PROFINET–Siemens SIMATIC S7 PLC Functions
This topic introduces the functions for PROFINET communication between a Siemens SIMATIC S7 PLC using the TIA Portal software and Mech-Mind Software Suite.
Function Descriptions
Start Mech-Vision Project
This function is used for applications that use Mech-Vision but not Mech-Viz. This function starts the Mech-Vision project that executes image capturing and performs vision recognition.
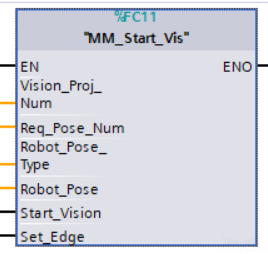
Parameters
Input parameters
-
Vision_Proj_Num: Mech-Vision project ID, which is the number before the project name in the Project List panel in Mech-Vision.
-
Req_Pose_Num: The number of vision points that Mech-Vision is requested to send, from 1 to 20, where 0 indicates “send all”.
-
Robot_Pose_Type: The type of robot pose to input to Mech-Vision. The value range is 0 to 3.
-
Robot_Pose: The pose received from the robot, value depends on the value of Robot_Pose_Type. Data type: two-dimensional array [0..1, 0..5] of DInt, array[0] is joint positions and array[1] is flange pose;
The following table explains the relationship between Robot_Pose_Type and Robot_Pose.
| Robot_Pose_Type value | Robot_Pose value | Description | Applicable Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
0 |
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 |
No need to input robot pose to Mech-Vision. |
Project is in the eye-to-hand mode. If the “Path Planning” Step is used in the Mech-Vision project, the planned path starts at the Home point set in the path planning tool. |
1 |
Current joint positions and flange pose of the robot |
Robot joint positions and flange pose must be input to Mech-Vision. |
Project is in the Eye-In-Hand setup. Applicable to most robots (excluding truss robots). |
2 |
Current flange pose of the robot |
Robot flange pose must be input to Mech-Vision. |
Project is in the Eye-In-Hand setup. The robot has no joint positions and only flange pose (such as truss robots). |
3 |
Joint positions of the start point of the planned path |
The joint positions of the path start point must be input to Mech-Vision. |
Project is in the Eye-In-Hand setup and the Mech-Vision project contains the “Path Planning” Step, whose start point needs to be set from the robot side. |
| Before assigning to the Robot_Pose array, multiply the floating-point numbers that represent joint positions or the robot flange pose by 10000 to convert the data to 32-bit signed integers. |
-
Start_Vision: Trigger the start of the Mech-Vision project at the rising edge.
-
Set_Edge: Store the value of Start_Vision in the last cycle to prevent unnecessary repetition of triggering.
Returned data from the CameraIO data block FromCamera:
-
STATUS_CODE: 1102 is returned if no error occurred. For other values, please refer to Status Codes and Troubleshooting for the corresponding error.
Example
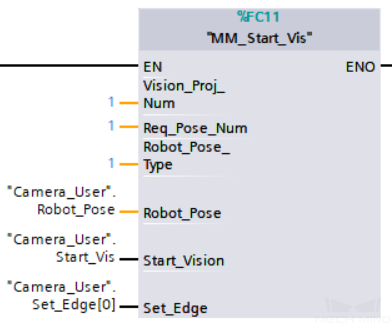
Example Description
When “Camera_User”.Start_Vis is at the rising edge, this example runs Mech-Vision project No.1, asks the Mech-Vision project to send over 1 vision point, and sends the robot joint positions when the Mech-Vision project is started as the image-capturing pose to Mech-Center.
Obtain Vision Target(s)
This function is used for applications that use Mech-Vision but not Mech-Viz. It obtains the vision result from the corresponding Mech-Vision project.
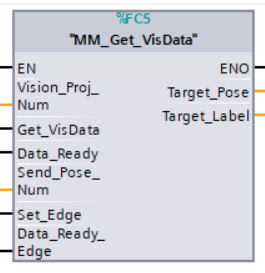
Parameters
Input parameters
-
Vision_Proj_Num: Mech-Vision project ID, which is the number before the project name in the Project List panel in Mech-Vision.
