Use the Classification Module
Please click here to download an image dataset of condensers, an example project in Mech-DLK. In this topic, we will use the Classification module to train a model that can distinguish between the front and back sides of the condensers.
| You can also use your own data. The usage process is overall the same, but the labeling part is different. |
Workflow
-
Create a New Project and add the Classification module: Click New Project in the interface, name the project, and select a directory to save the project. Click
 in the upper right corner of the Modules panel and add the Classification module.
in the upper right corner of the Modules panel and add the Classification module.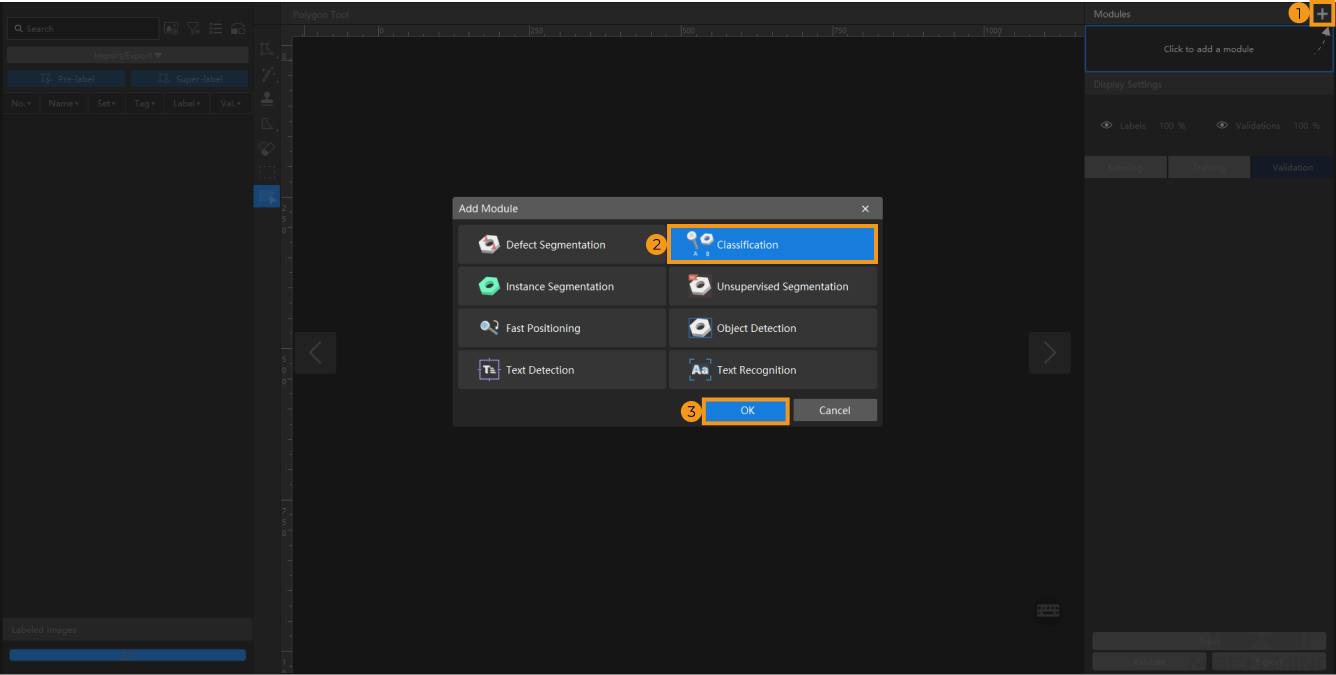
-
Import the image data of condensers: Unzip the downloaded file. Click the Import/Export button in the upper left corner, select Import Folder, and import the image folder.
