Picking with array
When the Picking Method is set to Picking with array, you can configure the following parameters.
In addition, you should refer to Configure the Tool to configure the corresponding end tool.
Move-Type Step Common Parameters
Send Waypoint
Selected by default to send waypoint poses to the receiver, such as the robot. When this option is unselected, the waypoint pose will not be sent. However, the waypoint will remain in the planned path.
Try Continuously Running through Succeeding Non-Moves
Unselected by default. When non-move Steps, such as Vision Look, Set DO, Check DI, etc., are connected between move-type Steps, the robot’s path planning will be interrupted, and the actual robot will take a short pause, reducing the smoothness of running.
When this option is selected, the project will continue to run without waiting for the current move-type Step to complete execution, and therefore the robot can move in a smooth way without pauses. However, enabling this option may cause the execution of the Step to end prematurely.
Why will this option cause the execution of the Step to end prematurely?
Mech-Viz will send multiple poses simultaneously to the robot when the project is running. When the currently returned JPs of the robot correspond to the last pose sent by Mech-Viz, Mech-Viz will assume that the robot has moved to the last position.
For example, there are 10 move-type Steps in a path, and the pose of the 5th move-type Step is the same as that of the last move-type Step. When the robot moves at low speed, it sends JPs to Mech-Viz when it moves to the 5th move-type Step, Mech-Viz may mistakenly determine that the robot has finished the move-type Steps and prematurely ends the Steps since the poses of the 5th move-type Step and the last move-type Step are the same in the path.
Do Not Check Collision with Placed Workobject
Unselected by default, namely that the collision with the already placed objects will not be detected. When this option is selected, the collisions between the robot, end tool, and placed objects will be detected.
In palletizing scenarios, the two possible cases of error are as follows:
-
When the robot is placing a carton, the robot may come into light contact with the placed cartons while no deformation will be caused. After Mech-Viz detects this collision in simulation, it will plan other positions for placing the carton, and therefore a full stack cannot be formed.
-
Usually, the TCP of a suction cup is inside the suction cup model instead of on the surface of it. Under this circumstance, the suction cup may be embedded in the model of the picked carton in the simulation of picking, while the software does not detect the collision between the end tool and the picked object. After the robot places the object and the carton model turns into an object model in the scene, a collision between the suction cup and the carton will be detected and the palletizing cannot be completed.
When this option is selected, no collision between the robot, end tool, and the placed object will be detected, and the above two cases of errors can be avoided.
Point Cloud Collision Detection Mode
Select the proper mode according to the requirement of the on-site situation. Usually, the default setting Auto can be used. Do not check collision mode can be used in move-type Steps before the robot picks the object, and Check collision mode can be used after the robot picks the object.
Auto |
Default setting. Collision with point cloud is checked only for the “Vision Move” Step and the “Relative Move” Step that depends on the “Vision Move” Step, but not for all move-type Steps. |
Do not check collision |
Point cloud collisions for all move-type Steps will not be detected. |
Check collision |
Point cloud collisions for all move-type Steps will be detected. |
| When is switched on, Mech-Viz will detect collisions between the robot model, end tool model, and point cloud when planning the path. Normally, Mech-Viz detects whether the robot collides with workobjects during picking and placing. When there are point cloud outliers, non-exiting collisions will be detected, which leads to errors in path planning. |
Ignore Workobject Symmetry
This parameter will only take effect when Waypoint type of the Step is set to Workobject pose.
None |
Default setting, i.e., do not disable symmetry on any axis. |
Around workobject frame Z axis |
Only disable symmetry on Z-axis of the workobject reference frame. |
Around workobject frame X&Y axis |
Disable symmetry on X-axis and Y-axis of the workobject reference frame. |
Around all axes |
Once the object symmetry is disabled, the robot will place the objects strictly according to the workobject poses. |
| In some special cases, objects are not pickable due to their peculiar poses. Setting Rotational symmetry under in Resources may solve this problem. Candidate poses of the recognized workobjects will be calculated according to the set rotational symmetry angle. When Mech-Viz plans to pick workpieces, if the default pose is not feasible for picking, the candidate poses will be tried. As the candidate poses calculated based on the settings of Rotational symmetry are different from the original poses output from Mech-Vision, the consistency of the objects’ place poses cannot be guaranteed. |
Plan Failure Out Port
Once this parameter is selected, a “Plan failure” exit port will be added to the Step.
During the planning process, planning is carried out along the branch after the “Success” exit port. If the planning fails in the current Step, the branch process after the “Planning failure” exit port will be executed.