-
Get_VisData: Obtain vision points from Mech-Vision project when a rising edge occurs.
-
Data_Ready: Indicates the pose data is readable when receiving multiple sets of robot pose data.
-
Send_Pose_Num: The number of poses to be sent, from 0 to 20.
-
Set_Edge: Store the value of Start_Vision in the last cycle to prevent unnecessary repetition of triggering.
-
Data_Ready_Edge: This parameter does not need to be set by the user. It stores the value of “Data_Ready” in the last scan cycle to prevent unnecessary repetition of reading.
Output Parameters
-
Target_Pose: Obtained pose data (TCP) of waypoints. The data type is array[0..19, 0..5] of DInt. This array should be divided by 10000 before being used.
-
Target_Label: The label information of the object recognized by Mech-Vision. The data type is array[0..19] of UDInt. The returned values are integers.
Returned data from the CameraIO data block FromCamera:
-
STATUS_CODE: 1100 is returned if no error occurred. For other values, please refer to Status Codes and Troubleshooting for the corresponding error.
-
SEND_POSE_TYPE: The value returned by Mech-Vision via Command 102 is 2, which suggests that the type of poses obtained is in TCP.
Example
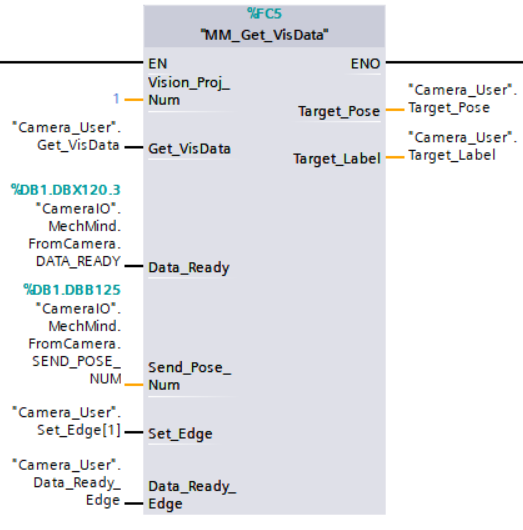
Example Description
When “Camera_User”.Get_VisData is at the rising edge, this example obtains the vision result from Mech-Vision project No.1.
Switch Mech-Vision Recipe
This function specifies the parameter recipe used by the Mech-Vision project. Parameter recipes can be used to switch parameter settings, including point cloud model for matching, ROI, confidence threshold, etc, in the same Mech-Vision project when it is used to recognize different workpieces. This function must be called BEFORE MM_Start_Vis.
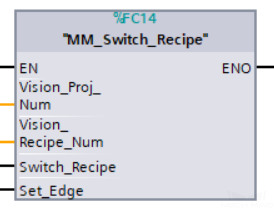
Parameters
Input parameters
-
Vision_Proj_Num: Mech-Vision project ID, which is the number before the project name in the Project List panel in Mech-Vision.
-
Vision_Recipe_Num: The ID of a parameter recipe in the Mech-Vision project, from 1 to 99.
-
Switch_Recipe: Switch the parameter recipe used by the Mech-Vision project when a rising edge occurs.
-
Set_Edge: Store the value of Start_Vision in the last cycle to prevent unnecessary repetition of triggering.
Returned data from the CameraIO data block FromCamera:
-
STATUS_CODE: 1107 is returned if no error occurred. For other values, please refer to Status Codes and Troubleshooting for the corresponding error.
Example
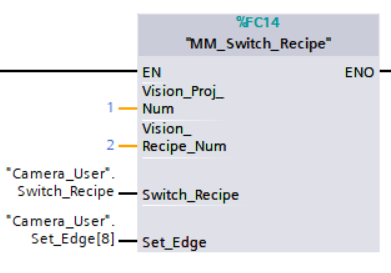
Example Description
When “Camera_User”.Switch_Recipe is at the rising edge, this example switches the parameter recipe used to No.2 in Mech-Vision project No.1.
