PROFINET Interface Commands
Command 101: Start Mech-Vision Project
This command starts the Mech-Vision project that executes image capturing and performs vision recognition. This command is for applications that use only Mech-Vision but not Mech-Viz.
Parameters in Sent Command
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Command |
101 |
Vision_Proj_Num |
Mech-Vision project ID |
Req_Pose_Num |
Expected number of vision points |
Robot_Pose_Type |
Robot pose type |
Robot_Pose_JPS / Robot_Pose_TCP |
Robot joint positions/flange pose |
Mech-Vision project ID
You can view the Mech-Vision project ID in the Project List panel of Mech-Vision. The number before the project name is the Project ID.
Expected number of vision points
The expected number of vision points for Mech-Vision to send. The vision point contains the vision pose, corresponding point cloud, label, scaling, etc.
-
0: Receive all vision points in the recognition result from the Mech-Vision project. -
Integer greater than 0: The sender expects to receive the specified number of vision points in the recognition result from the Mech-Vision project.-
If the total number of vision points is less than the parameter value, all vision points in the recognition result will be sent.
-
If the total number of vision points is greater than or equal to the parameter value, the specified number of vision points will be sent.
-
Robot pose type and robot joint positions/flange pose
-
Robot pose type specifies the type of pose of the real robot to be input to Mech-Vision. The value range is 0–3.
-
The values of robot joint positions/flange pose depend on the value of robot pose type.
The following table explains the relationship between Robot_Pose_Type and Robot_Pose_JPS/Robot_Pose_TCP.
| Robot_Pose_Type | Robot_Pose_JPS | Robot_Pose_TCP | Description | Applicable scenario |
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 |
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 |
No need to input robot pose to Mech-Vision |
The project is in the eye-to-hand setup. If the “Path Planning” Step is used in the Mech-Vision project, the planned path starts at the Home position set in the path planning tool. |
1 |
Current joint positions of the robot |
Current flange pose of the robot |
Robot joint positions and flange pose must be input to Mech-Vision |
The project is in the eye-in-hand setup. Applicable to most robots (excluding truss robots). |
2 |
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 |
Current flange pose of the robot |
Robot flange pose must be input to Mech-Vision |
The project is in the eye-in-hand setup. The robot has no joint positions and only flange pose (such as truss robots). |
3 |
Joint positions of the start point of the planned path |
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 |
The joint positions of the path start point must be input to Mech-Vision. |
The project is in the eye-to-hand setup and the Mech-Vision project contains the “Path Planning” Step, whose start point needs to be set from the robot side. |
| Before assigning values to the Robot_Pose_JPS or Robot_Pose_TCP module, multiply the floating-point data of the joint positions or flange pose by 10000. |
Command 102: Get Vision Target(s)
This command is called after command 101 to obtain the vision points output by Mech-Vision and automatically transform the vision points into vision targets.
The transformation process, in which the poses of vision points are transformed into the robot TCP, is as follows:
-
Rotate the poses around their X axes by 180 degrees.
-
Determine whether the definition of the reference frame used by the robot model involves robot base height, and add a vertical offset accordingly.
| This command can only fetch at most 20 vision targets at a time. Therefore, to obtain more than 20 vision targets, please repeat the calling of this command. |
Parameters in Sent Command
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Command |
102 |
Vision_Proj_Num |
Mech-Vision project ID |
Mech-Vision project ID
You can view the Mech-Vision project ID in the Project List panel of Mech-Vision. The number before the project name is the Project ID.
Parameters in Returned Data
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Status Code |
Status code |
Send_Pose_Num |
Number of vision targets |
Send_Pose_Type |
Pose type |
Target_Pose |
Obtained robot TCPs |
Target_Label |
Obtained labels |
Status code
If there is no error, status code 1100 will be returned. Otherwise, the corresponding error code will be returned.
After this command is called, if the vision result from Mech-Vision is not returned within 10 seconds, the error code for timeout will be returned.
Number of vision targets
The number of received vision targets.
Pose type
This parameter indicates that the target object pose in the vision point output by Mech-Vision is converted to robot TCP.
The value of this parameter is 2 by default, which stands for TCP.
