Process Profile by Filter
Description
This Step is used to process the profile by a filter to obtain a better profile. The optional filters include Gaussian, median, mean, decimation, and gap filling.
Workflow
The process of configuring this Step is shown below.
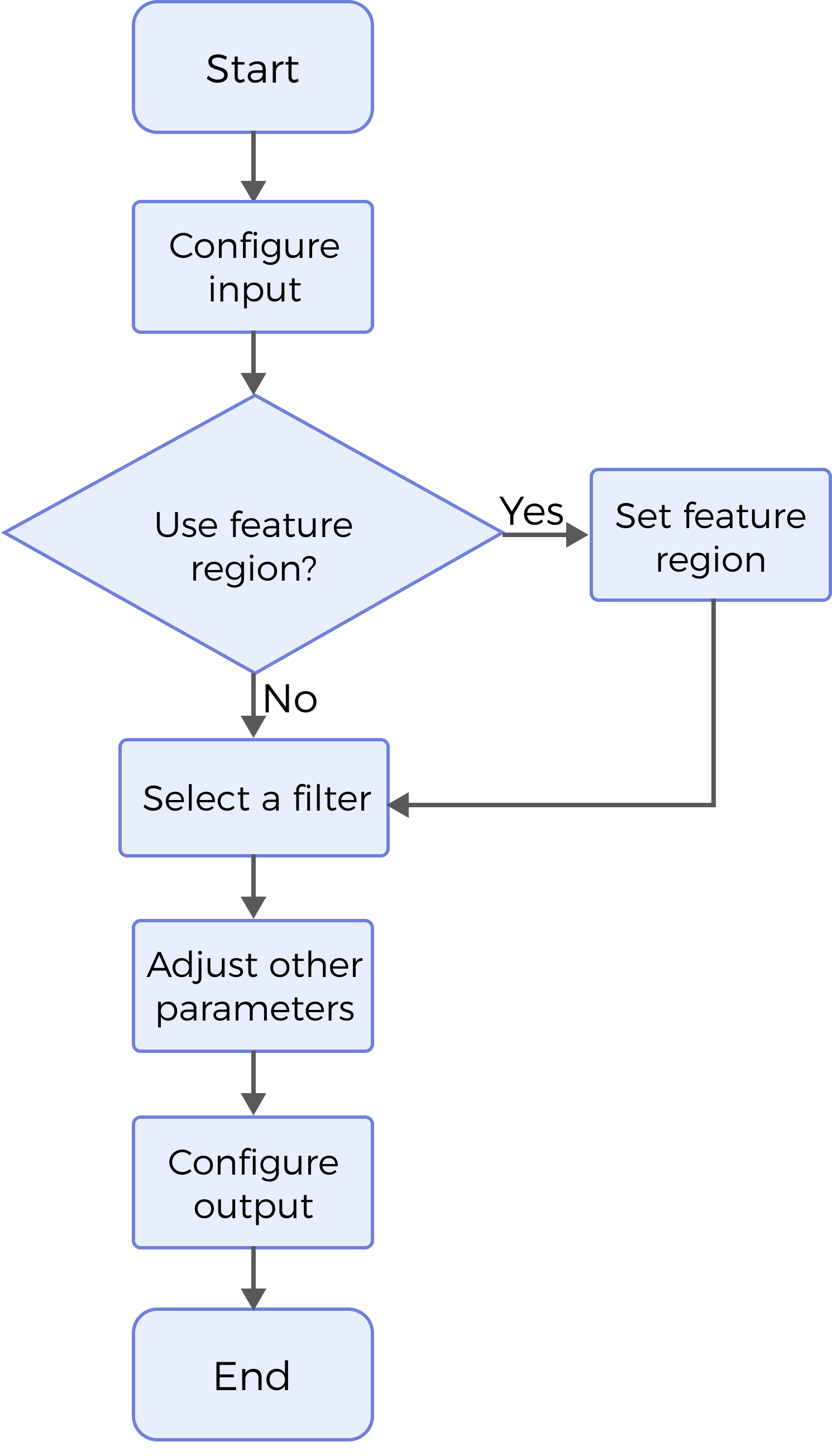
-
Configure the input. Connect the ports manually in the graphical programming workspace or select the input(s) under Input in the parameter configuration panel.
