Predefined Pallet Pattern
Function
This Step is used to automatically generate the pallet pattern through setting the parameters. Compared to the “Custom Pallet Pattern” Step, this Step is easier to use and there is no need to manually edit the pallet pattern.
Parameter Description
Move-Type Step Common Parameters
Send Waypoint
Selected by default to send waypoint poses to the receiver, such as the robot. When this option is unselected, the waypoint pose will not be sent. However, the waypoint will remain in the planned path.
Try Continuously Running through Succeeding Non-Moves
Unselected by default. When non-move Steps, such as Vision Look, Set DO, Check DI, etc., are connected between move-type Steps, the robot’s path planning will be interrupted, and the actual robot will take a short pause, reducing the smoothness of running.
When this option is selected, the project will continue to run without waiting for the current move-type Step to complete execution, and therefore the robot can move in a smooth way without pauses. However, enabling this option may cause the execution of the Step to end prematurely.
Why will this option cause the execution of the Step to end prematurely?
Mech-Viz will send multiple poses simultaneously to the robot when the project is running. When the currently returned JPs of the robot correspond to the last pose sent by Mech-Viz, Mech-Viz will assume that the robot has moved to the last position.
For example, there are 10 move-type Steps in a path, and the pose of the 5th move-type Step is the same as that of the last move-type Step. When the robot moves at low speed, it sends JPs to Mech-Viz when it moves to the 5th move-type Step, Mech-Viz may mistakenly determine that the robot has finished the move-type Steps and prematurely ends the Steps since the poses of the 5th move-type Step and the last move-type Step are the same in the path.
Do Not Check Collision with Placed Workobject
Unselected by default, namely that the collision with the already placed objects will not be detected. When this option is selected, the collisions between the robot, end tool, and placed objects will be detected.
In palletizing scenarios, the two possible cases of error are as follows:
-
When the robot is placing a carton, the robot may come into light contact with the placed cartons while no deformation will be caused. After Mech-Viz detects this collision in simulation, it will plan other positions for placing the carton, and therefore a full stack cannot be formed.
-
Usually, the TCP of a suction cup is inside the suction cup model instead of on the surface of it. Under this circumstance, the suction cup may be embedded in the model of the picked carton in the simulation of picking, while the software does not detect the collision between the end tool and the picked object. After the robot places the object and the carton model turns into an object model in the scene, a collision between the suction cup and the carton will be detected and the palletizing cannot be completed.
When this option is selected, no collision between the robot, end tool, and the placed object will be detected, and the above two cases of errors can be avoided.
Point Cloud Collision Detection Mode
Select the proper mode according to the requirement of the on-site situation. Usually, the default setting Auto can be used. Do not check collision mode can be used in move-type Steps before the robot picks the object, and Check collision mode can be used after the robot picks the object.
Auto |
Default setting. Collision with point cloud is checked only for the “Vision Move” Step and the “Relative Move” Step that depends on the “Vision Move” Step, but not for all move-type Steps. |
Do not check collision |
Point cloud collisions for all move-type Steps will not be detected. |
Check collision |
Point cloud collisions for all move-type Steps will be detected. |
| When is switched on, Mech-Viz will detect collisions between the robot model, end tool model, and point cloud when planning the path. Normally, Mech-Viz detects whether the robot collides with workobjects during picking and placing. When there are point cloud outliers, non-exiting collisions will be detected, which leads to errors in path planning. |
Ignore Workobject Symmetry
This parameter will only take effect when Waypoint type of the Step is set to Workobject pose.
None |
Default setting, i.e., do not disable symmetry on any axis. |
Around workobject frame Z axis |
Only disable symmetry on Z-axis of the workobject reference frame. |
Around workobject frame X&Y axis |
Disable symmetry on X-axis and Y-axis of the workobject reference frame. |
Around all axes |
Once the object symmetry is disabled, the robot will place the objects strictly according to the workobject poses. |
| In some special cases, objects are not pickable due to their peculiar poses. Setting Rotational symmetry under in Resources may solve this problem. Candidate poses of the recognized workobjects will be calculated according to the set rotational symmetry angle. When Mech-Viz plans to pick workpieces, if the default pose is not feasible for picking, the candidate poses will be tried. As the candidate poses calculated based on the settings of Rotational symmetry are different from the original poses output from Mech-Vision, the consistency of the objects’ place poses cannot be guaranteed. |
Plan Failure Out Port
Once this parameter is selected, a “Plan failure” exit port will be added to the Step.