When you select Import Dataset, you can only import datasets in the DLKDB format (.dlkdb), which are datasets exported from Mech-DLK. 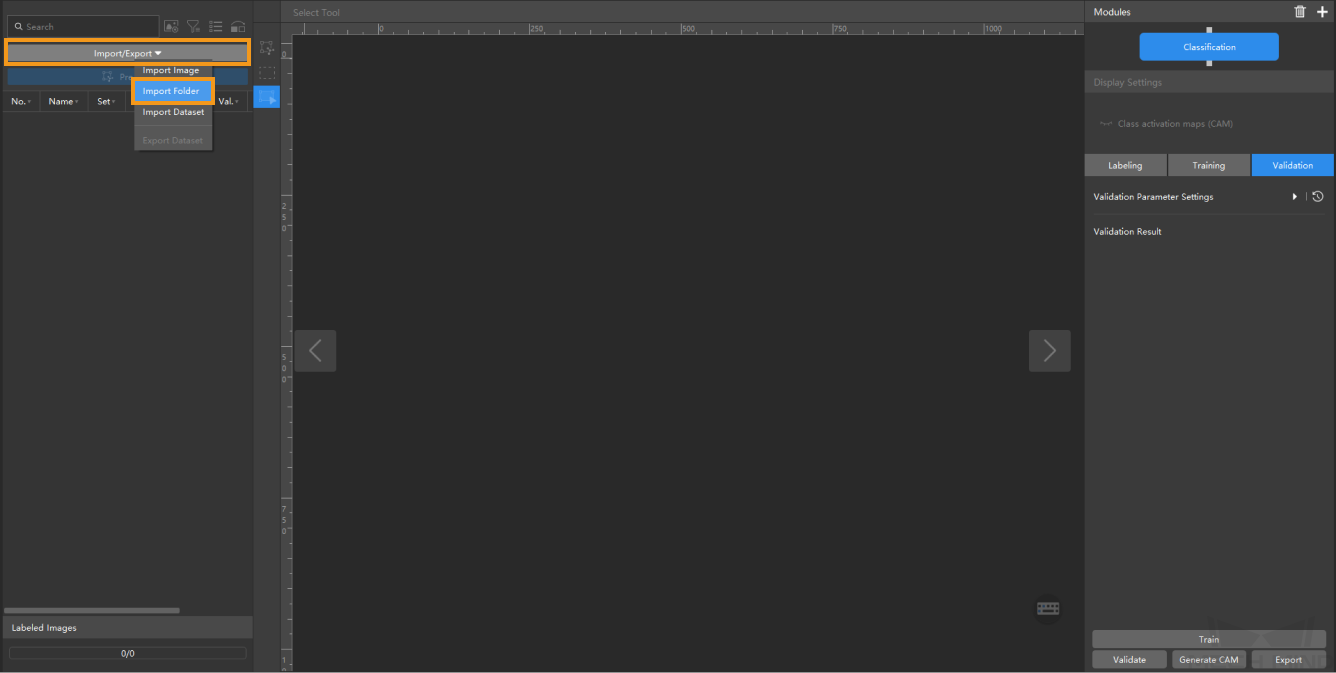
-
Create Labels: Select Labeling and click the + button to create labels based on the type or feature of different objects. In this example, the labels are named front and back to distinguish between the front and back sides of the condenser.
When you select a label, you can right-click the label and select Merge Into to change the current data type to another type. If you perform the Merge Into operation after you trained the model, it is recommended that you train the model again. -
Label images: Classify the images with corresponding labels. You can select multiple images and label them together. Please make sure that you have labeled the images accurately. Click here to view how to use labeling tools.
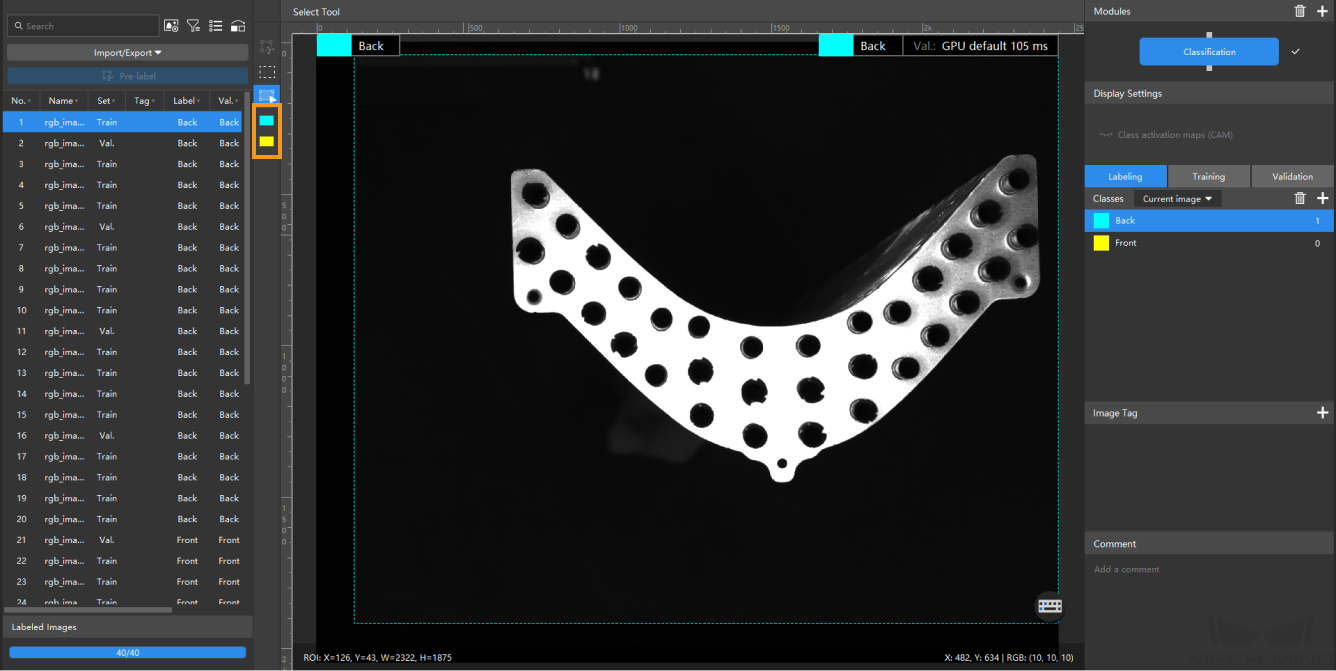
