Diffuse Reflection, Specular Reflection, and Interreflection
Light reflects after striking the surface of a target object. The type of reflection varies with surface materials.
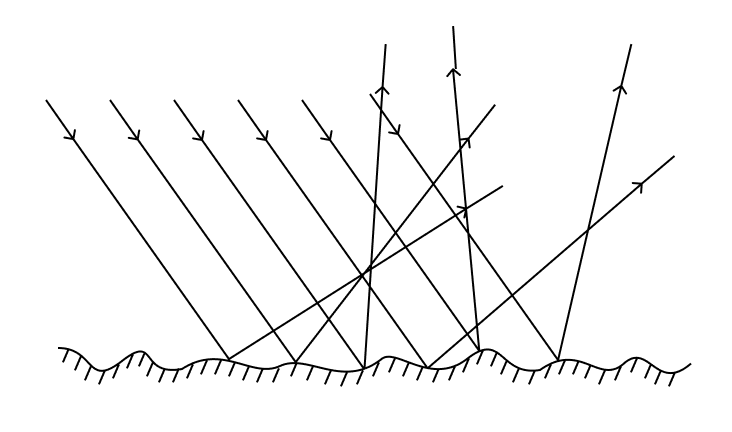
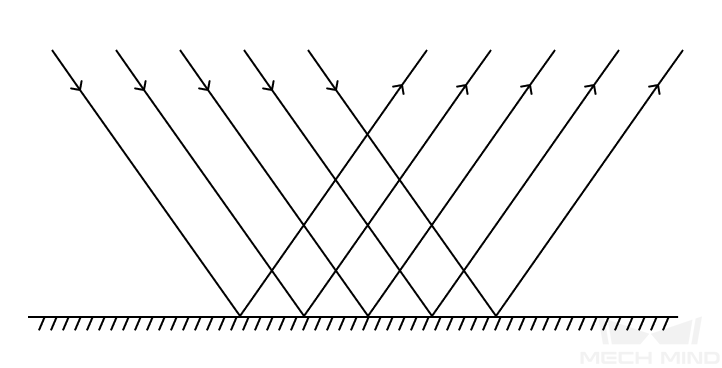
Diffuse Reflection and Specular Reflection
| Diffuse reflection | Specular reflection | |
|---|---|---|
Description |
|
|
Typical scenarios |
Rough, matte surfaces, such as cartons, unpolished metal objects, and opaque, plastic objects |
Smooth, glossy surfaces, such as polished metal objects |
The main influences of diffuse reflection and specular reflection on data acquisition are as follows:
-
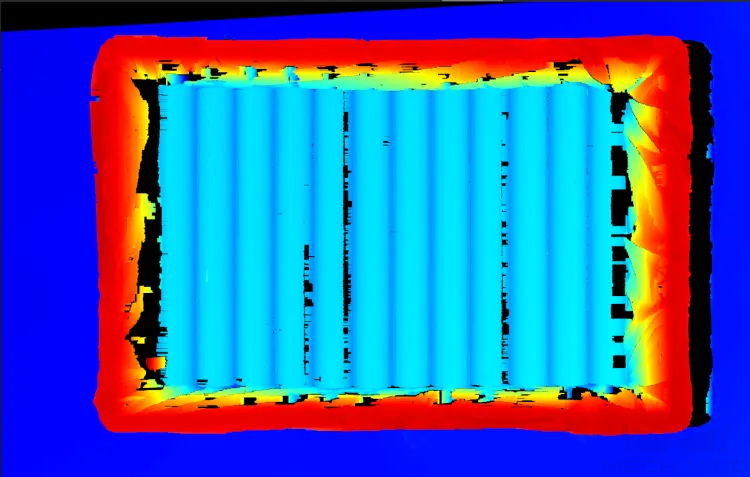
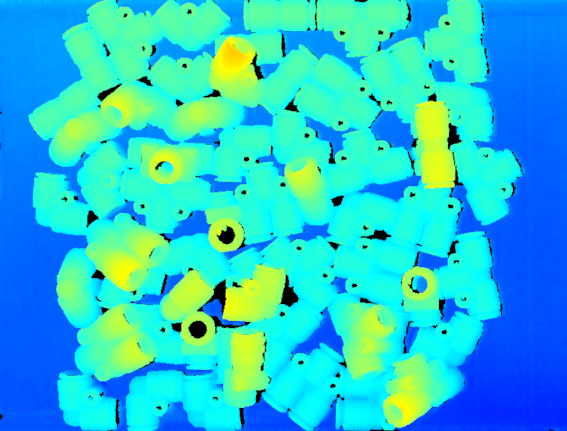
When predominantly diffuse reflection occurs on the surface of the target object, adjusting parameter settings appropriately can yield 2D images with proper brightness and rather complete and accurate depth data.