Get Result of Step “Path Planning” in Mech-Vision
After calling MM_Start_Vis, call this function to obtain the collision-free picking path planned by the “Path Planning” Step in the Mech-Vision project.
When using this function, set the Port Type parameter of the “Procedure Out” Step in the Mech-Vision project to “Predefined (robot path)”.
| Before executing this function, please set Req_Pose_Num in MM_Start_Vis to 0 to reduce the times of execution of this function. If Req_Pose_Num in MM_Start_Vis is set to 1, then every time this function is executed, only 1 waypoint is returned, and this function must be executed multiple times to obtain all the waypoints. |

Parameters
Input parameters
-
Vision_Proj_Num: Mech-Vision project ID, which is the number before the project name in the Project List panel in Mech-Vision.
-
Request_Pose_Type: Specify the type of waypoint pose returned by the “Path Planning” Step, 1 or 2.
-
1: The waypoint poses are returned in the form of joint positions (JPs). -
2: The waypoint poses are returned in the form of tool center point (TCP).
-
-
Get_VisData: Obtains the planned path from the “Path Planning” Step in Mech-Vision at the rising edge.
-
Data_Ready: Indicate that all the pose data is available to read when receiving multiple groups of robot poses.
-
Send_Pose_Num: The number of poses to be sent, from 0 to 20.
-
Set_Edge: Store the value of Get_VisData in the last cycle to prevent unnecessary repetition of triggering.
-
Data_Ready_Edge: This parameter does not need to be set by the user. It stores the value of “Data_Ready” in the last scan cycle to prevent unnecessary repetition of reading.
Output Parameters
-
Target_Pose: TCP of the waypoint. The data type is Array[0..19, 0..5] of DInt. This array should be divided by 10000 before being used.
-
Target_Label: Label of the vision target. The data type is Array[0..19] of UDInt.
-
Target_Speed: The speed in percentage set in the move-type Step parameters, from 1 to 100.
Returned data from the CameraIO data block FromCamera:
-
STATUS_CODE: If there is no error, status code 1103 will be returned. Otherwise, the corresponding error code will be returned.
-
SEND_POSE_TYPE: The pose type of the waypoint, which is consistent with that of the Request_Pose_Type input parameter. 1 indicates JPs, while 2 indicates TCP.
-
VISUAL_POINT_INDEX: The position of the Vision Move Step, i.e., the move to the vision pose (usually the pose for picking the object) in the entire robot motion path.
Example
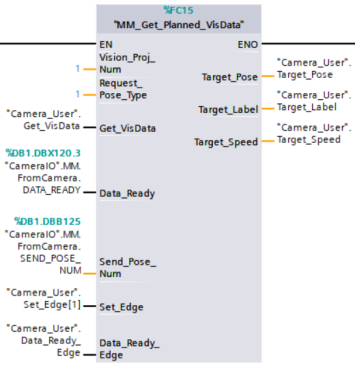
Example Description
When there is a rising edge on the variable Camera_User.Get_VisData, the path planned by the Mech-Vision project No.1 will be obtained in the form of joint positions.
Start Mech-Viz Project
This function block is for applications that use both Mech-Vision and Mech-Viz. It runs the corresponding Mech-Viz project (which triggers the corresponding Mech-Vision project to run), and then plans the path for picking.
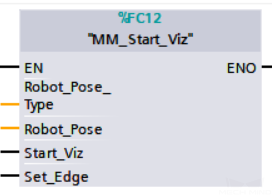
Parameters
Input parameters
-
Robot_Pose_Type: The type of robot pose to input to Mech-Viz. The value range is 0 to 2.
