Select Protective Glass
In application scenarios where a 3D camera requires protection, the camera can be put inside a protective housing with a glass window. The optical quality of the glass window and its installation method directly affect the lens imaging performance, which in turn impacts the measurement accuracy of the 3D camera. Therefore, the selection and design of the protective glass must ensure adequate protection while minimizing adverse effects on imaging and measurement accuracy.
The following table lists the requirements for the protective glass. Please select suitable protective glass and design an appropriate installation method based on the actual application scenario.
| Key point | Requirements |
|---|---|
Material |
Low refraction index, high Abbe number, low absorption rate, high optical homogeneity, and high surface flatness. |
Surface flatness |
< λ/4 @ 637 nm; use high-flatness glass, do not use physically tempered glass. |
Thickness |
1–3 mm; as thin as possible while maintaining high surface flatness. |
Thickness tolerance |
< ± 0.1 mm |
Parallelism |
< 3′ |
Coating |
Use double-sided anti-reflection (AR) coating; visible light transmittance ≥ 98.5%. |
Dimensions |
When designing the protective glass dimensions, please visit the Mech-Mind Download Center to view the camera’s 3D model and obtain the detailed dimensions of each component. |
Installation method |
Position the protective glass as close as possible to the camera window, and ensure that its surface is as parallel to the camera window as possible. Also, make sure the glass does not deform due to external forces. |
|
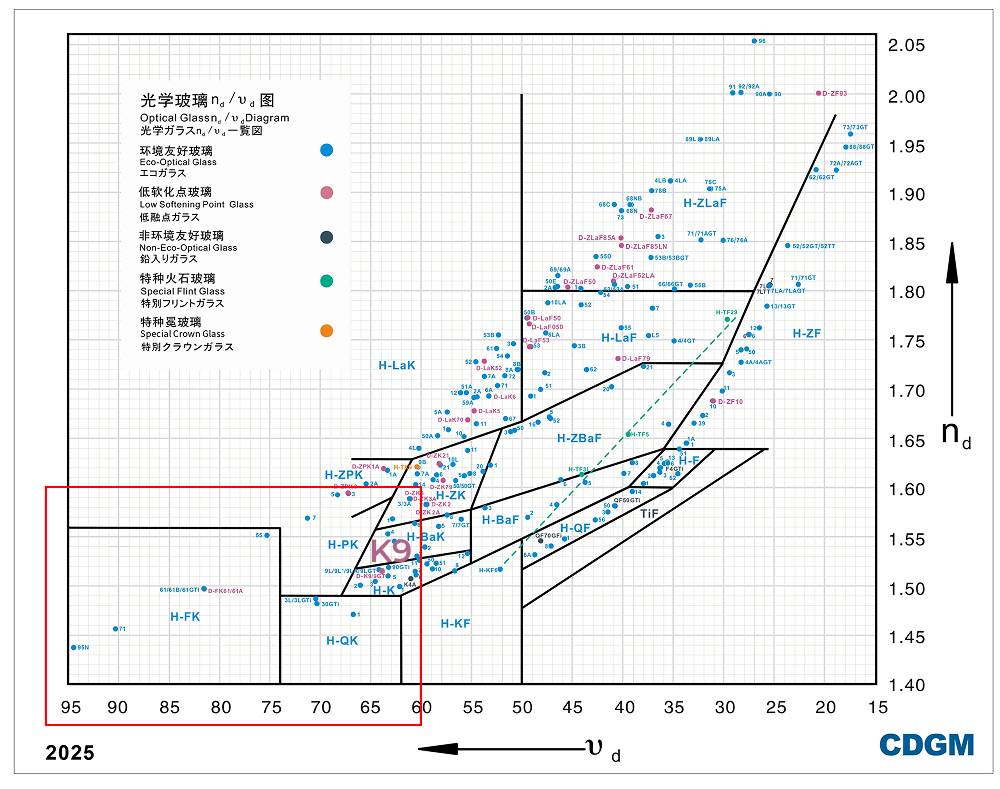
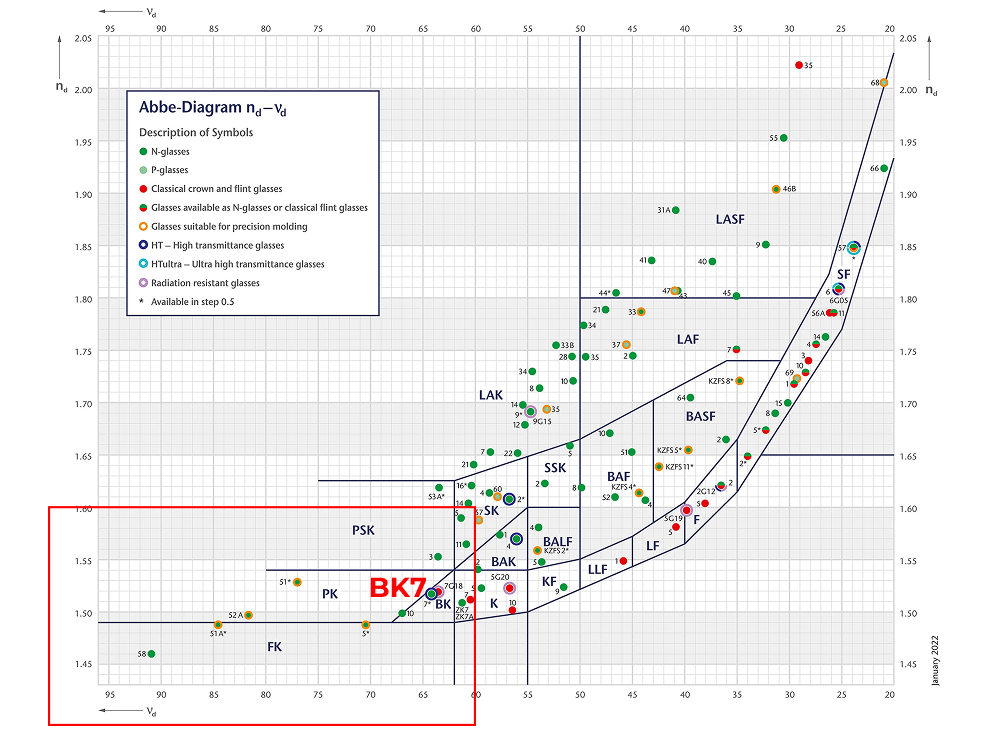
Based on the above requirements, it is recommended to use K9 or H-K9L (environmentally friendly K9) glass manufactured by CDGM, as well as BK7 or N-BK7 (environmentally friendly BK7) glass manufactured by Schott in Germany. The positions of K9 and BK7 glass in the Abbe diagrams are shown in the following figures.