-
Determine whether to use a feature region. For more information, refer to Use Feature Region.
-
Select the filter type and set the corresponding parameters. For more information on the available filters, refer to Filter Type.
-
Select the output item Profile (selected by default).
Parameter Description
- Use Feature Region
-
Feature region defines the area to be preprocessed. When this option is selected, this Step will only process data within or outside the feature region.
Default setting: unselected
Instruction: Set the parameter according to the actual requirement.
|
For more information on how to set the feature region, please refer to Set the Feature Region. |
- Filter Type
-
The filter for profile preprocessing.
Options: Mean, Gaussian, Median, GapFilling, Decimation.
-
Mean
The mean filter can smooth the image by calculating the neighbors of pixels in the image and replacing the pixel values in the original image with the calculated average.
-
X-Direction Window Size
The number of points in the window along the X direction. It defines how many neighboring data points along the X direction are considered for mean filtering.
Instruction: The larger the window size, the smoother the profile, but the profile details may be lost.
-
-
Gaussian
Gaussian filtering is used to remove the noise in the profile, smoothing the profile without losing major details.
-
X-Direction Window Size
The number of points in the window along the X direction. It defines how many neighboring data points along the X direction are considered for Gaussian filtering.
-
Sigma
Sigma, the standard deviation, is used to control the shape of the Gaussian distribution. A larger sigma is accompanied by a flatter Gaussian distribution curve and a better smoothing effect.
-
-
Median
Median filtering is used to smooth and sharpen the profile by removing unwanted fluctuations and outliers.
-
X-Direction Window Size
The number of points in the window along the X direction. It defines how many neighboring data points along the X direction are considered for median filtering.
Instruction: As the window size increases, the filtering effect becomes more pronounced, resulting in greater noise reduction. However, this also leads to longer computing time.
-
-
GapFilling
With the maximum or minimum Z values of the nearest neighbors or linear interpolation between neighboring values, this filter fills in missing data in the specified window.
-
Gap Filling Type
Option Description Min Z point filling
Use the minimum Z value of the nearest neighbors to fill the gap.
Max Z point filling
Use the maximum Z value of the nearest neighbors to fill the gap.
Linear interpolation filling
Use the Z values of the nearest neighbors for linear interpolation to fill the gap.
-
X-Direction Window Size
Maximum gap width along the X direction. Only gaps equal to or narrower than this width will be filled.
Instruction: Gap filling may distort features with abrupt depth variations, such as object edges. Adjust this parameter according to the size of the gap to be filled.
-
-
Decimation
Decimation reduces the size or resolution of the image. During decimation, some pixels in the raw image will be discarded or merged to generate a small-sized image.
-
X-Direction Window Size
The sampling interval along the X direction. For instance, if the value is set to 2, the filter will begin selecting data points from the leftmost end of the profile and move in step size of 2 away from that starting point.
-
-
Output Description
The output of this Step is a processed profile that can be used as input to other Steps.
Troubleshooting
Invalid Type
| No. | Error | Possible Causes | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
The selected gap filling type is invalid. |
An invalid gap filling type was selected. |
Select a valid gap filling type in the “Gap Filling Type” drop-down list. |
2 |
The selected filter type is invalid. |
The filter type was not selected properly. |
Select a valid filter type in the “Filter Type” drop-down list. |
Invalid Parameter
| No. | Error | Possible Causes | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Inappropriate value of “Sigma” |
The set sigma value is less than 0. |
Reset the sigma to ensure that its value is equal to or greater than 0. |
2 |
The set “X-Direction Window Size” is less than 3. |
- |
Reset the X-direction window size of the filter to ensure that it is greater than or equal to 3. |