-
Robot_Pose: The pose received from the robot, value depends on the value of Robot_Pose_Type. Data type: two-dimensional array [0..1, 0..5] of DInt, array[0] is joint positions and array[1] is flange pose;
The following table explains the relationship between Robot_Pose_Type and Robot_Pose.
| Robot_Pose_Type value | Robot_Pose value | Description | Applicable Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
0 |
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 |
No need to input the robot pose to Mech-Viz. The simulated robot in Mech-Viz moves from the initial pose JPs = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] to the first waypoint. |
Project is in the eye-to-hand mode. This setting is not recommended. |
1 |
Current joint positions and flange pose of the robot |
Robot joint positions and flange pose must be input to Mech-Viz. The simulated robot in Mech-Viz moves from the input JPs to the first waypoint. |
This setting is recommended for projects in the Eye-In-Hand setup. |
2 |
Specific joint positions of the robot |
The robot joint positions of a point determined by teaching must be input to Mech-Viz. The input joint positions are used to trigger Mech-Viz to plan the next path in advance while the robot is not in the camera capture region, as shown below. The simulated robot in Mech-Viz moves from the input joint positions to the first waypoint. |
This setting is recommended for projects in the eye-to-hand mode. |
|
The reason for setting Robot_Pose_Type to 2 when the project is in the eye-to-hand mode:
In the eye-to-hand mode, the camera can perform image capturing for the next round of path planning before the robot returns to the camera capture region and picking region, shortening the cycle time. If Robot_Pose_Type is set to 1, the robot’s current pose is sent to Mech-Viz. The simulated robot will move from the input pose to the first waypoint in the planned path, while the real robot might move to another point first, and then move to the first waypoint. Therefore, the path of the real robot may contain unpredicted collisions, leading to safety hazards. In conclusion, Robot_Pose_Type should be set to 2 for projects in the Eye-To-Hand setup. 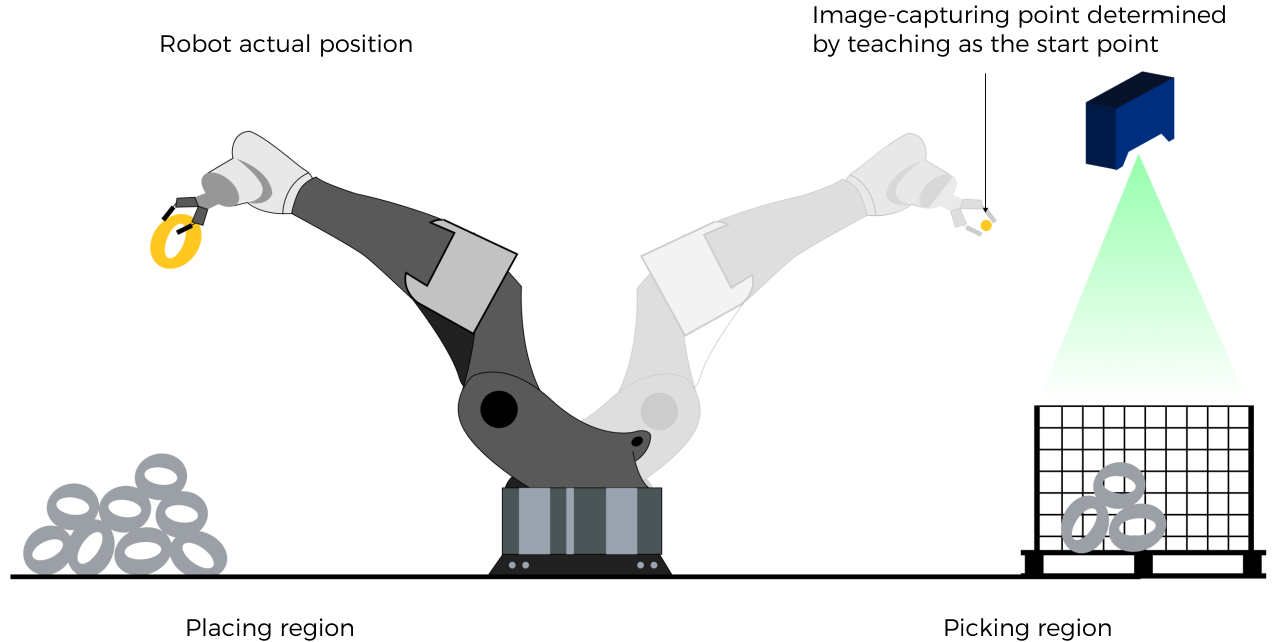
|
| Before assigning to the Robot_Pose array, multiply the floating-point numbers that represent joint positions or the robot flange pose by 10000 to convert the data to 32-bit signed integers. |
-
Start_Viz: Triggers the Mech-Viz project to run at the rising edge.