The Classification module supports selecting multiple images for labeling in batches. -
Split the dataset into the training set and validation set: By default, 80% of the images in the dataset will be split into the training set, and the rest 20% will be split into the validation set. Please make sure that both the training set and validation set include images in all different classes, which will guarantee that the model can learn all the different features and validate the images of different classes properly. If the default training set and validation set cannot meet this requirement, please right-click the name of the image and then click Switch to training set or Switch to validation set to adjust the set to which the image belongs.
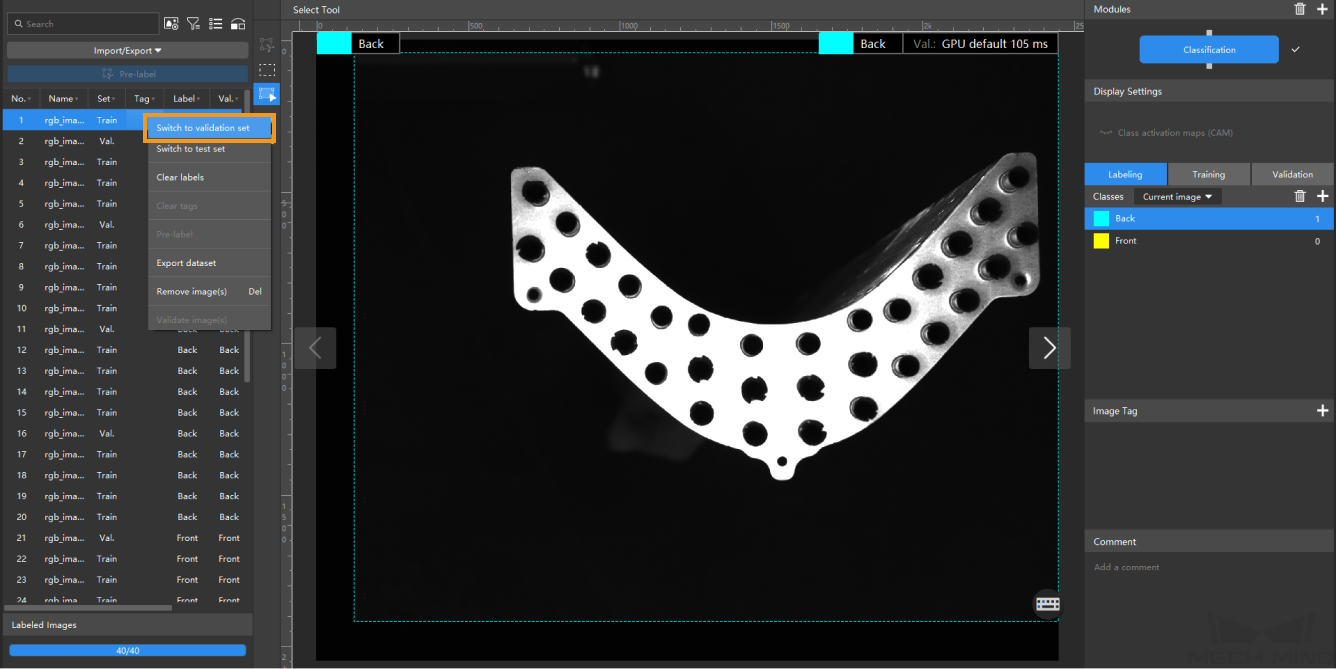
-
Train the model: Keep the default training parameter settings and click Train to start training the model.
