasping logic here, such as "setdo DO_1, 1;"
Stop;
!move to departure waypoint of picking
MoveL RelTool(pickpoint,0,0,-100),v1000,fine,gripper1;
!move to intermediate waypoint of placing
MoveJ drop_waypoint,v1000,z50,gripper1;
!move to approach waypoint of placing
MoveL RelTool(drop,0,0,-100),v1000,fine,gripper1;
!move to placing waypoint
MoveL drop,v300,fine,gripper1;
!add object releasing logic here, such as "setdo DO_1, 0;"
Stop;
!move to departure waypoint of placing
MoveL RelTool(drop,0,0,-100),v1000,fine,gripper1;
!move back to robot home position
MoveAbsJ home\NoEOffs,v3000,fine,gripper1;
ENDPROC
ENDMODULEThe workflow corresponding to the above example program code is shown in the figure below.
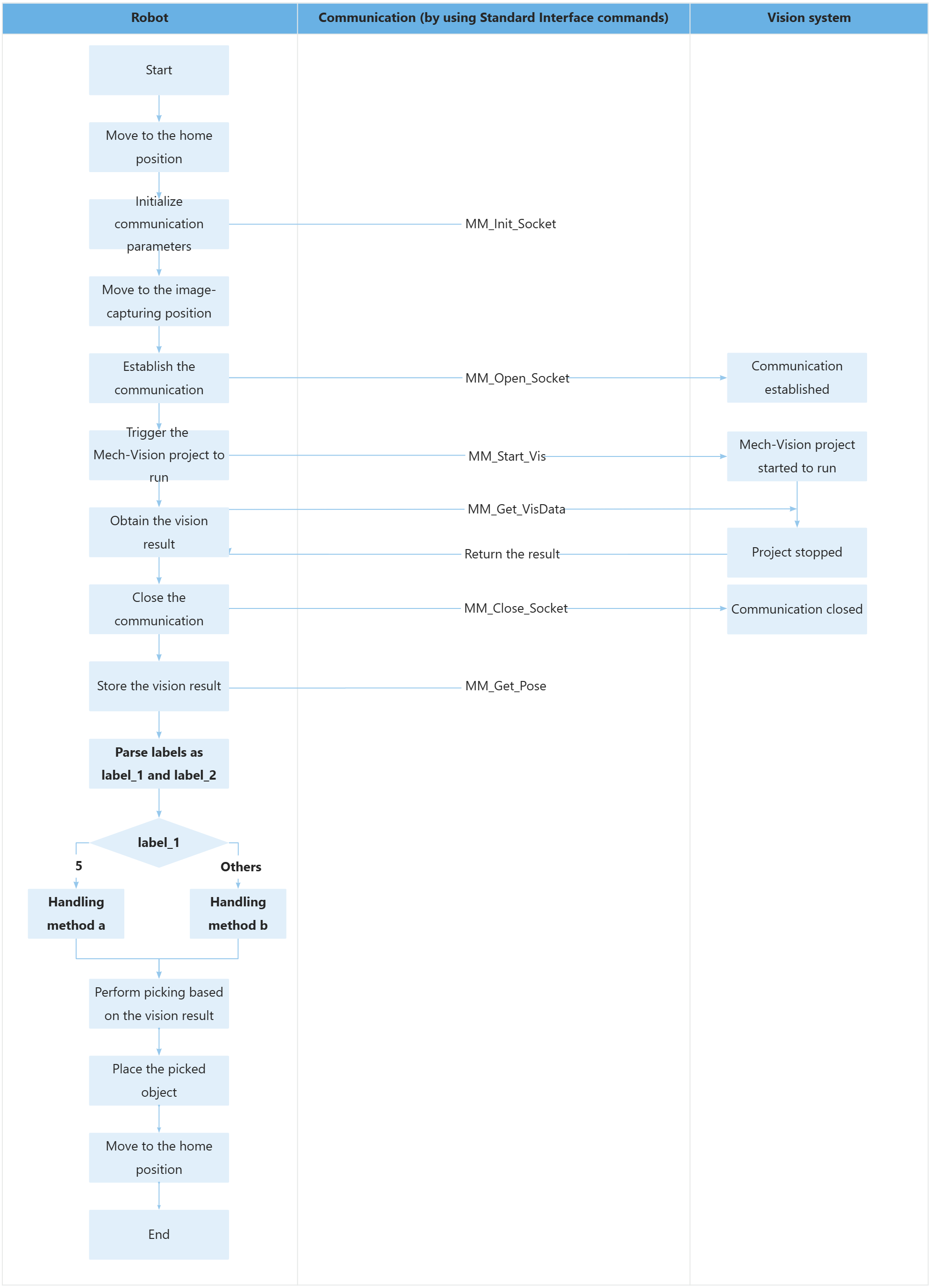
The table below describes the feature of parsing labels. You can click the hyperlink to the command name to view its detailed description.
| Feature | Code and description |
|---|---|
Parse labels as label_1 and label_2 |
The MM_Get_Pose command stores the TCP, label and tool ID of the vision point in the pickpoint, label and toolid variables respectively. In this example, the label variable is set to 56, label DIV 10 stands for the quotient of the label value divided by 10 (i.e., 5), and label MOD 10 stands for the remainder of the label value divided by 10 (i.e., 6). In this way, the label is parsed into label_1 and label_2 (i.e., 56 into 5 and 6). |
Adopt a handling method into based on the parsed label result |
The above code indicates that if label_1 is 5, logic a will be executed; otherwise, logic b will be executed. The handling method varies based on the parsed label result. You can adopt a handling method based on your business requirement. |