Obtained robot TCPs
Each TCP consists of the Cartesian coordinates (XYZ) and Euler angles (ABC).
Obtained labels
The integer labels corresponding to the obtained poses. If the labels in the Mech-Vision project are strings, please use the “Label Mapping” Step before the “Procedure Out” Step to map the labels to integers. If there are no labels in the project, the value of this parameter is 0 by default.
| For details on sending and receiving the poses, please refer to Communication Control Workflow. The Data_Ready, Data_Acknowledge, and Command_Complete signals are used for process control. |
Command 103: Switch Mech-Vision Recipe
This function specifies the parameter recipe to be used in the Mech-Vision project.
In Mech-Vision, you can change the values of Step parameters by switching the parameter recipe in use.
The parameters that can be altered by switching parameter recipes usually include the point cloud matching model, image matching template, ROI, and confidence threshold.
| This command must be called before command 101 is called. |
Parameters in Sent Command
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Command |
103 |
Vision_Proj_Num |
Mech-Vision project ID |
Vision_Recipe_Num |
Mech-Vision recipe ID |
Mech-Vision project ID
You can view the Mech-Vision project ID in the Project List panel of Mech-Vision. The number before the project name is the Project ID.
Mech-Vision recipe ID
The ID of the parameter recipe in the Mech-Vision project. The ID is a positive integer in the range of 1 to 99. To view the parameter recipe ID, in the lower right of Mech-Vision, click .
Command 105: Get Result of Step “Path Planning” in Mech-Vision
After calling command 101, call this command to obtain the collision-free picking path planned by the “Path Planning” Step in the Mech-Vision project.
When using this command, set the Port Type parameter of the “Procedure Out” Step in the Mech-Vision project to “Predefined (robot path)”.
| Before calling command 105, please set expected number of vision points of command 101 to 0 to reduce the times of calling command 105. If expected number of vision points of command 101 is set to 1, then every time command 105 is called, only 1 waypoint is returned, and command 105 must be called multiple times to obtain all the waypoints. |
Parameters in Sent Command
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Command |
105 |
Vision_Proj_Num |
Mech-Vision project ID |
Req_Pose_Type |
Waypoint pose type |
Mech-Vision project ID
You can view the Mech-Vision project ID in the Project List panel of Mech-Vision. The number before the project name is the Project ID.
Waypoint pose type
This parameter specifies the type of waypoint poses returned by the “Path Planning” Step.
-
1: The waypoint poses are returned in the form of joint positions. -
2: The waypoint poses are returned in the form of TCP.
Parameters in Returned Data
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Status Code |
Status code |
Send_Pose_Num |
Number of waypoints |
Send_Pose_Type |
Pose type |
Visual_Point_Index |
Position of “Vision Move” |
Target_Pose |
All waypoint poses returned |
Target_Label |
All waypoint labels returned |
Target_Speed |
Velocities of all waypoints returned |
Status code
If there is no error, status code 1103 will be returned. Otherwise, the corresponding error code will be returned.
Number of waypoints
The number of waypoints returned. The value range is 0 to 20. If the planned path contains more than 20 waypoints, please repeat the calling of this command.
Pose type
The value of this parameter is the same as that of “Req_Pose_Type” in the sent command.
-
1: Joint positions -
2: TCP
Position of “Vision Move”
The position of the “Vision Move” waypoint in the entire planned path in the Path Planning tool.
For example, if the planned path consists of waypoints “Fixed-Point Move_1”, “Fixed-Point Move_2”, “Vision Move”, and “Fixed-Point Move_3” sequentially, the position of “Vision Move” is 3.
If the path does not contain any “Vision Move”, the value of this parameter is 0.
All waypoint poses returned
The Cartesian coordinates (XYZ in mm) and Euler angles (ABC in degrees), or joint positions (in degrees). The type is determined by the “waypoint pose type” parameter in the sent command.
All waypoint labels returned
The integer labels corresponding to the obtained poses. If the labels in the Mech-Vision project are strings, please use the “Label Mapping” Step before the “Procedure Out” Step to map the labels to integers. If there are no labels in the project, the value of this parameter is 0.
Velocities of all waypoints returned
The velocities set in the Path Planning tool.
