Product Specification
A typical vision-guided robotic application usually consists of the robot, camera(s), industrial personal computer (IPC), and Mech-Mind’s software products.
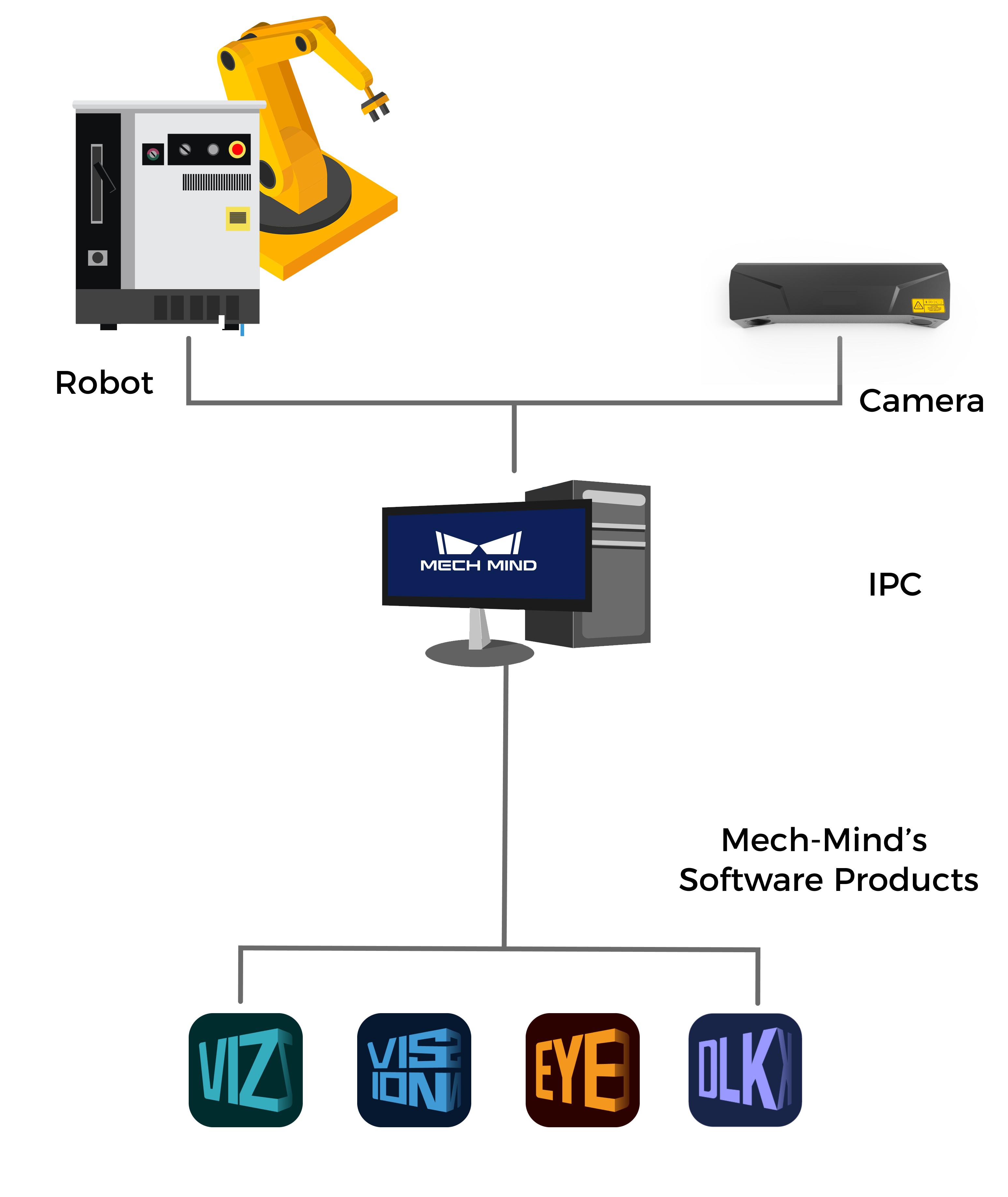
- Robot
-
A robot is a programmable multi-purpose handling device with some autonomy that can perform tasks such as movement, manipulation, or positioning. In the Mech-Mind Vision System, it performs intelligent tasks based on the results output by the vision system.