Held Workobject Collision Detection Settings
Do Not Check Collision with Scene Object/Robot
Unselected by default. Once this option is selected, the collisions between the held workobject with the scene objects or robot will not be detected, and therefore the calculation workload of collision detection will be reduced, the planning speed can be increased, and the cycle time can be shortened. It is usually enabled in the first one or two move-type Steps after the robot picks the object.
Please enable this option cautiously as there may be collision risks.
When Detect collision between held workobject and others under is enabled, the software will detect whether the model of the held object collides with the models of the scene objects and the robot.
In palletizing projects, the calculated carton dimensions have millimeter-level errors with the actual dimensions, and frictions between cartons may occur during picking but no collisions will occur. For some move-type Steps that will obviously not cause collisions, detecting such collisions only adds to the calculation workload and planning time, and consequently extending the cycle time. In palletizing projects, enabling Do Not Check Collision with Scene Objects does not affect the collision detection between the held carton and the placed cartons. This option can be enabled when there are scene objects under the stack to avoid failure of finding the palletizing solution.
Do Not Check Collision with Point Cloud
Unselected by default. Once this option is selected, the collisions between the held workobject with the point clouds in the scene will not be detected, and therefore the calculation workload of collision detection will be reduced, the planning speed can be increased, and the cycle time can be shortened.
-
When both Detect collision between held workobject and others under and Configuration on point cloud ‣ Detect collision between point cloud and others are enabled, the software will detect whether the model of the held workobject will collide with the point cloud in the scene.
-
When Mech-Vision sends the point cloud and object model to Mech-Viz, the point cloud and the object model are fitted together. After the robot picks the object, the model moves along the planned path, and the collision between the model of the held workobject and the point cloud will occur.
-
It is known that the model of the held workobject will have false collisions with the point cloud. Detecting such collisions unnecessarily adds to the calculation workload and extends the planning time.
Vision Result Global Usage
All Vision Poses in One Move
Usually, Vision Move will only use one pose of the corresponding vision result. However, once this parameter is selected, the robot will move through all waypoints corresponding to the vision poses at one time.
This parameter is usually used when the robot moves in a fixed path where no DO signals will be sent, such as the gluing application.
Reuse Vision Result
When this feature is not enabled, each time “Vision Move” plans a robot picking path successfully, the rest unused vision results will be discarded. If this feature is enabled, the vision result that leads to a planning failure and the rest unused vision results will be retained and used for the next planning. This feature should be used with the “Is Vision Result Used Up” Step.
When there are multiple pickable objects in one vision result and it can be guaranteed that picking one object will not affect the poses of other objects, this option can be selected. The vision result will be reused and no new image will be captured until all vision results are used up.
Application Example
Share Vision Result
This feature enables multiple “Vision Move” Steps in which the same vision service is selected to share the vision result.
When one “Vision Move” Step plans successfully, the corresponding vision result will be used, and the unused vision result will be used by the next “Vision Move” Step with this feature enabled. After all “Vision Move” Steps that share the vision result complete planning, the rest results will be discarded.
In addition, this feature can be used in conjunction with the “Reuse Vision Result” feature. When “Reuse Vision Result” is selected, the rest vision results will not be discarded even after all “Vision Move” Steps have completed one round of planning.
Application Example
(To be supplemented)
Remove Point Cloud of Target Workobject
Remove Point Cloud of Target Workobject
Select to remove the point cloud of the target workobject to be picked, and only collision between the robot end tool and non-target workobjects will be detected.
To avoid picking non-target boxes, the software will remove the point cloud of the target box and keep the point cloud of its adjacent boxes. During path planning, the software will discard a solution that may lead to a wrong picking due to the detected collision between the model of the vacuum gripper’s buffer and the point cloud of adjacent boxes.
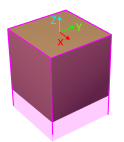
The default range for point cloud removal is a cuboid whose top surface is the top surface of the target box with an infinite height whose direction is the Z-direction of the box’s vision pose.
You can adjust the “XY-Plane Point Cloud Removal Range Expansion” and “Z-Direction Point Cloud Removal Range Expansion” to expand the point cloud removal range for removing the point cloud near the target workobject.
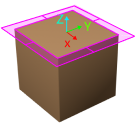
XY-Plane Point Cloud Removal Range Expansion
Based on the original workobject dimensions, the XOY plane of the workobject pose is the top surface for the point cloud removal range. This parameter specifies the extended length from actual workobject edges on this surface.