-
Set_Edge: Store the value of Start_Vision in the last cycle to prevent unnecessary repetition of triggering.
Returned data from the CameraIO data block FromCamera:
-
STATUS_CODE: 2103 is returned if Mech-Viz is successfully started and no error occurred. For other values, please refer to Status Codes and Troubleshooting for the corresponding error.
Example
Example Description
When the variable “Camera_User”.Start_Viz is at the rising edge, this example runs the corresponding Mech-Viz project, and sends the current joint positions of the robot to Mech-Center.
StopMech-Viz Project
This function stops the execution of the Mech-Viz Project. This function is only needed if the Mech-Viz project falls into an infinite loop or cannot be stopped normally. This function is only needed if the Mech-Viz project falls into an infinite loop or cannot be stopped normally.
Parameters
Input parameters
-
Stop_Viz: Stop the execution of the Mech-Viz project at the rising edge.
-
Set_Edge: Store the value of Start_Vision in the last cycle to prevent unnecessary repetition of triggering.
Returned data from the CameraIO data block FromCamera:
-
STATUS_CODE: 2104 is returned if Mech-Viz is successfully stopped and no error occurred. For other values, please refer to Status Codes and Troubleshooting for the corresponding error.
Example
Example Description
When “Camera_User”.Stop_Viz is at the rising edge, this example stops the execution of the Mech-Viz project.
Select Mech-Viz Branch
This function is used to select along which branch the Mech-Viz project should proceed. Such branching is achieved by adding Branch by Msg Step(s) to the project. MM_START_VIZ must be called BEFORE this function. When the next Step to be executed in Mech-Viz is a Branch by Msg Step, the system will wait for this function to send the exit port number by the Command 203.
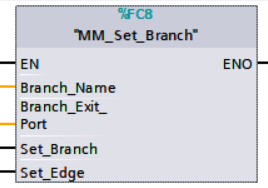
Parameters
Input parameters
-
Branch_Name: Step ID of the Branch by Msg Step, which is a positive integer.
-
Branch_Exit_Port: The number of the exit port to take, from 1 to 99.
-
This parameter value should be 1 greater than the exit port number displayed in the Mech-Viz Step. For example, the port 0 displayed in the interface corresponds to Branch_Exit_Port 1.
-
Branch_Name, Branch_Exit_Port, and Index_Name and Index_Counter in the function MM_Set_Index correspond to the same VIZ_TASK_NAME and VIZ_TASK_VALUE tags in the CameraIO data block respectively. If the set values are different, they cannot take effect at the same time.
-
-
Set_Branch: Specify the port which Branch by Msg Step should take.
-
Set_Edge: Store the value of Start_Vision in the last cycle to prevent unnecessary repetition of triggering.
Returned data from the CameraIO data block FromCamera:
-
STATUS_CODE: 2105 is returned if the branch is successfully selected and no error occurred. For other values, please refer to Status Codes and Troubleshooting for the corresponding error.
Example
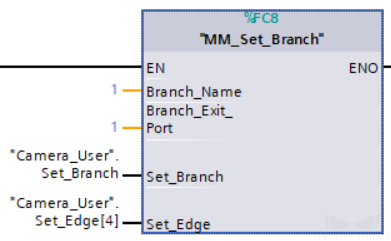
Example Description
When “Camera_User”.Set_Branch is at the rising edge, this example tells Mech-Viz to take exit port 1 for the Branch by Msg Step whose Step ID is 1.
Set Move Index
This function sets the value for the Current Index parameter of Steps. Steps that have this parameter include Move by List, Move by Grid, Custom Pallet Pattern, and Smart Pallet Pattern. MM_Start_Viz must be called BEFORE this function.