During the planning process, planning is carried out along the branch after the “Success” exit port. If the planning fails in the current Step, the branch process after the “Planning failure” exit port will be executed.
Index
Basic Pallet Settings
Motion Control
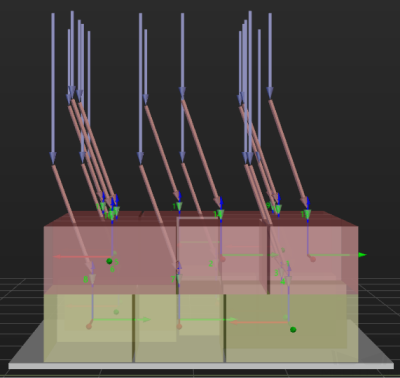
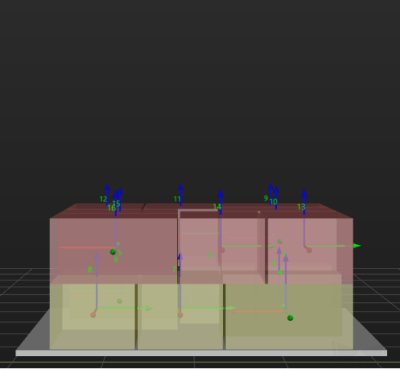
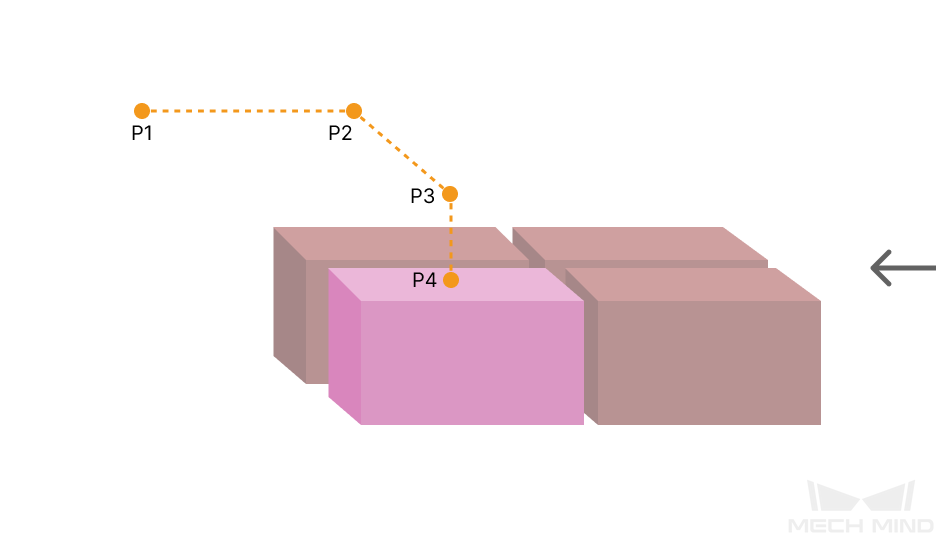
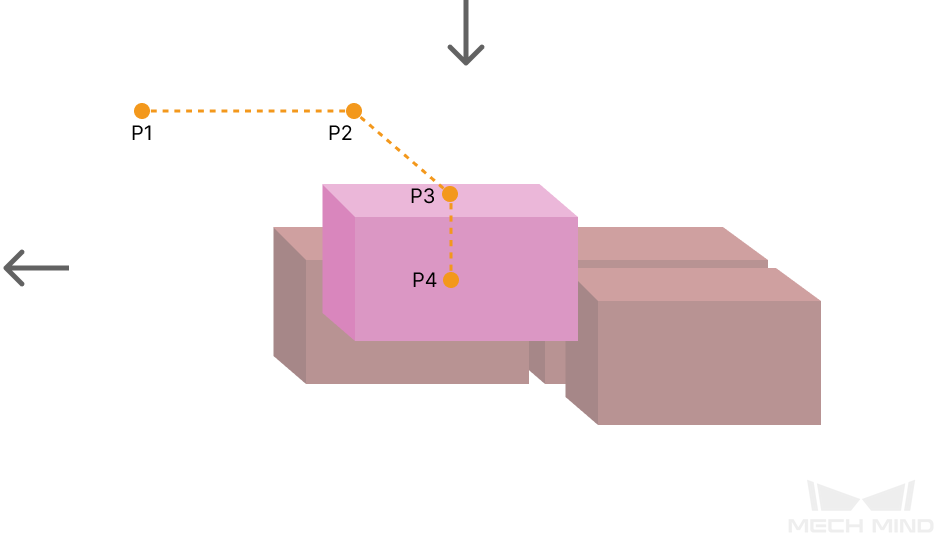
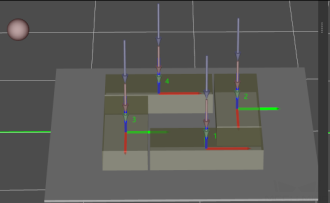
Some of the trajectories during box palletization are shown in the figure below.
|
|
|
|
Among them,
-
P1: middle point; P2: entry point; P3: adjustment point; P4: placement point.
-
P1-P2: entry section; P2-P3: adjustment section; P3-P4: placement section.
Auto Middle Point Force MoveJ
The path between the move waypoint before this Step and the middle point (P1) is the middle point force.
Selected by default. This is a joint move.
Entry Force MoveJ/Adjust Force MoveJ/Place Force MoveJ
Unselected by default. This is a linear move.