Command 201: Start Mech-Viz Project
This function is for applications that use both Mech-Vision and Mech-Viz. This command runs the Mech-Viz project (which triggers the corresponding Mech-Vision project to run), and Mech-Viz will plan a robot motion path based on the vision result received from Mech-Vision.
| In Mech-Viz, right-click the project name in the Resources panel and select Autoload Project. |
Parameters in Sent Command
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Command |
201 |
Robot_Pose_Type |
Robot pose type |
Robot_Pose_JPS / Robot_Pose_TCP |
Robot joint positions/flange pose |
Robot pose type and robot joint positions/flange pose
-
Robot pose type specifies the type of pose of the real robot to be input to Mech-Viz. The value range is 0 to 2.
-
The values of robot joint positions/flange pose depend on the value of robot pose type.
The following table explains the relationship between Robot_Pose_Type and Robot_Pose_JPS/Robot_Pose_TCP.
| Robot_Pose_Type | Robot_Pose_JPS | Robot_Pose_TCP | Description | Applicable scenario |
|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 |
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 |
No need to input the robot pose to Mech-Viz. The simulated robot in Mech-Viz moves from the initial pose JPs = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] to the first waypoint. |
The project is in the eye-to-hand setup. This setting is not recommended. |
1 |
Current joint positions of the robot |
Current flange pose of the robot |
Robot joint positions and flange pose must be input to Mech-Viz. The simulated robot in Mech-Viz moves from the input JPs to the first waypoint. |
This setting is recommended for projects in the eye-in-hand setup. |
2 |
Specific joint positions of the robot |
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 |
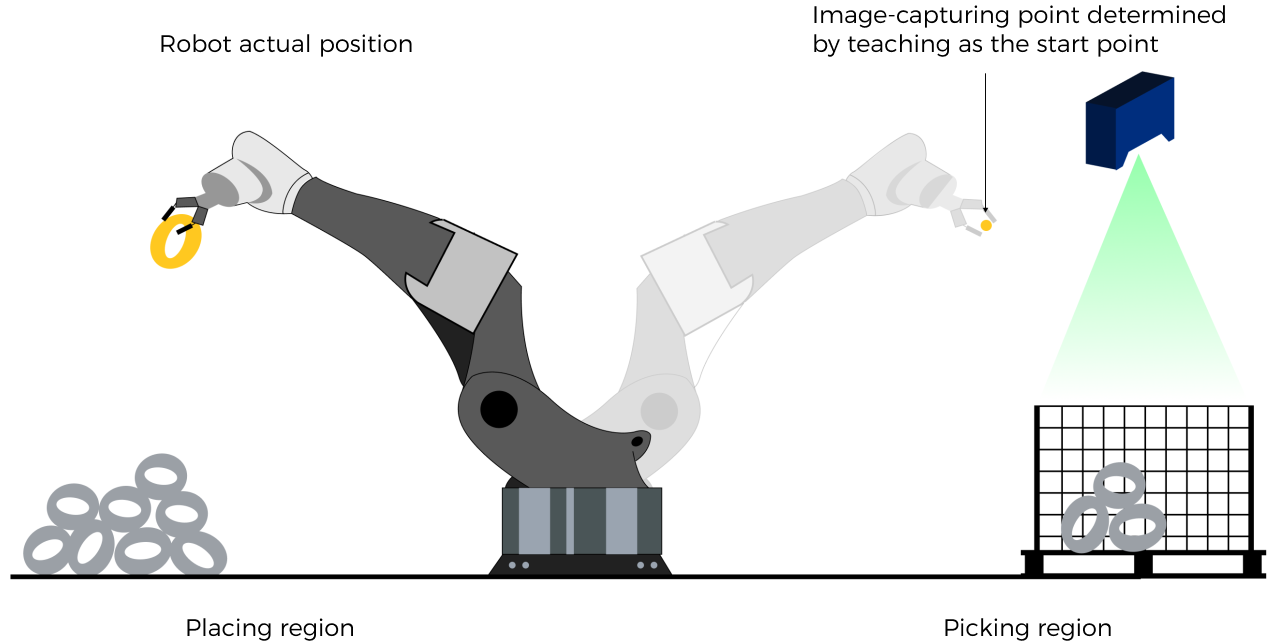
The robot joint positions of a point determined by teaching must be input to Mech-Viz. The input joint positions are used to trigger Mech-Viz to plan the next path in advance while the robot is not in the camera capture region, as shown below. The simulated robot in Mech-Viz moves from the input joint positions to the first waypoint. |
This setting is recommended for projects in the eye-to-hand setup. |
The reason for setting Robot_Pose_Type to 2 when the project is in the eye-to-hand setup:
In the eye-to-hand setup, the camera can perform image capturing for the next round of path planning before the robot returns to the camera capture region and picking region, shortening the cycle time.