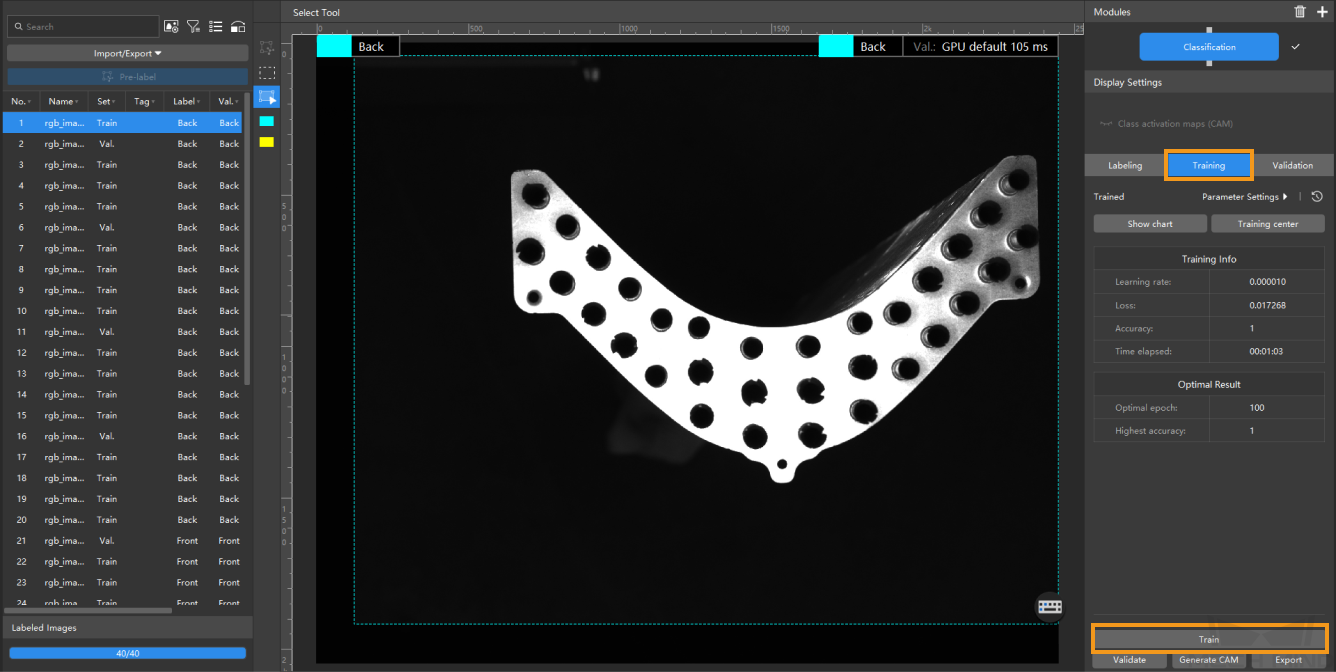
-
Show Class Activation Maps: After the training of the Classification model is completed, click Generate CAM to generate the class activation maps, and click Class activation maps (CAM). The class activation maps show the feature regions in the images that are paid attention to when training the model, and they help check the classification performance, thus providing references for optimizing the mode.