2D image Point cloud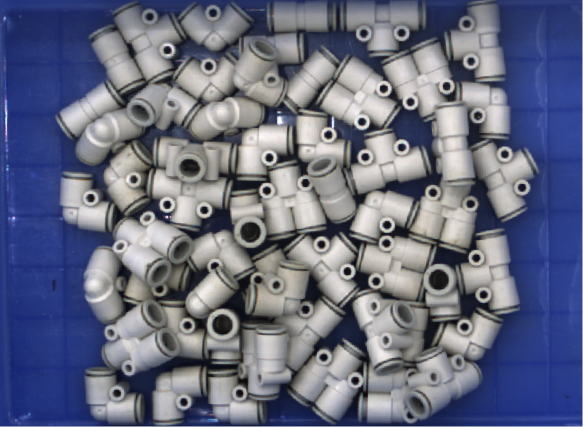 
-
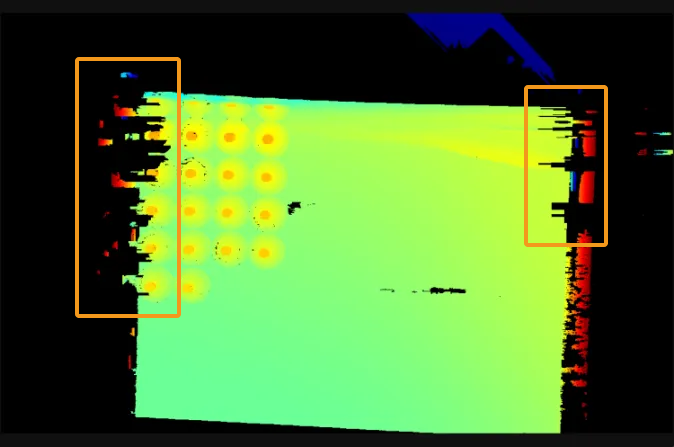
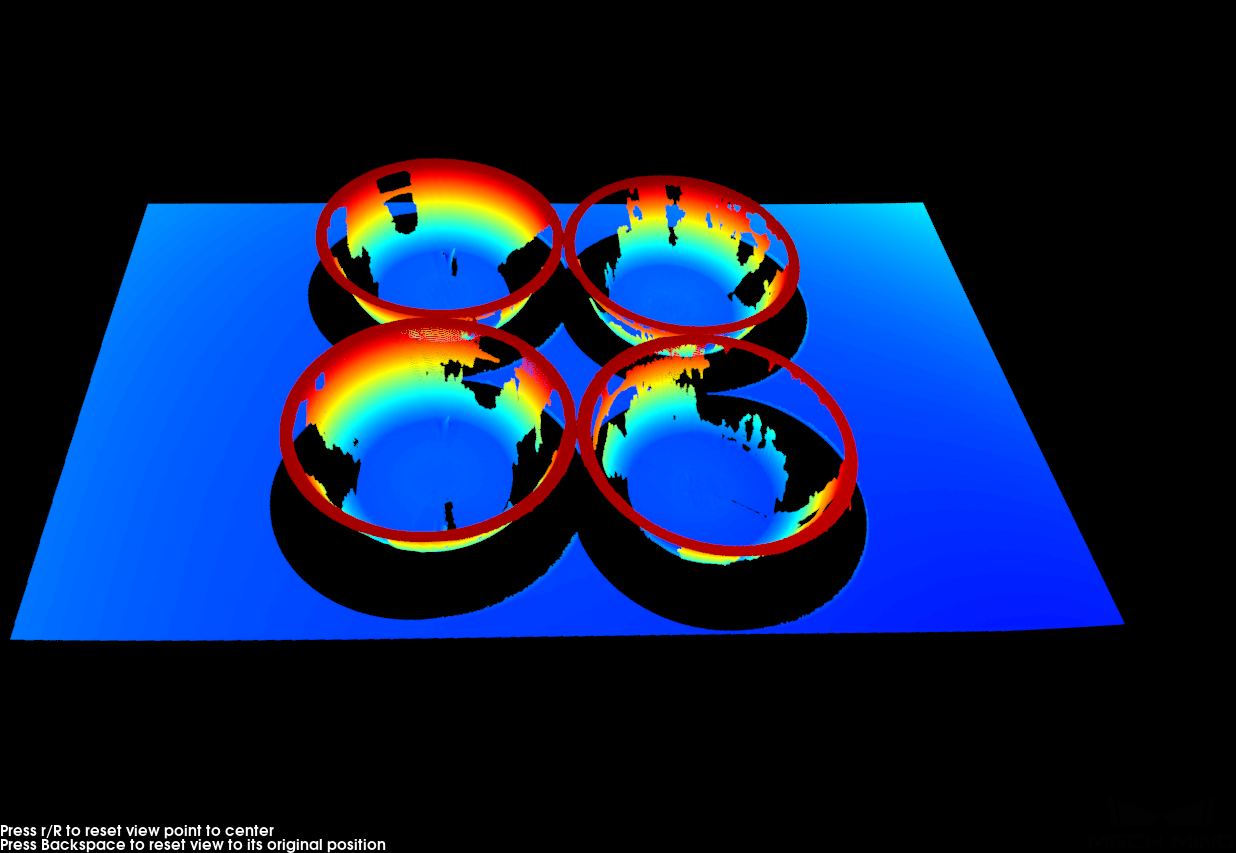
When specular reflection occurs on the surface of the target object, most of the light striking certain areas is reflected to the sensor, causing overexposure, while very little of the light striking other areas is reflected to the sensor, causing