- Camera
-
It is the Mech-Eye industrial 3D camera developed by Mech-Mind, which is used to capture image and location information of the objects.
- IPC
-
It refers to the computer that provides the operating environment for the Mech-Mind’s software products.
- Mech-Mind’s software products
-
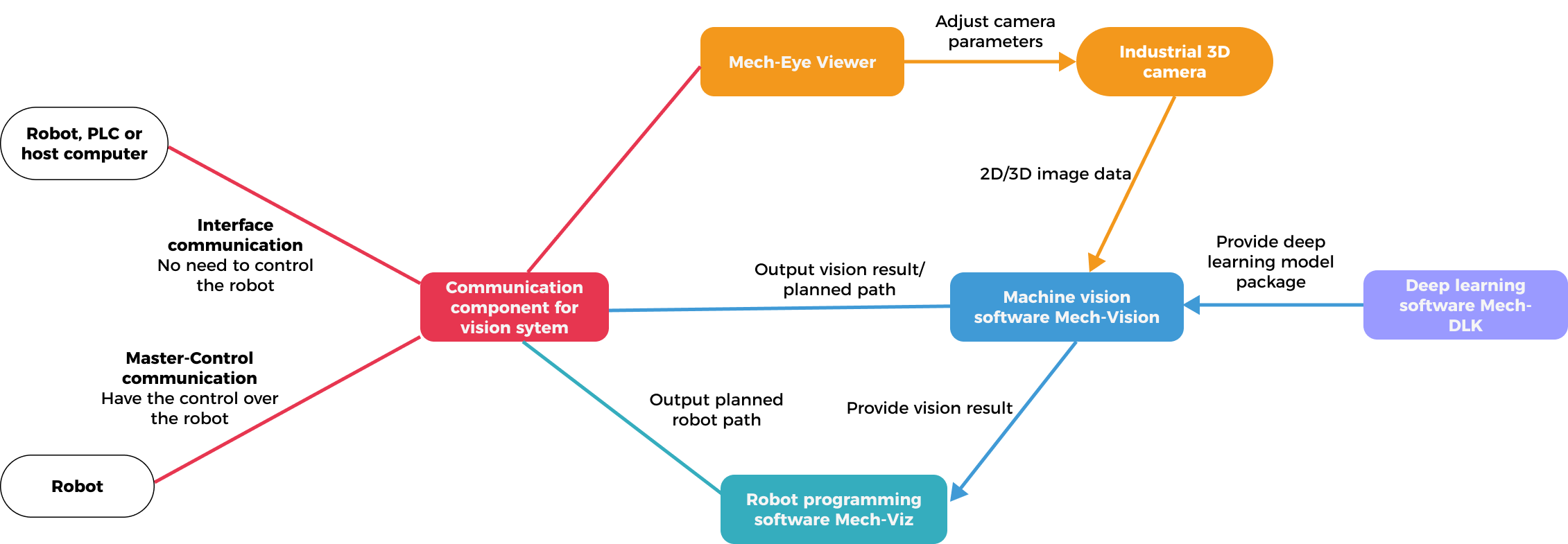
Mech-Mind’s software products perform vision processing based on image and location information captured by the camera, and output the location and orientation of the objects and the planned motion path of the robot, thus guiding the robots to complete intelligent tasks, such as picking, depalletizing and palletizing, gluing, sorting, etc. Different Mech-Mind’s software provides different functions.
