Measure Feature Point Height
Description
This Step is used to locate the feature point(s) of the profile and measure the height of feature point(s) relative to a reference line or a base point.
Workflow
The process of configuring this Step is shown below.
-
Configure the input. Connect the ports manually or select the input(s) under Input in the parameter configuration panel.
-
Set the feature region.
-
Set other parameters.
-
Select the desired output(s) under Output. For an expandable output item, click ▶ and configure the Min and Max values of the acceptable range.
Parameter Description
- Feature Region
-
This parameter is used to add feature regions (1–16) for locating feature points on the profile.
-
For more information on how to set the feature region, please refer to Set the Feature Region.
-
For more information on feature point types, please refer to Feature Point Types.
-
- Reference Line
-
When this parameter is selected, a reference line will be fitted using the data within the set line region(s).
-
Line Regions (1–2): This parameter defines a region on the profile, and the data points within the region will be used to fit the reference line.
-
Fitting Method: The method of fitting a reference line with the defined reference region. Choose between Simple and Robust.
-
Simple: High speed, but low accuracy.
-
Robust: An iterative fitting method. High accuracy, but low speed.
-
Outlier Fraction: The proportion of outliers to be removed during line fitting, thus resulting in a better result.
-
-
-
- Use Base Point
-
This parameter defines a region for locating a base point, which facilitates the measurement of feature point height.
-
Base Point Region: Configure the base point region by adjusting Center X / Z, Width, and Height of the base point region.
-
Feature Point Type: Select a type of feature points within the region as the base point. For more information, please refer to Feature Point Types.
-
Height Measurement Method
There are four ways to measure feature point height, corresponding to the following four calculation methods. You can choose among them according to the actual measurement requirements.
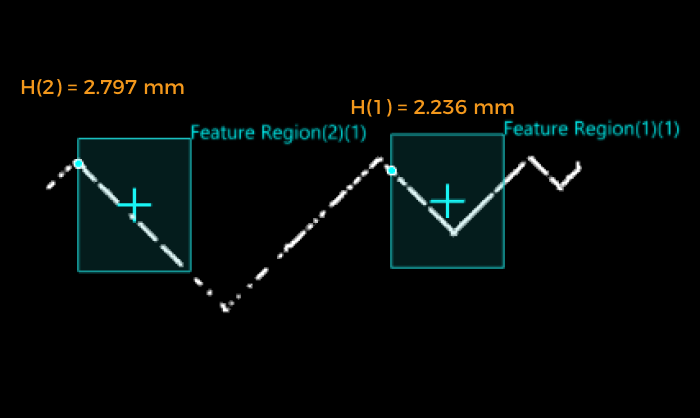
- Feature Region Only
-
It is possible to set 1–16 feature region(s), and the 1–16 feature point height(s) can be measured at once. In this case, take the line with Z = 0 as the reference line, and calculate the distance from the feature point to this line as the feature point height. The height is positive for points above the line and negative for points below the line.
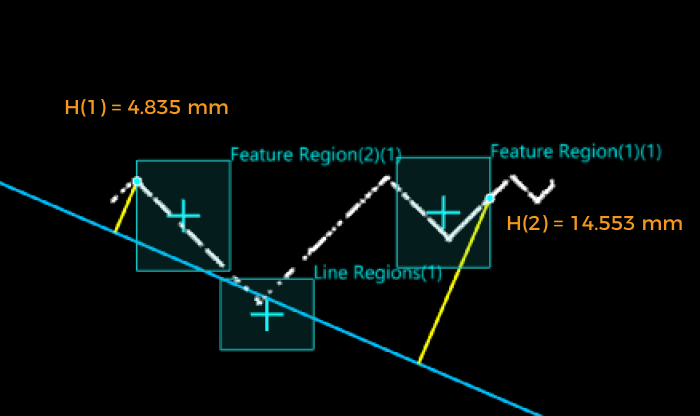
- Feature Region + Reference Line
-
Calculate the distance from the feature point to the reference line as the feature point height. The height is positive for points above the line and negative for points below the line.
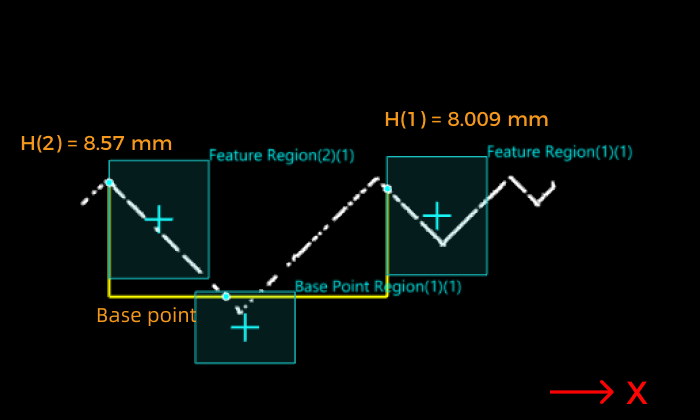
- Feature Region + Base Point
-
Make a reference line parallel to the X-axis through the base point, and calculate the distance from the feature point to the line. The height is positive for points above the line and negative for points below the line.