This parameter will not be selected when palletizing in a site where the operation space is small and the linear move is required. As linear move may lead to singularity problems, you can set joint move in entry section / adjustment section / placement section selectively.
Acc&Vel Scale Ratio
This parameter is mainly used to slow down the robot during the placement process to ensure a more stable placement of the boxes.
-
The velocity (acceleration) of the entry section is the same as the set velocity (acceleration) in the “Basic Move Settings.”
-
The velocity (acceleration) of the adjustment section and placement section: the velocity (acceleration) of the entry section ✖ this parameter (Acc&Vel Scale Ratio).
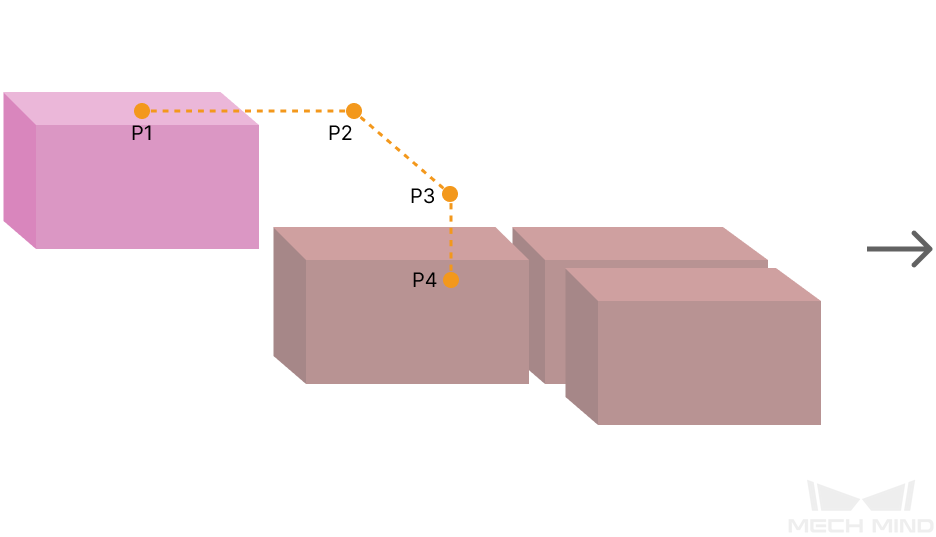
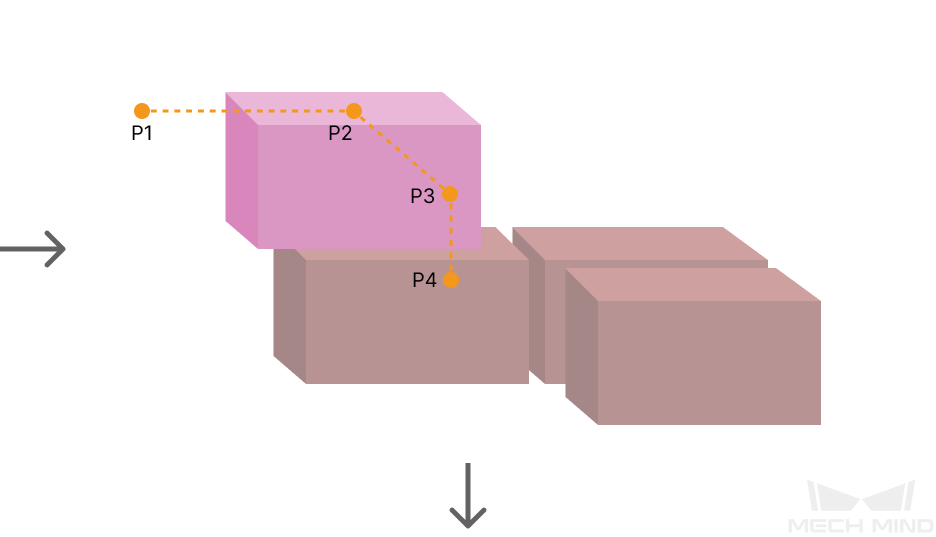
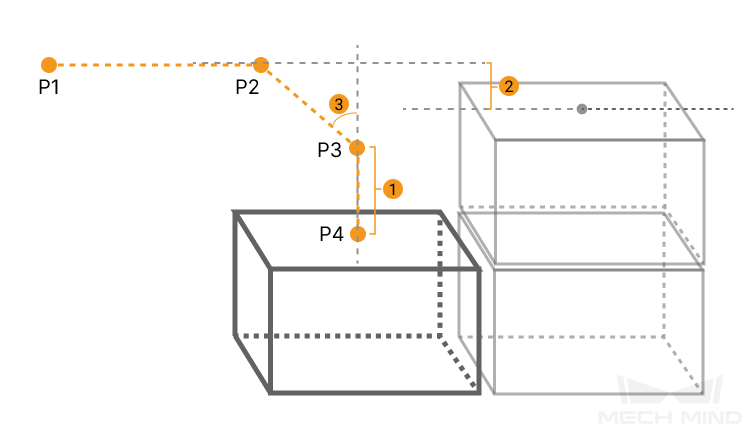
Entry Adjust
The three parameters together determines the path along which the robot enters the stack area. Adjust the entry path to make the held box approaches the palletized boxes at a specified angle, and then the held box will be placed vertically. If the box is directly placed on the stack in a vertical path, collisions may occur between the robot, held box, and the palletized boxes possibly due to accuracy and other factors.
For each box, there are four points to enter the stack area. This parameter determines three points: entry point (P2); adjustment point (P3); and placement point (P4).
|
1: Vertical Adjust Length; 2: Vertical Margin; 3: Entry Angle Z |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Vertical Adjust Length Ratio |
As shown in the right figure, vertical adjust length ratio = vertical adjust length (1) / the height of the box. |
Value range: 0~1; recommended value: 50%. |
|
Vertical Margin |
As shown in the right tag 2. |
Value range: 0~+∞; unit: mm; the specified values depend on different application scenarios. |
|
Entry Angle Z |
As shown in the right tag 3. |
Value range: -80°~80°; recommended value: 30°~45°. |
Auto Middle Point
The Auto Middle Point is the direction indication of entering into the stack area, not the actual point reached by the robot. To avoid squeezing and collisions during the placement of boxes, the auto middle point should be as far away from the pallet as possible to ensure adequate safety spacing.