-
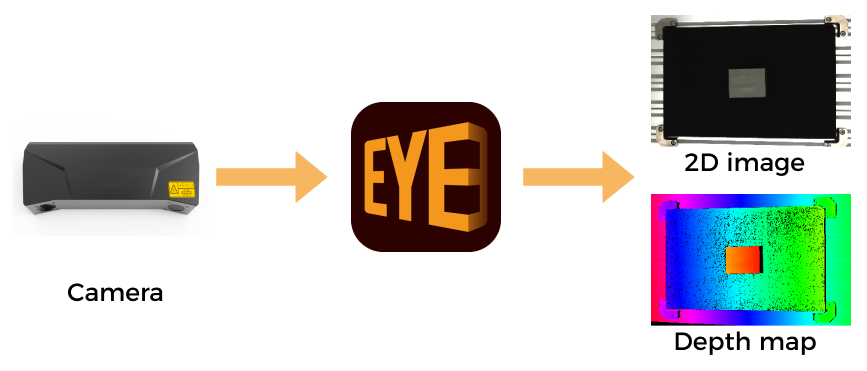
Mech-Eye Viewer
Mech-Eye Viewer allows users to adjust the parameters of the Mech-Eye industrial 3D camera according to the characteristics of the target object, and obtain high-quality 2D images, depth maps, and point clouds.
-
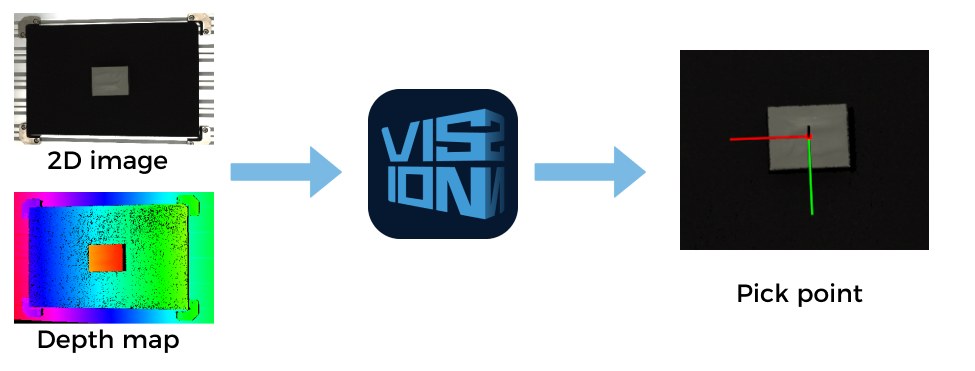
Mech-Vision
Mech-Vision is a state-of-the-art machine vision software. With its fully graphical interface, advanced machine vision applications such as piece picking, high-precision positioning, assembly, industrial inspection/measurement, and automatic path planning can be completed without writing codes.
Based on the image data captured on-site, this software performs a series of vision processing and outputs the vision results (such as the position and orientation of the target object). In addition, based on the vision results, this software can perform collision-free path planning for the robot, and output the planned picking path.
-
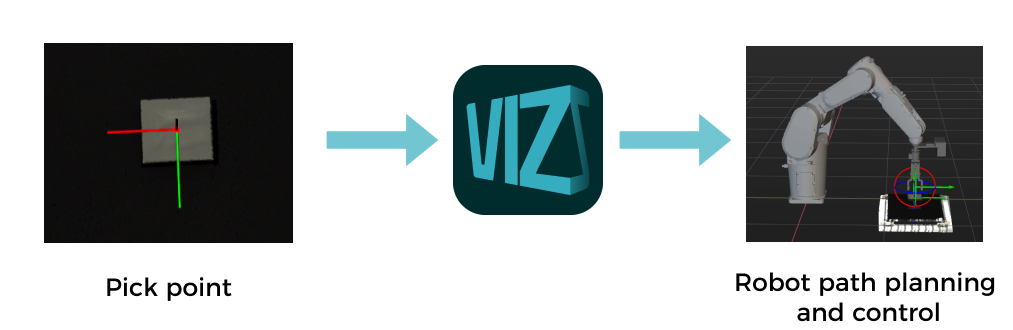
Mech-Viz
Mech-Viz is a robot path planning software. It uses the information provided by Mech-Vision, including the point clouds and target object positions, to intelligently plan the robot path for picking, carrying, palletizing and depalletizing, and other complex application scenarios.
