Camera Mounting Requirements
There are two common methods to mount a camera:
-
Eye to hand (ETH): The camera is mounted on a camera mounting frame independent of the robot.
-
Eye in hand (EIH): The camera is mounted on the last joint of the robot and moves with the robot.
The requirements for mounting the camera mounting frame and cabling vary with different mounting methods.
Camera Mounting Requirements (ETH)
When the camera is mounted on a camera mounting frame (stand) independent of the robot, you need to consider its stability, reliability and cabling to ensure the accuracy of image capturing. Specific notes are as follows:
-
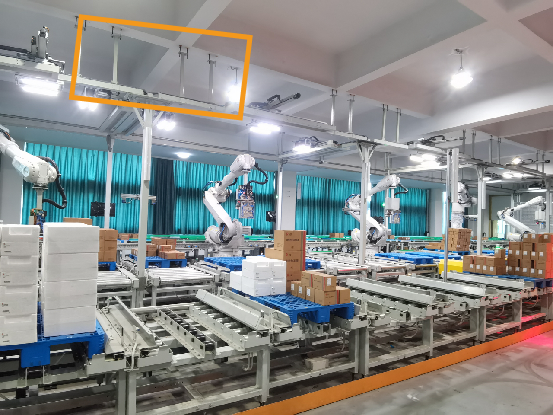
Secure the camera mounting frame
You can use either chemical bolts or expansion bolts to secure the camera mounting frame to the ground, wall, etc., which can provide stable and reliable support to ensure that the camera will not shake.
The number and type of foundation bolts depend on the height and structure of the camera mounting frame. When the camera is not mounted on the ground, you may need to reinforce the camera mounting frame by side walls, the floor, or the ceiling, as shown in the figure below.

-
Cabling
Install the camera cables in the cable trays arranged on the surface of the columns for neat and organized routing. This not only ensures the safety and aesthetic appeal of the cables but also facilitates easy maintenance.
-
Adjust camera mounting angle
Normally, the camera is mounted vertically downward. However, for project sites with limited ceiling height, you can tilt the camera to adjust the mounting angle. In the early stages of designing your project, it is recommended to perform emulation and simulation tests on your project to ensure that the angle meets the actual requirements.
Camera Mounting Requirements (EIH)
Pay attention to the following notes when you mount the camera on the last joint of the robot:
-
Install the camera mounting frame
When you install the camera mounting frame (bracket), you should take measures to prevent it from loosening, such as applying thread glue to the mounting bolts, using anti-loosening washers, etc.
-
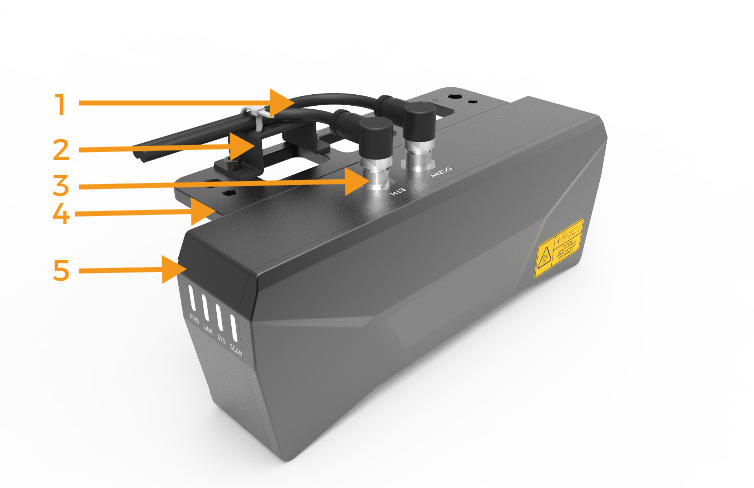
Secure cables
It is necessary to secure the cables near the camera connector to prevent force on it. When bundling cables, it is important to consider the rotational allowance of the robot’s end flange to avoid insufficient cable release, which could lead to pulling on the camera cables, and even cause irreversible damage to the camera cable connector. The way to secure cables is shown in the figure below: 1-camera cable, 2-tube clamp, 3-cable connector, 4-camera bracket, 5-camera.