In this case, the base point height is the distance from the base point to the line with Z = 0.
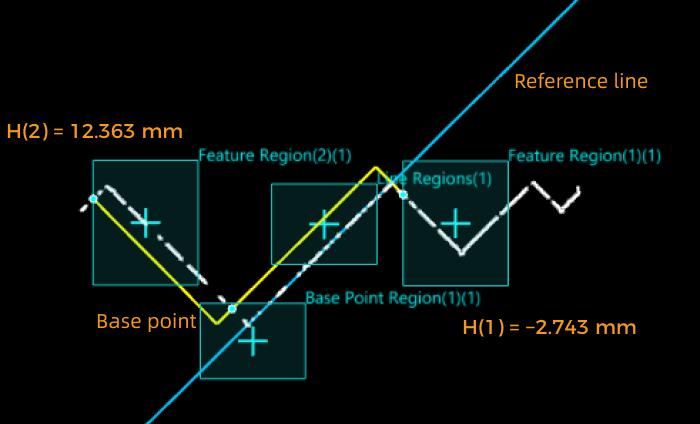
- Feature Region + Reference Line + Base Point
-
Make a line parallel to the reference line through the base point, and calculate the distance from the feature point to the line. The height is positive for points above the line and negative for points below the line.
In this case, the base point height is the distance from the base point to the reference line. The height is positive for points above the line and negative for points below the line.
Output Description
Select the output item(s) according to the actual measurement requirements. Then the corresponding data will be output after the Step is run.
|
If you select an expandable output item, you must expand it by clicking ▶, and then set the Min and Max values to determine the acceptable range. If the output value of the measurement item falls within the acceptable range, it is judged as okay (OK), or else it is judged as not good (NG). |
| Output Item | Description |
|---|---|
Height of Feature Point |
The height of a feature point to the reference line or that of a feature point to the base point. The height is positive for feature points above the reference line or base point, and negative for feature points below the reference line or base point.
|
Height of Base Point |
Without reference line, the base point height is the distance from the base point to the line with Z = 0.
|
Troubleshooting
Invalid Type
| No. | Error | Possible Causes | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Invalid feature point type |
The feature point type is not selected properly. |
Select a valid feature point type in the “Feature Point Type” drop-down list. |
Invalid Parameter
| No. | Error | Possible Causes | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Incorrect setting of percentile |
The value of “Low Percentile” is greater than that of “High Percentile,” or either of them is not within 0–100%. |
Reset the percentile to ensure that the percentile is within 0–100% and that the value of “Low Percentile” is lower than that of “High Percentile.” |
2 |
Inappropriate setting of “Outlier Fraction” |
The set outlier fraction is not within 0–100%. |
Reset “Outlier Fraction” to ensure that the value is within 0–100%. |
3 |
“Index” value out of range |
- |
Adjust the “Index” value to ensure that it is no greater than the number of turning points. |
Invalid ROI
| No. | Error | Error Description | Possible Causes | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Insufficient data points defined by the Region2 |
When the feature point type is “Contact,” there are not enough points in Region2, and thus circle fitting failed. |
The number of points in Region2 is smaller than 3, which leads to the failure of circle fitting. |
Adjust Reon2 to ensure that the number of points in it is equal to or greater than 3. |
2 |
No point of “Contact” detected |
When the feature point type was set to “Contact,” no valid points of contact were detected. |
The fitted line and circle are separated. |
Adjust the feature region to ensure that the fitted line and circle intersect or are tangent. |
3 |
Insufficient data points defined by the Region2 |
When the feature point type is “Intersection,” there are not enough points in the Region2, which leads to the failure of line fitting. |
If the number of points in Region2 is less than 2, no line can be fitted. |
Adjust the feature region to ensure that the number of points in Region2 is equal to or greater than 2. |
4 |
No point of “Intersection” detected |
When the feature point type was “Intersection,” no point of intersection was detected. |
The fitted two lines are parallel. |
Adjust the feature regions to ensure that the fit two lines can intersect. |
5 |
No point of “Inflection” detected |
- |
|
|
6 |
Insufficient data points defined by reference region(s) |
When the “Reference” option is selected, there are not enough points in the line region(s). |
The number of points in the line region(s) is smaller than 2, which leads to the failure of line fitting. |
Adjust the line region(s) to ensure that the number of points in the region is greater than or equal to 2. |