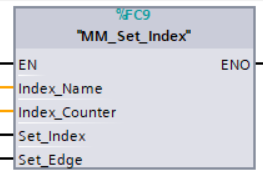
Parameters
Input parameters
-
Index_Name: Step ID of the Step with the index parameter, which is a positive integer.
-
Index_Counter: The index value that should be set the next time this Step is executed. When this function is sent, the current index value in Mech-Viz will become the parameter value minus 1. When the Mech-Viz project runs to the Step specified by this function, the current index value in Mech-Viz will be increased by 1 to become the parameter’s value.
Index_Name、Index_Counter, and Branch_Name and Branch_Exit_Port in the function MM_Set_Branch correspond to the same VIZ_TASK_NAME and VIZ_TASK_VALUE tags in the CameraIO data block respectively. If the set values are different, they cannot take effect at the same time. -
Set_Index: The trigger signal to set the index. The rising edge does the trigger.
-
Set_Edge: Store the value of Start_Vision in the last cycle to prevent unnecessary repetition of triggering.
Returned data from the CameraIO data block FromCamera:
-
STATUS_CODE: 2106 is returned if the index is successfully set and no error occurred. For other values, please refer to Status Codes and Troubleshooting for the corresponding error.
Example
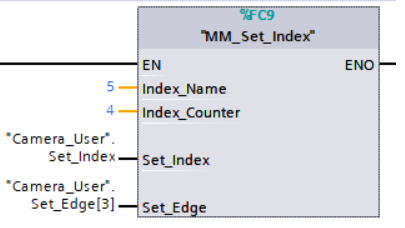
Example Description
When “Camera_User”.Set_Index is at the rising edge, this example sets the Current Index value to 3 for the Step in the Mech-Viz project whose Step ID is 5. When the Step is executed, the Current Index value will be added 1 and become 4.
Get Planned Path
This function obtains the planned path from Mech-Viz.
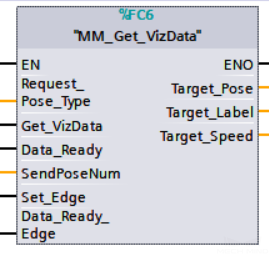
Parameters
Input parameters
-
Request_Pose_Type: Specify the type of waypoint pose returned, 1 or 2.
-
1: The pose type returned by Mech-Viz is joint positions.
-
2: Mech-Viz sends waypoints in TCPs.
-
-
Get_VizData: Obtains the planned path from Mech-Viz at the rising edge.
-
Data_Ready: Indicates the pose data is readable when receiving multiple sets of robot pose data.
-
Send_Pose_Num: The number of waypoints returned by Mech-Viz, from 0 to 20.
-
Set_Edge: Store the value of Start_Vision in the last cycle to prevent unnecessary repetition of triggering.
-
Data_Ready_Edge: This parameter does not need to be set by the user. It stores the value of “Data_Ready” in the last scan cycle to prevent unnecessary repetition of reading.
Output Parameters
-
Target_Pose: Obtained pose data (TCP) of waypoints. The data type is array[0..19, 0..5] of DInt. This array should be divided by 10000 before being used.
-
Target_Label: The label information of the object recognized by Mech-Vision. The data type is array[0..19] of UDInt. The returned values are integers.
-
Target_Speed: The speed set in the Step related to move. Range: [1, 100].
Returned data from the CameraIO data block FromCamera:
-
STATUS_CODE: 2100 is returned if no error occurred. For other values, please refer to Status Codes and Troubleshooting for the corresponding error.
-
SEND_POSE_TYPE: The pose type of the waypoint, which is consistent with that of the Request_Pose_Type input parameter. 1 indicates JPs, while 2 indicates TCP.
-
VISUAL_POINT_INDEX: The position of the vision point, which is generated from the “Vision Move” Step, in the planned path.