Minimum Height Z
The minimum height in the Z-direction of the robot entering into the entry section (the purple path).
Maximum Height Z
The maximum height in the Z-direction of the robot entering into the entry section (the purple path).
Is Middle Point Traj Vertical
|
|
Unselected by default, i.e., the robot will approach the stack from the auto middle point. |
After selecting, the robot will approach the stack in a direction perpendicular to the pallet. |
Extended Distance For Entry
This parameter is used to extend the distance for entry.
When the tool is larger than the object being picked, the default entry path may not be long enough, resulting in a collision between the tool and placed boxes. In this case, extending the distance for entry can improve safety, avoiding the collision between the robot and placed boxes or other barriers in the process of robot movement.
Adjust Pallet via Vision
Select “Need Adjust Pallet Pose” and then set the “Vision Service Name” to apply a vision project for the stack recognition, thus adjusting the pallet dynamically.
When the project runs this Step, the software will execute the corresponding vision project and update the position of the pallet based on the vision result.
Pallet Size
Pallet X Len |
Set the pallet edge length (mm) along the X-direction. The pallet pattern will change with the pallet size in real-time. |
Pallet Y Len |
Set the pallet edge length (mm) along the Y-direction. The pallet pattern will change with the pallet size in real-time. |
Common Settings
Geometry Type
Currently supported: Sphere, Cuboid, Cylinder, Disc, Quadrangular prism, and Hexagonal prism. Please select the geometry type according to actual situation.
Pallet Type
Currently supported: Block, Pinwheel 1, Pinwheel 2, Automatic layout, and three special patterns. Please select the pallet type according to actual need.
The parameters that can be set are slightly different when the pallet type is different.
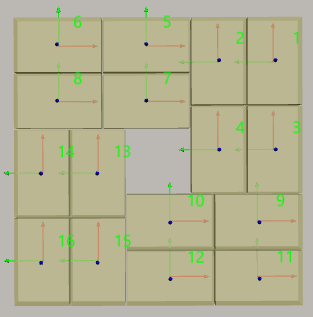
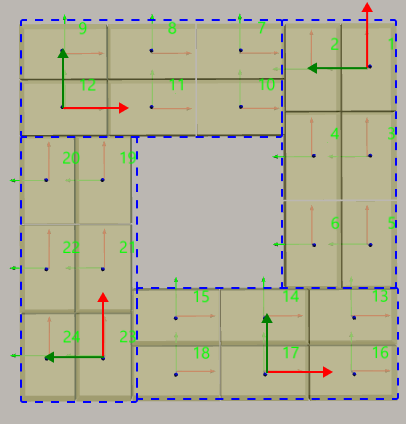
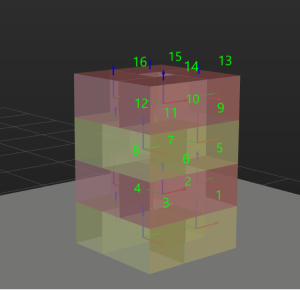
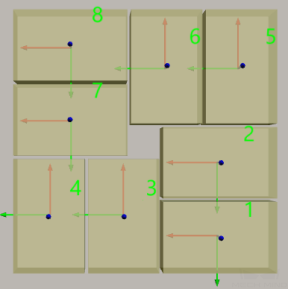
Pinwheel
The pinwheel pallet pattern is shown in the following figure.
-
Rows/Unit: the rows of the stacked boxes in each pallet pattern unit.
-
Cols/Unit: the columns of the stacked boxes in each pallet pattern unit.
In the following figure, the Rows/Unit is 3, and the Cols/Unit is 2:
-
A blue dashed box is a unit.
-
In the cell, the X-direction (red arrow) of the box pose represents the column, and the Y-direction (green arrow) represents the row.