If Robot_Pose_Type is set to 1, the robot’s current pose is sent to the simulated robot in Mech-Viz, which may cause inconsistent paths of the simulated robot and the real robot. Therefore, the path of the real robot may contain unpredicted collisions, leading to safety hazards.
The simulated robot in Mech-Viz will move from the current pose to the waypoint set in the first move-type Step, while the real robot might move to another point first, and then move to that waypoint.
In conclusion, Robot_Pose_Type should be set to 2 for projects in the eye-to-hand setup.
Command 202: Stop Mech-Viz Project
This command stops the execution of Mech-Viz. This command is only needed if the Mech-Viz project falls into an infinite loop or cannot be stopped normally.
Command 203: Select Mech-Viz Branch
This command selects along which branch the Mech-Viz project should proceed. Such branching is achieved by adding the “Branch by Msg” Step(s) to the Mech-Viz project.
Before calling this command, please call command 201 first.
When the next Step to execute is a “Branch by Msg” Step, the Mech-Viz project will wait for this command to specify the exit port to take.
Parameters in Sent Command
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Command |
203 |
Viz_Task_ID |
Step ID of the “Branch by Msg” Step |
Viz_Task_Value |
Exit port number |
Step ID of the “Branch by Msg” Step
Step ID of the “Branch by Msg” Step. The value should be a positive integer. The Step ID is displayed in the parameters of the Step.
Exit port number
The number of the exit port to take. The Mech-Viz project will proceed along the workflow connected to this exit port. The value is a positive integer in the range of 1 to 99.
| This exit port number should be the output port number displayed in the Step plus 1. For example, if the output port number of the branch is 0, then the exit port number is 1. |
Command 204: Set Move Index
This command sets the value for the Current Index parameter of Mech-Viz Steps. Steps that have this parameter include “Move by List”, “Move by Grid”, “Custom Pallet Pattern”, and “Predefined Pallet Pattern”.
Before calling this command, please call command 201 first.
Parameters in Sent Command
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Command |
204 |
Viz_Task_ID |
Step ID |
Viz_Task_Value |
Current Index value |
Step ID
The Step ID of the Step whose Current Index value needs to be set.
The value of this parameter should be a positive integer. The Step ID is displayed in the parameters of the Step.
Current Index value
The Current Index value that should be set the next time this Step is executed.
When this procedure is sent, the current index value in Mech-Viz will become the parameter value minus 1.
When the Mech-Viz project runs to the Step specified by this command, the Current Index value in Mech-Viz will be increased by 1 to become the parameter’s value.
Command 205: Get Planned Path
This command obtains the planned path from Mech-Viz. It should be used after calling command 201.
This command can only fetch at most 20 waypoints at a time. Therefore, to obtain more than 20 waypoints, please repeat the calling of this command.
|
If the waypoint of a move-type Step should not be sent to the robot, please clear the “Send Waypoint” option in the parameters of this Step. |
Parameters in Sent Command
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Command |
205 |
Req_Pose_Type |
Waypoint pose type |
Waypoint pose type
This parameter specifies the type of waypoint pose returned by Mech-Viz.
-
1: The waypoint poses are returned in the form of joint positions (JPs). -
2: The waypoint poses are returned in the form of tool center point (TCP).