underexposure. Consequently, depth data may be lost. For details, refer to support:point-cloud-missing.adoc#specular-reflection.
Target object Point cloud 
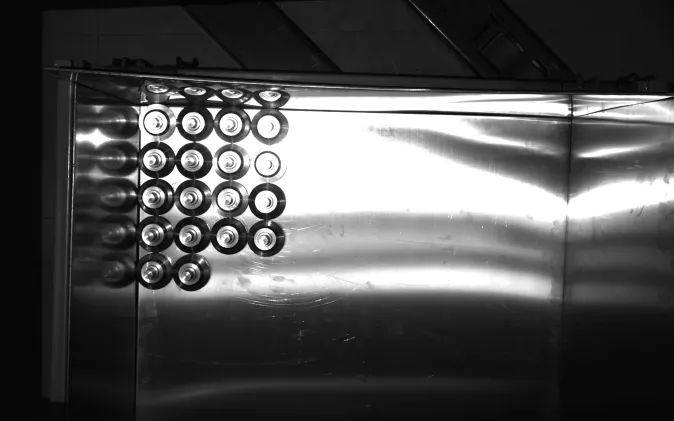
Interreflection
As illustrated by the image below, the phenomenon where the complex shape of the target object leads to multiple reflections of light among several surfaces is called interreflection.