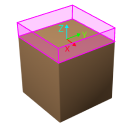
Z-Direction Point Cloud Removal Range Expansion
Based on the original workobject dimensions, the extended height in the positive Z-direction of the workobject pose for the point cloud removal range.
Supplementary Features
Update Bin Pose with Vision
Once the “Update Bin Pose with Vision” parameter is selected, the bin will be recognized and located simultaneously while the camera captures the image for workobject recognition. Therefore, the bin pose in the simulation area can be updated dynamically, which facilitates the collision detection algorithm to effectively prevent the robot from colliding with the bin.
This feature will provide three fields, “scene_object_names,” “scene_object_sizes,” and “scene_object_poses,” in the vision result to define the name, dimensions, and position of the scene object to be updated.
Result Must Be in Specified Bin
Result Must Be in Specified Bin
This feature limits that the vision result received by the current “Vision Move” Step must be in a specified bin. The vision result out of the effective bin range will not be used.
The effective range for each bin can be configured separately in the corresponding configuration window. Only bins with “Set effective range for pose” enabled can be selected in the drop-down menu.
Application Example
Add “Bin1”, and select the “Set effective range for pose” parameter for this bin.
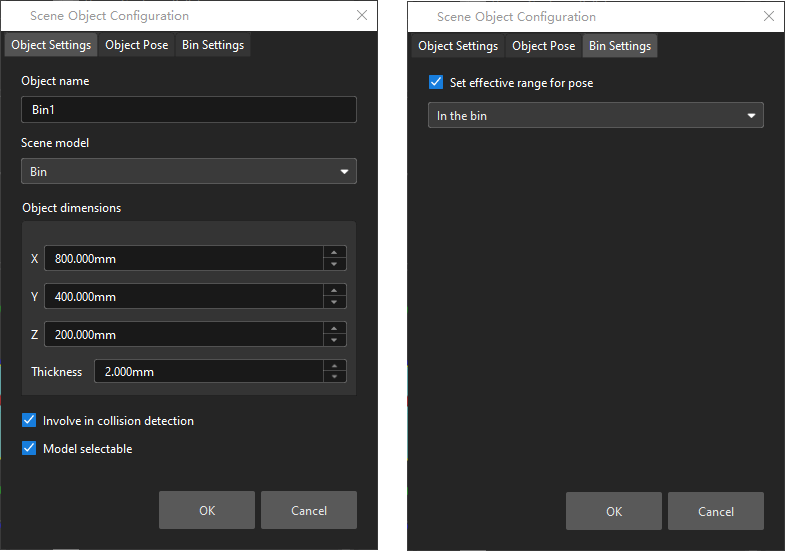
Select “Bin1” in the drop-down menu.
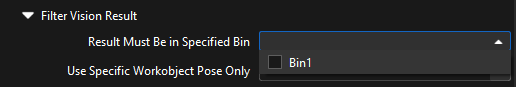
Use Specific Workobject Pose Only
This parameter is used to filter the workobjects corresponding to the specified “labels” field in the vision results.
If you need to use this parameter, you need to add the corresponding workobjects in the resource tree whose name is the same as the “labels” field name, and then select the workobject in the dropdown menu on the right side of the parameter.

Filter Out Unlikely Pick Point
This parameter group is mainly used to avoid picking on the same pick point in scenarios where the object cannot be picked successfully.
Once the “Filter Out Unlikely Pick Point” parameter is selected, you can adjust the following parameters.
-
Filter Subject
-
Pick point: only pick points with high failure rates will be deprioritized in the picking and discarded in some rounds.
-
Workobject: if any one pick point on the workobject is considered to have a high failure rate, all pick points on this workobject will be deprioritized in the picking and discarded in some rounds.
-
-
Priority Downgrade Radius
A sphere with this parameter value as its radius and the pick point successfully planned in the last round as its center will be introduced. If a pick point in the latest vision result falls within this sphere, the pick point will be put off for picking with a decreased picking priority.
-
Discard Attempt Radius
A sphere with this parameter value as its radius and the pick point successfully planned in the last round as its center will be introduced. If a pick point in the latest vision result falls within this sphere, the pick point will be discarded in this round of planning.
For example, if the robot only moves the crankshaft but fails to pick it on the first attempt, there is a possibility of successful picking on the next attempt. Therefore, Priority Downgrade Radius can be set to downgrade the priority of the pick point, while the pick point will not be discarded. When the robot fails to move the crankshaft at all in the first attempt, it is highly unlikely that the crankshaft can be picked successfully in the next attempt, and therefore Discard Attempt Radius can be set to discard the pose directly.