-
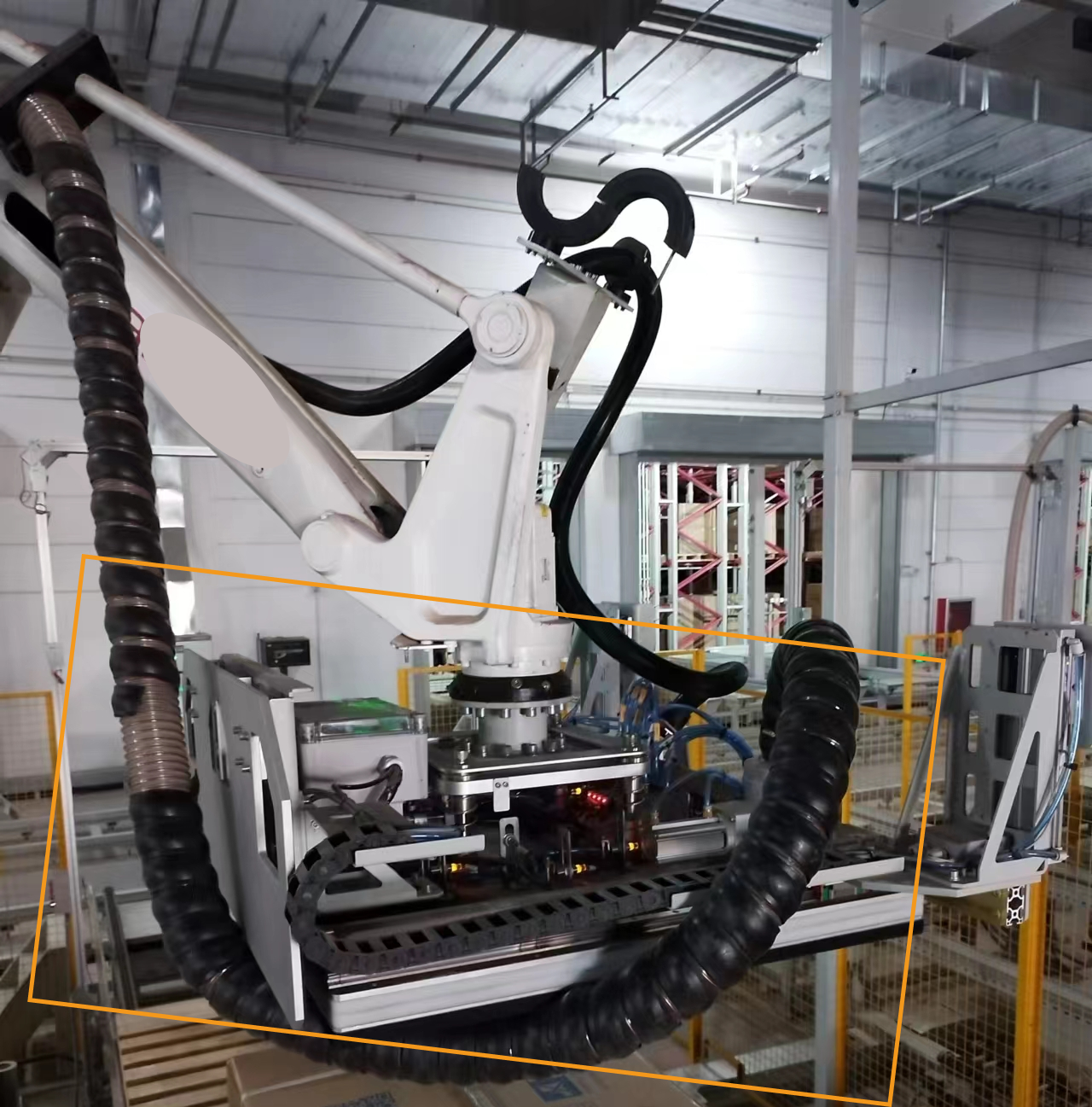
Cabling
The routing of cables should be arranged properly to avoid the cables in the dresspack being too long or too short. The following figure shows an incorrect example of excessively long cables.

-
Cable protection
Use the dresspack to protect cables and pay attention to the following notes:
-
The dresspack shall not use self-winding cable conduits or fabric cable wrap.
-
Choose standard complete sets of corrugated pipe fittings for the dresspack (including but not limited to: tube clamps, half-shells, protection sleeves, etc.).
-
Both the dresspack and cables should be secured and assembled properly to prevent additional torque on the cables during robot motion.

-