Parameters in Returned Data
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Status Code |
Status code |
Send_Pose_Num |
Number of waypoints |
Send_Pose_Type |
Pose type |
Visual_Point_Index |
Position of “Vision Move” |
Target_Pose |
All waypoint poses returned |
Target_Label |
All waypoint labels returned |
Target_Speed |
Velocities of all waypoints returned |
Status code
If there is no error, status code 2100 will be returned. Otherwise, the corresponding error code will be returned.
| When calling this command, Mech-Viz will wait for the result from Mech-Viz and then send it to the robot. The default wait time is 10 seconds. If a timeout occurs, a timeout error code will be returned to the robot. |
Number of waypoints
The number of waypoints returned. The value range is 0 to 20. This command can only fetch at most 20 waypoints at a time. Therefore, to obtain more than 20 waypoints, please repeat the calling of this command.
Pose type
The value of this parameter is the same as that of “Req_Pose_Type” in the sent command.
-
1: Joint positions -
2: TCP
Position of “Vision Move”
The position of the “Vision Move” waypoint in the entire planned path.
For example, if the planned path consists of waypoints “Fixed-Point Move_1”, “Fixed-Point Move_2”, “Vision Move”, and “Fixed-Point Move_3” sequentially, the position of “Vision Move” is 3.
If the path does not contain any “Vision Move”, the value of this parameter is 0.
All waypoint poses returned
The Cartesian coordinates (XYZ in mm) and Euler angles (ABC in degrees), or joint positions (in degrees). The type is determined by the “waypoint pose type” parameter in the sent command.
All waypoint labels returned
The integer labels corresponding to the obtained poses. If the labels in the Mech-Vision project are strings, please map them to integers by using the “Label Mapping” Step before output. If there are no labels in the project, the value of this parameter is 0.
Velocities of all waypoints returned
The non-zero values in front of the percentage sign in the “Velocity” parameter values of move-type Steps.
| For details on sending and receiving the poses, please refer to Communication Control Workflow. The Data_Ready, Data_Acknowledge, and Command_Complete signals are used for process control. |
Command 206: Get DO List
This function gets the planned DO signal list. The DO signal list is used to control multiple grippers or multiple suction cup sections.
Before calling this command, please call command 205 to obtain the planned motion path from Mech-Viz.
Please deploy the Mech-Viz project based on the example project and set the corresponding suction cup configuration file. The example project is stored in the Mech-Mind Software Suite installation directory (in the Mech-Center\tool\viz_project\suction_zone folder).
In the parameters of the “Set DO List” Step in Mech-Viz:
-
Select the “Standard Interface” checkbox under “Receiver”.
-
Select the “Get DO List from ‘Vision Move’” checkbox.
-
Select a “Vision Move” Step that needs the DO signal list in the “Select ‘Vision Move’” drop-down list.
Parameters in Returned Data
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Status code |
Status code |
DO List |
DO signals returned by Mech-Viz |
Status code
If there is no error, status code 2102 will be returned. Otherwise, the corresponding error code will be returned.
DO signals returned by Mech-Viz
DO_LIST consists of eight bytes (0 to 7). Each byte consists of eight bits (0 to 7). As such, DO_LIST contains 0 to 63 bits, which correspond to 0 to 63 DO signals. For example, the 0 bit in the DO list corresponds to the 0 DO signal. If the 0 bit indicates True, the 0 DO signal is valid. If the 0 bit indicates False, the 0 DO signal is invalid.
Value range: 0–999.
Placeholder value: -1.
Command 501: Input Object Dimensions to Mech-Vision
This function is used for dynamically inputting object dimensions into the Mech-Vision project. Please check the actual object dimensions before running the Mech-Vision project.
The Mech-Vision project should contain the “Read Object Dimensions” Step, and the Read Sizes from Properties parameter of this Step should be checked.
Parameters in Sent Command
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Command |
501 |
Vision_Proj_Num |
Mech-Vision project ID |
Ext_Input_Data |
Object dimensions |
Mech-Vision project ID
You can view the Mech-Vision project ID in the Project List panel of Mech-Vision. The number before the project name is the Project ID.
Object dimensions
The object dimensions (length, width, height) to be inputted to the Mech-Vision project. The dimensions will be read into the “Read Object Dimensions” Step.
Unit: mm
Command 901: Get Software Status
This function is designed for obtaining the execution status of Mech-Vision, Mech-Viz, and Mech-Center.
Currently, this command is capable of checking whether Mech-Vision is ready to run projects.