Measure Surface Flatness
Workflow
The process of configuring this Step is shown below.
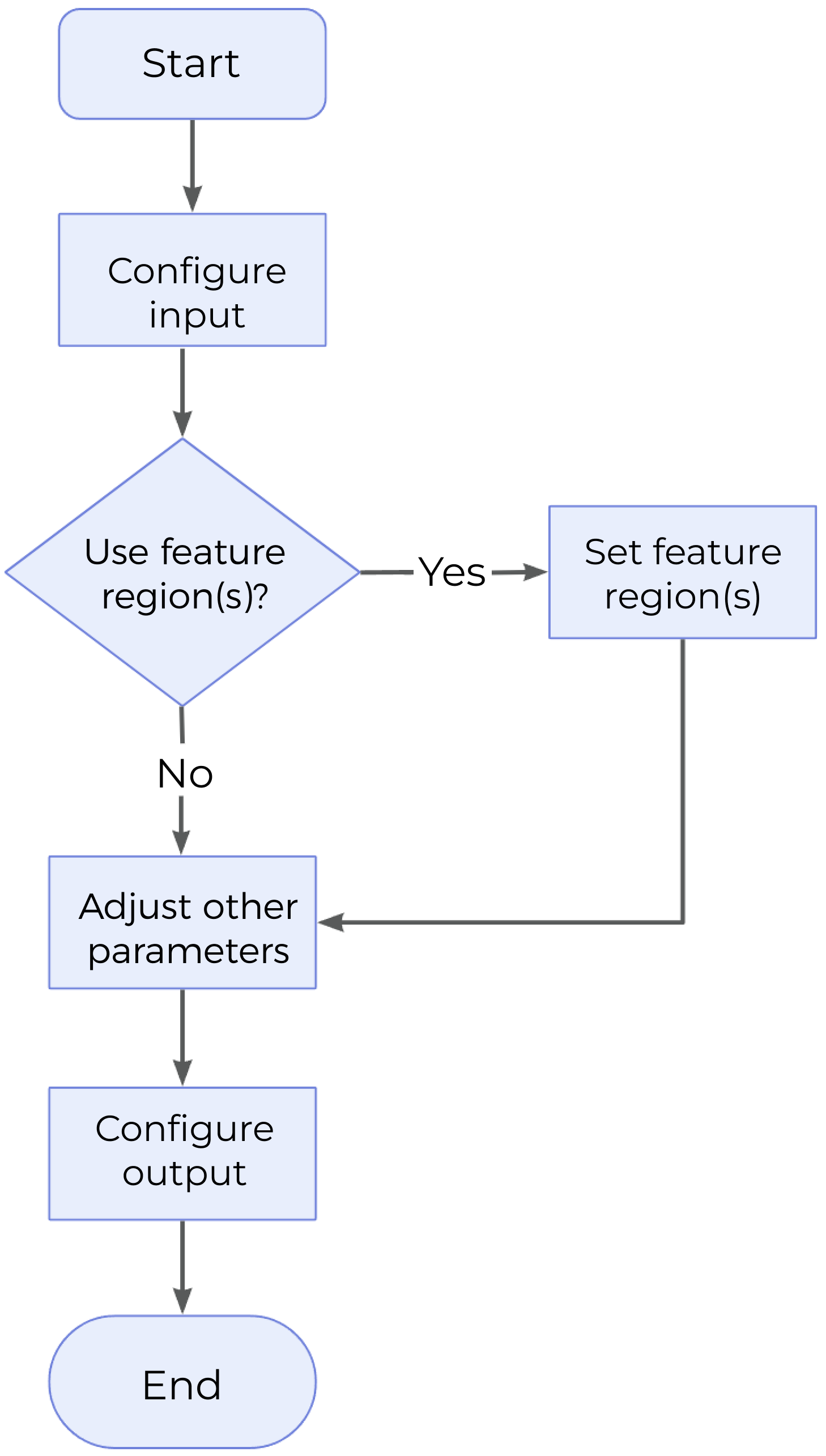
-
Configure the input. Connect the ports manually or select the input(s) under Input in the parameter configuration panel.
-
Determine whether to use feature region.
-
Set other parameters.
-
Select the desired output(s) under Output. For an expandable output item, click ▶ and configure the Min and Max values of the acceptable range.
Parameter Description
| Parameter | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Use Feature Region |
Feature region defines the processing area to facilitate fitting the optimal plane. Once this parameter is selected, only data within or outside the feature region will be processed. |
||
Feature Region Mode |
Once “Use Feature Region” is selected, this parameter is used to set the mode of the feature region, i.e., to choose whether to use the data within the feature region to fit the plane and calculate the flatness, or to use the data outside the feature region to fit the plane and calculate the flatness. |
||
Feature Region |
For more information on how to set and adjust the feature region, see Feature Region. |
||
Global Flatness Mode |
This parameter determines which points on the surface are used to calculate global flatness.
|
||
Data Filtering Mode |
This parameter is used to select the data filtering method. Filter the data points according to the actual Z values before fitting the plane and calculating flatness.
|
Output Description
Select the output item(s) to add the output port(s) to the Step, and the corresponding data will be output after the Step is run. You can select the output according to the actual measurement requirements.
|
If you select an expandable output item, you must expand it by clicking ▶, and then set the Min and Max values to determine the acceptable range. If the output value falls within the acceptable range, the measurement item is judged as passing (OK), or else it is judged as failing (NG). |
| Output Item | Description |
|---|---|
Global Min |
The minimum distance from the data points involved in global plane fitting to the fitted global plane.
|
Global Max |
The maximum distance from the data points involved in global plane fitting to the fitted global plane.
|
Global Flatness |
The flatness of the globally fitted plane, which is the difference between Global Max and Global Min. |
Global Min Point |
The point representing Global Min. |
Global Max Point |
The point representing Global Max. |
Global Average Point |
The average point of all data points involved in global plane fitting. |
Global Median Point |
The median point of all data points involved in global plane fitting. |
Global Plane |
The fitted global plane. |
Local Min |
The minimum distance from the data points involved in local plane fitting to the fitted local plane.
|
Local Max |
The maximum distance from the data points involved in local plane fitting to the locally fitted plane.
|
Local Flatness |
The flatness of each fitted local plane, which is the difference between Local Max and Local Min. |
Local Min Points |
The points representing Local Min. |
Local Max Points |
The points representing Local Max. |
Local Average Points |
The average point of data points involved in the fitting of each local plane. |
Local Median Points |
The median point of data points involved in the fitting of each local plane. |
Local Planes |
Fitted local planes. |
Troubleshooting
|
CV-W3103
Error: The value of “Low Percentile” should not be greater than that of “High Percentile,” or either of them is not within [0, 1].
Possible cause: The value of “Low Percentile” is greater than that of “High Percentile,” or either of them is not within 0–100%.
Solution: Reset the percentile to ensure that the percentile is within 0–100% and that the value of “Low Percentile” is lower than that of “High Percentile.”
CV-W3104
Error: The selected data filtering mode is invalid.
Solution: Select a valid data filtering mode from the drop-down list.
CV-W3105
Error: Failed to fit the global plane.
Possible causes:
-
The number of points in the feature region is less than 3 and Global Flatness Mode is set to Single average point.
-
The number of points in the feature region is less than 3 and Global Flatness Mode is set to All points.
Solution:
-
When “Global Flatness Mode” is set to “Single average point”, adjust or add feature regions to ensure that the number of points in the feature region is equal to or greater than 3.
-
When “Global Flatness Mode” is set to “All points”, adjust or add feature regions to ensure that the number of points in the feature region is equal to or greater than 3.