Example
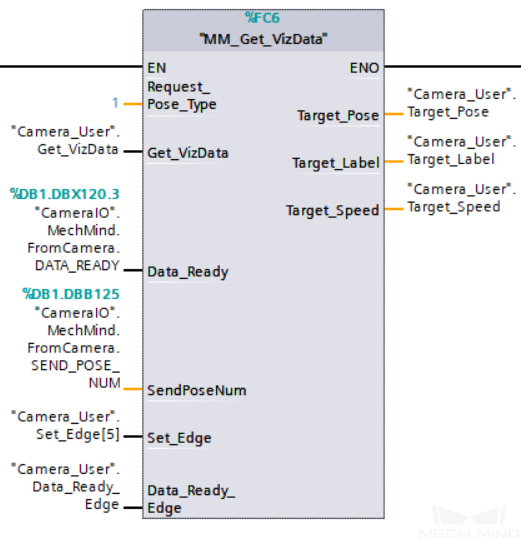
Example Description
When “Camera_User”.Get_VizData is at the rising edge, this example obtains the planned path from Mech-Viz in the form of TCPs.
Get DO Signal List
This function obtains the planned DO Signal list for controlling multiple sections of a sectioned vacuum gripper. MM_Get_VizData must be called BEFORE this function.
Please refer to the suction_zone.viz template in XXXX/Mech-Center-xxx/tool/viz_project/suction_zone, and set the suction cup configuration file before calling the function.
|
Parameters
Input parameters
-
Get_DoList: Obtain the planned DO signal list from Mech-Viz at the rising edge.
-
Set_Edge: Store the value of Start_Vision in the last cycle to prevent unnecessary repetition of triggering.
Returned data from the CameraIO data block FromCamera:
-
STATUS_CODE: 2102 is returned if the DO signal list is successfully obtained and no error occurred. For other values, please refer to Status Codes and Troubleshooting for the corresponding error.
-
DO_LIST: The list of 64 DO values, in the range of 0 to 999, with -1 being the placeholder value.
Example
Example Description
When “Camera_User”.Get_DoList is at the rising edge, this example obtains the planned DO signal list from Mech-Viz and stores it in the DO_LIST variable.
Input Object Dimensions to Mech-Vision
This function inputs object dimensions to the Mech-Vision project.
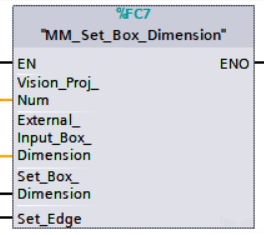
Parameters
Input parameters
-
Vision_Proj_Num: Mech-Vision project ID, which is the number before the project name in the Project List panel in Mech-Vision.
-
External_Input_Box_Dimension: The unit is in mm, for example, the dimensions of a box (length, width, height). Multiply each dimension by 10000 and then assign the results to External_Input_Box_Dimension[0-2];
External_Input_Box_Dimension here and External_Input_Pose in the function MM_Set_Pose correspond to the same EXT_INPUT_DATA tag of the CameraIO data struct. If the set values are different, they cannot take effect at the same time. -
Set_Box_Dimension: Inputs the object dimensions in the Mech-Vision project dynamically at the rising edge.
-
Set_Edge: Store the value of Start_Vision in the last cycle to prevent unnecessary repetition of triggering.
Returned data from the CameraIO data block FromCamera:
-
STATUS_CODE: 1108 is returned if no error occurred. For other values, please refer to Status Codes and Troubleshooting for the corresponding error.
Example
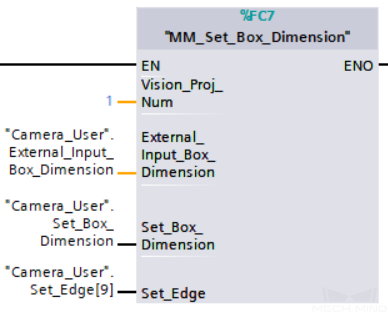
Example Description
When “Camera_User”.Set_Box_Dimension is at the rising edge, this example sets the object dimensions in the Read Object Dimensions Step in the Mech-Vision project No.1 to the values in External_Input_Box_Dimension.