-
List Length
A list of pick points with high failure rates. When the list length exceeds the upper limit, the pick point that is added to the list earliest will be removed from the list and can be used in the next round of planning.
Picking Sequence
Sorting Strategy
-
Sort by the workobject count in the combination: The workobject combinations will be sorted by the number of workobjects they contain, and those with more workobjects will be picked first.
-
In the strict order of vision result: Pick in the order of the result sent by the vision service. If the path planning fails by using a vision result, the current result will not be skipped and the path planning will fail.
-
In the partial order of vision result: Pick in the order of the result sent by the vision service. If the path planning fails by using a vision result, the current result will be skipped. Then the next vision result will be used for the subsequent path planning.
Matching Condition
Array Gripper Matching Strategy
You can choose between “Match position only” and “Match position and orientation.”
-
Match position only: Only the positions of the workobjects will be taken into account for matching, while the angles between the TCP and workobject poses will not.
-
Match position and orientation: Both the positions of the workobjects and the angles between the TCP and workobject poses will be taken into account for matching.
Distance Threshold
A circle with the “Distance Threshold” as its radius and the origin of workobject pose as its center will be introduced. If every end of the multi-end tool can fall within this circle, the matching is considered successful.
Application Example
-
The three workobjects are shown below, and the Distance Threshold is set to 30 mm.
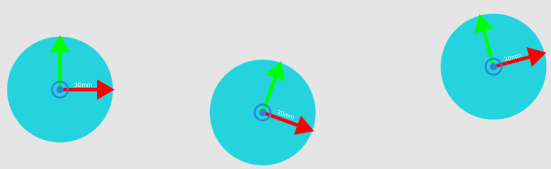
-
An array gripper with 3 end tools that are 100 mm away from each other is shown in the figure below.
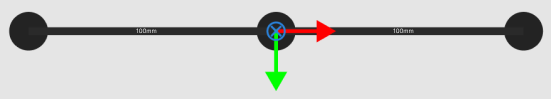
-
In the path planning, the software will find a position where all three TCPs fit in the blue circles as shown below.
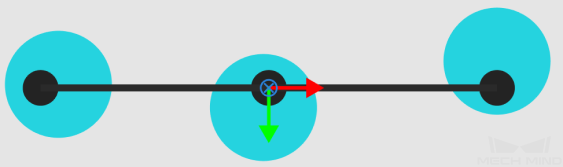
If three TCPs cannot be matched with the possible areas for picking at the same time, the software will try to match two TCPs instead.
Angle Threshold
If the angle between the X-axis of the TCP pose and the X-axis of each workobject pose is less than the “Angle Threshold,” the matching is considered successful.
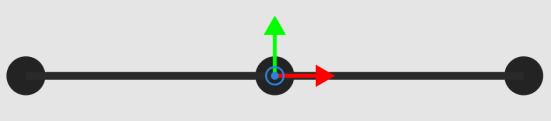
-
The TCP will be rotated 180° around its own X-axis so that its Z-axis will be upward and parallel with that of the workobject pose.
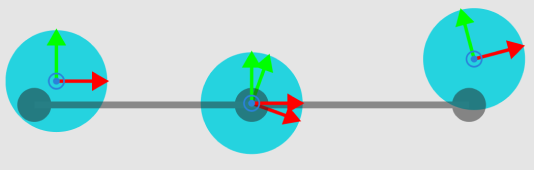
-
Calculate the angle between the X-axis of the workobject pose and each axis of the TCP pose. If the angle is within the Angle Threshold, the matching is considered successful, otherwise it fails.
In the Array gripper mode, it is acceptable that the object in the middle of a combination is missed as long as the combination is not rotationally symmetric.
For example, the array gripper has 4 ends, and the ends are numbered 0, 1, 2, and 3. If there are 3 objects to be picked whose position can be represented by OOXO (X for empty space), the 0, 1, and 3 ends need to be started. After being rotated 180°, the combination changes from OOXO to OXOO, which is not symmetric.
Count of Picked Workobjects
Limit Total Count
Select Limit Total Count and you can set the maximum Planned Count and other parameters.
Limit Count per Picking
-
No limit: There is no limit to the number of workobjects that can be picked at a time.
-
Maximum value: The maximum workobjects that can be picked at a time.
-
Specified value: Set a fixed limit on the number of workobjects to be picked at a time.