-
-
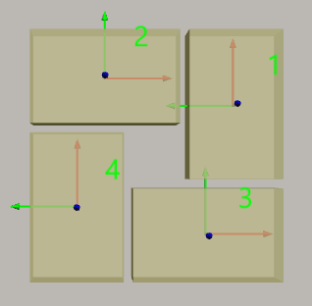
Is Antithetic: Select to stack the boxes in different orientations on the odd and even layers, which makes the stack more stable.
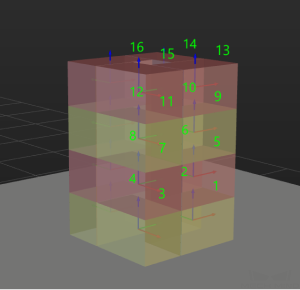
Unselected
Selected
-
Gap Width: Set the gap width of the boxes in the pallet pattern.
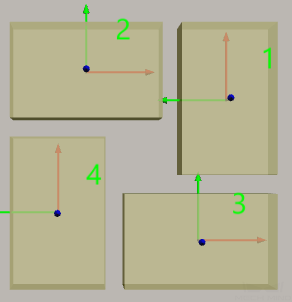
10mm
20mm
-
Rotate 90° Around Z-axis: Rotate the whole pallet pattern 90°around Z-aixs.
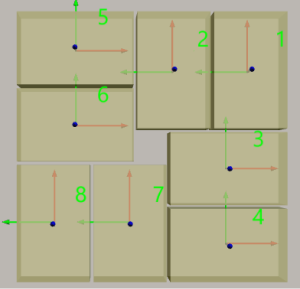
Not rotated
Rotated
Block
The block pallet pattern is shown in the following figure.
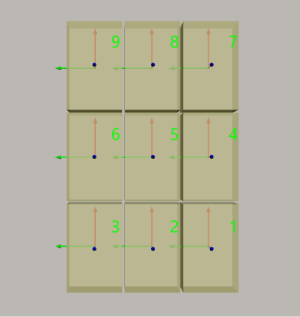
Rows/Unit |
The rows of the stacked boxes per layer. |
Cols/Unit |
The columns of the stacked boxes per layer. |
Transformation between Odd and Even Layers |
Stacking the boxes in different orientations on the odd and even layers can make the stack more stable. Five transformation methods are provided in the right drop-down menu. |
Gap Width |
Set the gap width of the boxes in the pallet pattern. |
Adjust to Square |
Adjust the pallet pattern to square. |
Rotate 90° Around Z-axis |
Rotate the whole pallet pattern 90°around Z-axis. |
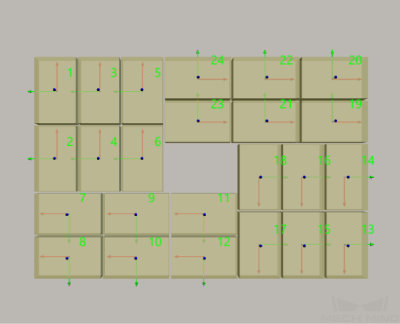
Pinwheel 2
The pallet pattern is shown in the following figure.
Is Antithetic |
Stacking the boxes in different orientations on the odd and even layers can make the stack more stable. |
Gap Width |
Set the gap width of the boxes in the pallet pattern. |
Rotate 90° Around Z-axis |
Rotate the whole pallet pattern 90°around Z-axis. |
X-Oriented Boxes’ Num of Rows/Cols |
Set the number of rows and columns of boxes in the X-orientation. |
Y-Oriented Boxes’ Num of Rows/Cols |
Set the number of rows and columns of boxes in the Y-orientation. |
Automatic layout
Stack Generation Preference |
Carton quantity first: Generate pallet pattern for as many boxes as possible, provided that other parameter constraints are met. |
Stack stability first: Generate more stable pallet pattern as much as possible, provided that other parameter constraints are met. |
|
Gap Width |
Set the gap width of the boxes in the pallet pattern. |
Stack Height Settings
Specified Layer Count |
Set the number of layers of the boxes in the pallet pattern. |
Limit Stack Height |
Once this parameter is selected, you can set the maximum height of the pallet pattern. |
Limit Box Count |
Once this parameter is selected, you can set the maximum number of the boxes for the pallet pattern. |