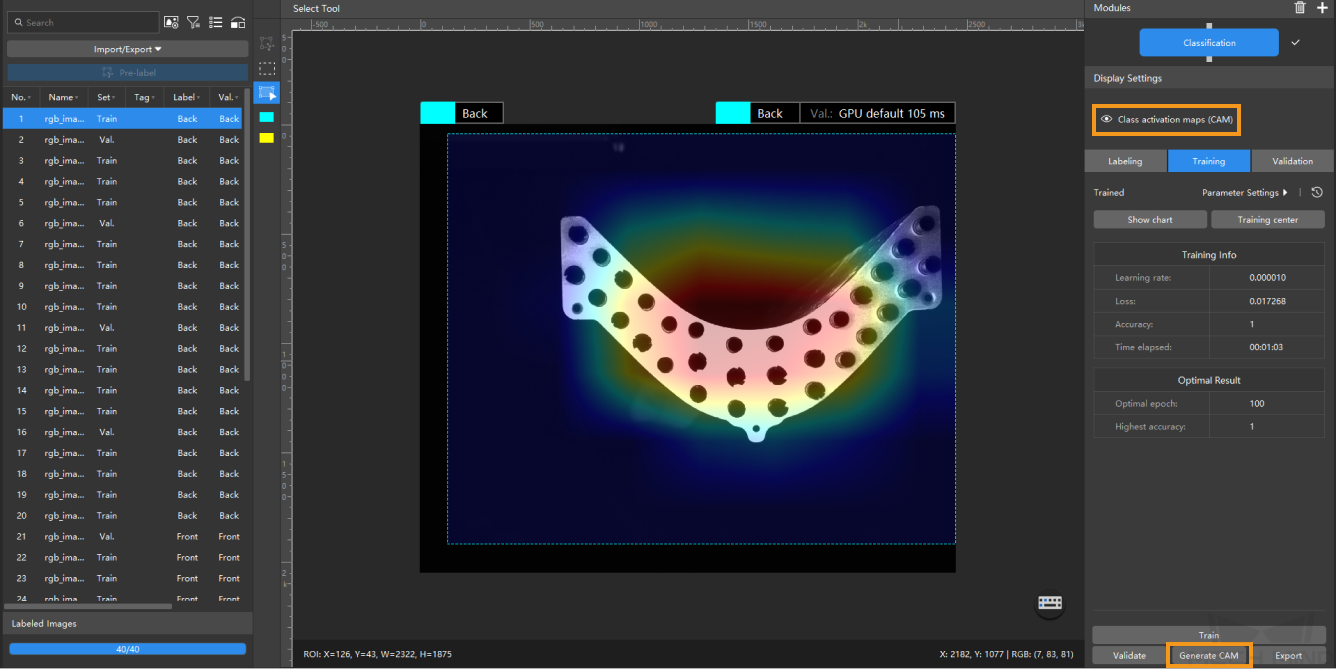
-
Validate the model: After the training is completed, click Validate to validate the model and check the results. You can also click
 > Wrong results > OK to filter the results and check the wrong ones.
> Wrong results > OK to filter the results and check the wrong ones.After you validate a model, you can import new image data to the current module and use the pre-labeling feature to perform auto-labeling based on this model. For more information, see Pre-labeling.
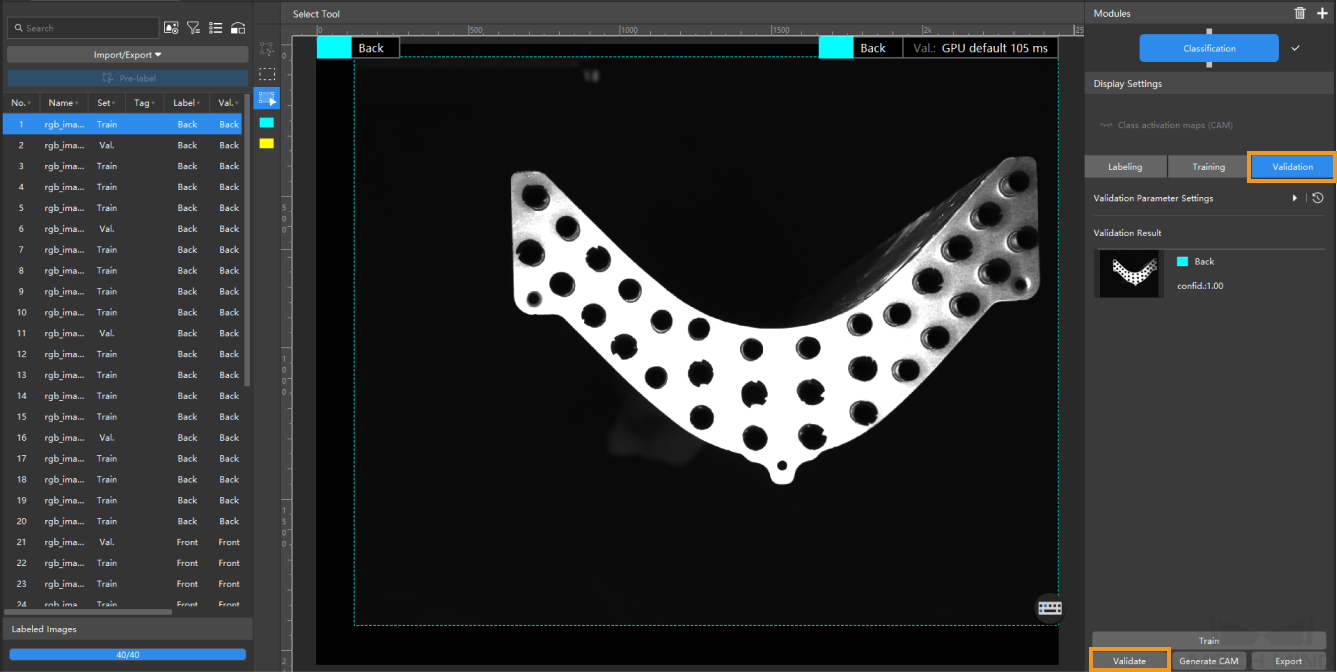
-
Export the model: Click Export, set the Class activation mapping (CAM) option of the model to be exported in the pop-up window, and then click Export and select a directory to save the exported model.