Input TCP to Mech-Viz
This function is used to dynamically input the pose data and should be used in conjunction with the External Move Step in Mech-Viz. This function must be executed BEFORE MM_Start_Viz.
Refer to the outer_move.viz project in XXXX/Mech-Center-xxx/tool/viz_project/outer_move, and put the External Move Step at a proper position in the workflow.
|
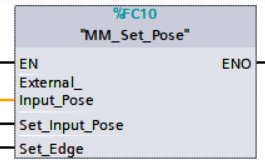
Parameters
Input parameters
-
External_Input_Pose: TCP of the robot in mm. Multiply the pose data by 10000 and then assign them Ext_Input_Data[0-5].
External_Input_Pose here and External_Input_Box_Dimension in the function MM_Set_Box_Dimension correspond to the same EXT_INPUT_DATA tag of the CameraIO data block. If the set values are different, they cannot take effect at the same time. -
Set_Input_Pose: Input the TCP data to the External Move Step at the rising edge.
-
Set_Edge: Store the value of Start_Vision in the last cycle to prevent unnecessary repetition of triggering.
Returned data from the CameraIO data block FromCamera:
-
Status Code: 2107 is returned if no error occurred. For other values, please refer to Status Codes and Troubleshooting for the corresponding error.
Example
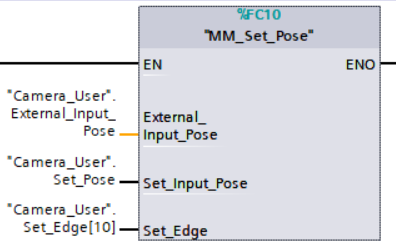
Example Description
When “Camera_User”.Set_Input_Pose is at the rising edge, this example sends the pose data stored in External_Input_Pose[0–5] to the External Move Step in the Mech-Viz project.
Get Software Status
This function is currently capable of checking whether Mech-Vision ready to run projects. In the future, this function can be used for obtaining the execution status of Mech-Vision, Mech-Viz, and Mech-Center.
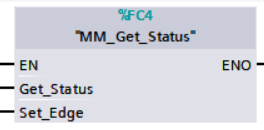
Parameters
Input parameters
-
Get_Status: Check whether Mech-Vision is ready to run projects at the rising edge.
-
Set_Edge: Store the value of Start_Vision in the last cycle to prevent unnecessary repetition of triggering.
Returned data from the CameraIO data block FromCamera:
-
Status code: Represent the software status.
Example
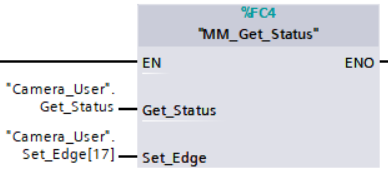
Example Description
When “Camera_User”.Get_Status is at the rising edge, this example checks the status code and stores it in STATUS_CODE.
Clear Target Data
This function clears the obtained data stored in the Target Pose, Target Label and Speed Percentage variables.
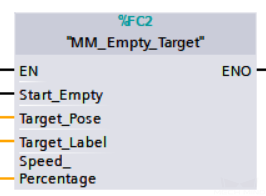
Parameters
Input parameters
-
Start_Empty: Clear the data stored in Target_Pose, Target_Label, and Speed_Percentage at the rising edge.
-
Target_Pose: Obtained target poses.
-
Target_Label: Obtained label.
-
Speed_Percentage: Obtained velocity settings.
Example
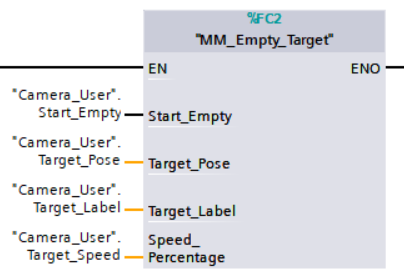
Example Description
When “Camera_User”.Start_Empty is at the rising edge, the data stored in the Target_Pose, Target_Label, and Speed_Percentage will be cleared.
Appendix
Description of the Status Codes
Please refer to Status Codes and Troubleshooting for detailed information.