Check Robot Repeatability
This section describes how to check the robot repeatability.
Check with Image-Capturing Position in EIH Setup
This feature is used to check the robot repeatability at the image-capturing position in EIH setup. In the picking process, if the robot has poor repeatability at the image-capturing position, the accuracy of the extrinsic parameters will be affected.
Build Project to Obtain Calibration Board Poses
-
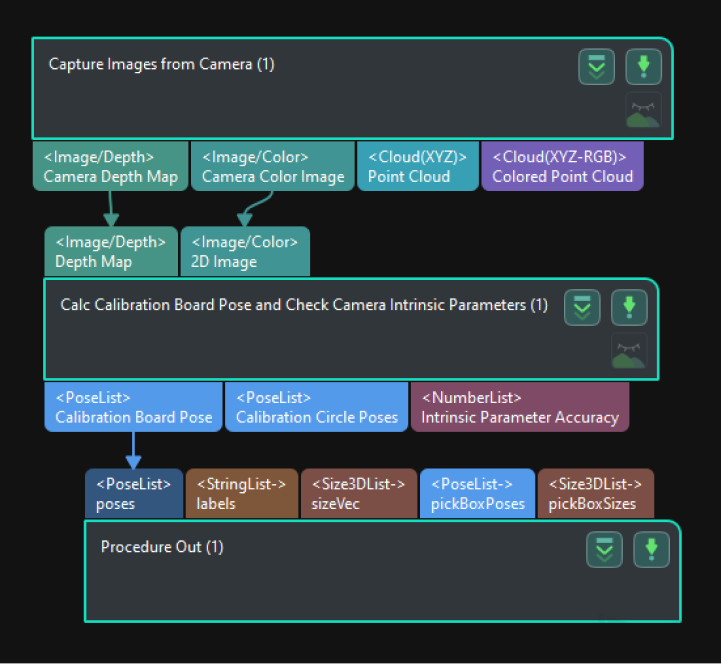
Add the “Capture Images from Camera” Step.
Create a new project and add the “Capture Images from Camera” Step, or select the Step in an opened project. Then click the Select camera button in the Step Parameters panel to select and connect the camera.
-
Add the “Calc Calibration Board Pose and Check Camera Intrinsic Parameters” Step.
Add the “Calc Calibration Board Pose and Check Camera Intrinsic Parameters” Step and connect it with the “Capture Images from Camera” Step.
-
Add the “Procedure Out” Step.
Add the “Procedure Out” Step, set Port Type to “Predefined (vision result),” and connect the “Calc Calibration Board Pose and Check Camera Intrinsic Parameters” Step with the “Procedure Out” Step to output the calculated pose of the calibration board.
The built project is shown as below.
-
Run the project and check the result.
Run the project and check the calculation result of the calibration board pose in the Log panel at the bottom.
Robot Carries the Camera to Capture Images of the Calibration Board from Different Positions
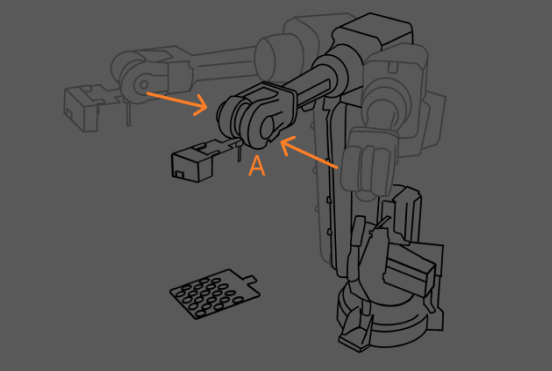
To obtain the calibration board poses from different positions, the robot should carry the camera to capture images of the calibration board from different positions, as shown below.
-
Record the position where the camera captures the image for the first time as point A and run the project at that point. Then obtain and record the calibration board pose in the camera reference frame.
-
Use the teach pendant to move the robot to another position next to the image-capturing point in the robot picking path. It is recommended to include both translation and rotation in the movement.
-
Use the teach pendant to move the robot to point A. Then obtain and record the calibration board pose.
-
Repeat steps 2 and 3 to obtain and record more calibration board poses. The poses obtained with the steps above will be used to check the robot repeatability.
Add Poses and Analyze Error
-
Click + to add a pose.
-
Click Analyze error to view the result.
If the error is too large, please add fixed waypoints near positions that require high accuracy, and then capture the images of the calibration board and analyze the error again. For example, add a waypoint near the image-capturing position or pick point. In this way, when the robot reaches that waypoint from a distance, the picking error due to poor repeatability can be reduced.
Check with Fixed Pick Point in ETH Setup
This feature is used to check the robot repeatability at the fixed pick point in ETH setup. In ETH scenarios, the robot needs to reach a fixed pick point from different waypoints, and poor robot repeatability will lead to poor picking accuracy.
Build Project to Obtain Calibration Board Poses
-
Add the “Capture Images from Camera” Step.
Create a new project and add the “Capture Images from Camera” Step, or select the Step in an opened project. Then click the Select camera button in the Step Parameters panel to select and connect the camera.
-
Add the “Calc Calibration Board Pose and Check Camera Intrinsic Parameters” Step.
Add the “Calc Calibration Board Pose and Check Camera Intrinsic Parameters” Step and connect it with the “Capture Images from Camera” Step.
-
Add the “Procedure Out” Step.
Add the “Procedure Out” Step, set Port Type to “Predefined (vision result),” and connect the “Calc Calibration Board Pose and Check Camera Intrinsic Parameters” Step with the “Procedure Out” Step to output the calculated pose of the calibration board.
The built project is shown as below.

-
Run the project and check the result.
Run the project and check the calculation result of the calibration board pose in the Log panel at the bottom.
Robot Carries the Calibration Board and Moves to the Fixed Pick Point from Different Poses
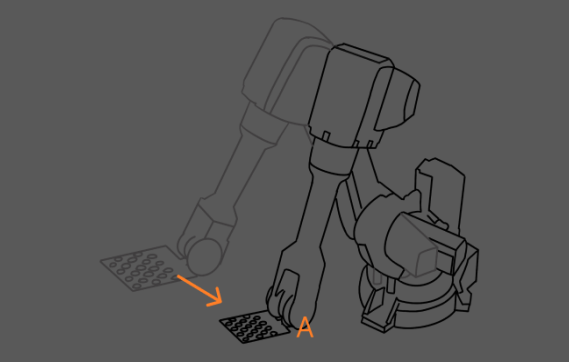
To check the robot repeatability at the pick point, the robot should carry the calibration board and move to the fixed pick point from different poses, as shown below.
-
Record the position where the robot performs picking for the first time as point A and run the project at that point. Then obtain and record the calibration board pose in the camera reference frame.
-
Use the teach pendant to move the robot to another position next to the image-capturing point in the robot picking path. It is recommended to include both translation and rotation in the movement.
-
Use the teach pendant to move the robot to point A. Then obtain and record the calibration board pose.
-
Repeat steps 2 and 3 to obtain and record more calibration board poses. The poses obtained with the steps above will be used to check the robot repeatability.
Add Poses and Analyze Error
-
Click + to add more poses.
-
Click Analyze error to view the result.
If the error is too large, please add fixed waypoints near positions that require high accuracy, and then capture the images of the calibration board and analyze the error again. For example, add a waypoint near the image-capturing position or pick point. In this way, when the robot reaches that waypoint from a distance, the picking error due to poor repeatability can be reduced.