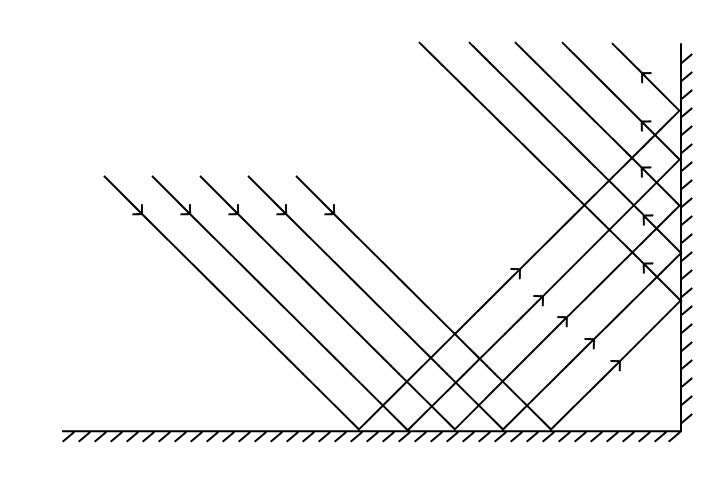
Interreflection can result in mistakes in the calculation of depth data. Consequently, data loss or inaccuracy may appear in the depth map and point cloud. For details, refer to support:point-cloud-missing.adoc#interreflection.
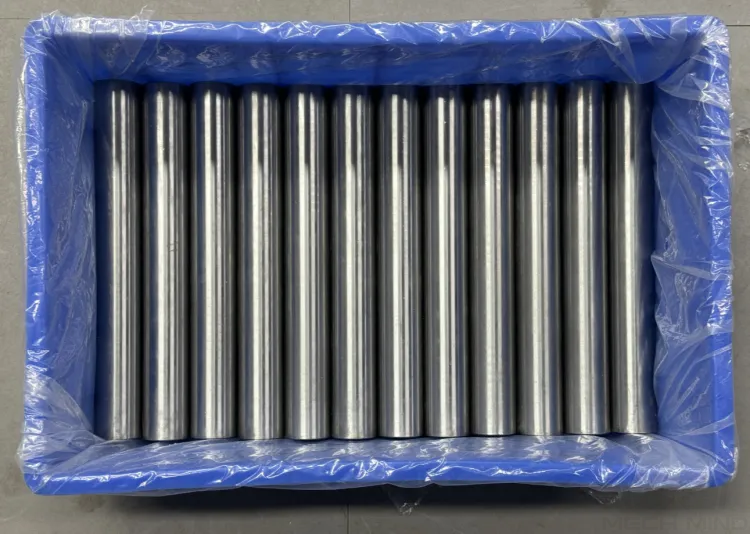
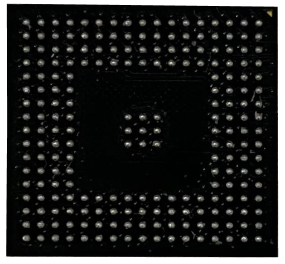
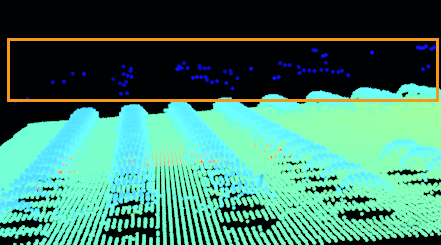
Typical scenarios of interreflection includes smooth, glossy bin walls, reflective closely arranged shafts, ball grid array (BGA), etc.
| Target object | Point cloud | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Interreflection between the metal bin wall and objects results in point cloud loss near the bin wall. |
|
|
Interreflection among the metal shafts results in point cloud loss on the surface of the shafts. |
|
|
Interreflection on the complex surface of the ball grid array (BGA) results in false data in the point cloud. |