This software allows users to build a workflow for the robot in a visualized manner and provides a 3D simulation function for validation before using the real robot. It has already been adapted to most major robot brands around the world.
-
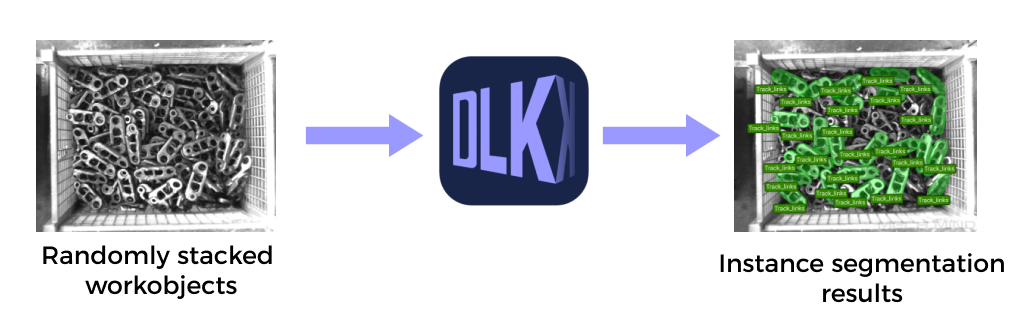
Mech-DLK
Mech-DLK is machine vision deep learning software. With a variety of built-in industry-leading deep learning algorithms, it can solve many problems that traditional machine vision cannot handle, such as highly difficult segmentation, positioning, and classification.
Through intuitive and simple UI interactions, even without programming or specialized deep learning knowledge, users can quickly implement model training and validation with this software.
-
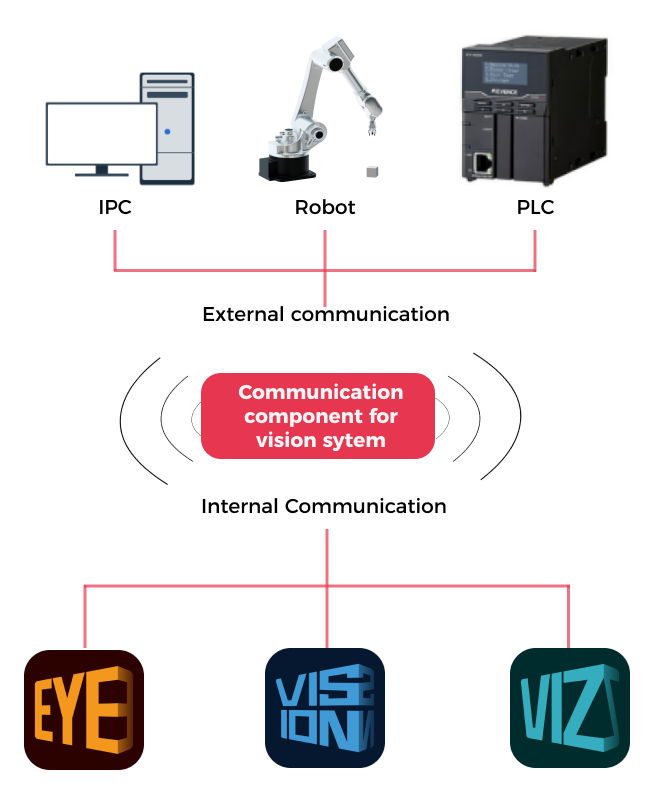
Communication Component for the Vision System
The communication component for the vision system (runs in the background) enables data exchange among software within the vision system and provides standardized and customized communication with external devices, such as robots, PLCs, and host computers, which makes vision-guided intelligent robotic applications possible.
The relationship between Mech-Mind’s software products is shown in the following figure.
-