By default, the Class activation mapping (CAM) option is disabled. The inference will slow down when the model saved with CAMs is used in Mech-Vision. 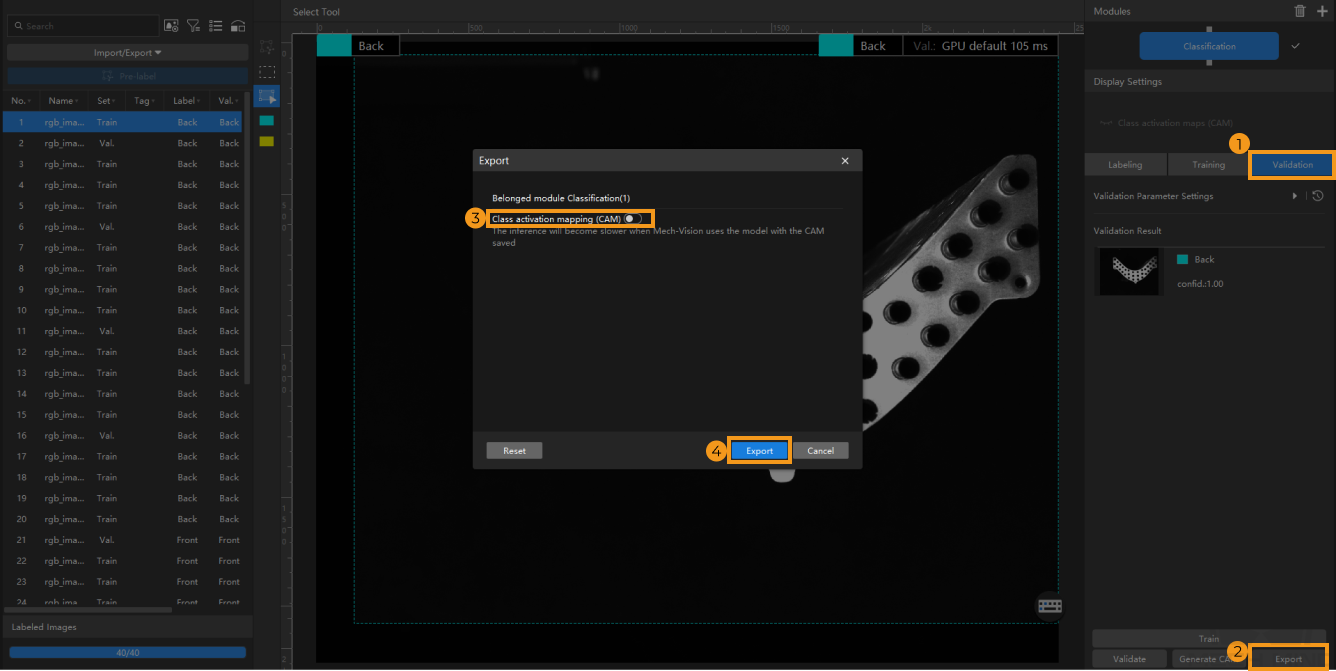
The exported model can be used in Mech-Vision and Mech-DLK SDK. Click here to view the details.