Check Whether the Robot Absolute Accuracy Has Declined
This article guides you through quickly checking whether the robot absolute accuracy has declined.
Mech-Vision a tool for checking the robot absolute accuracy, facilitating the quick troubleshooting of robot absolute accuracy issues.
Select the in the menu bar, and then select in the Error Analysis window.
Check for Robot Zero Position Loss
Check method:
After restoring the robot to its standard zero position, check whether the graduation lines on each axis are aligned.
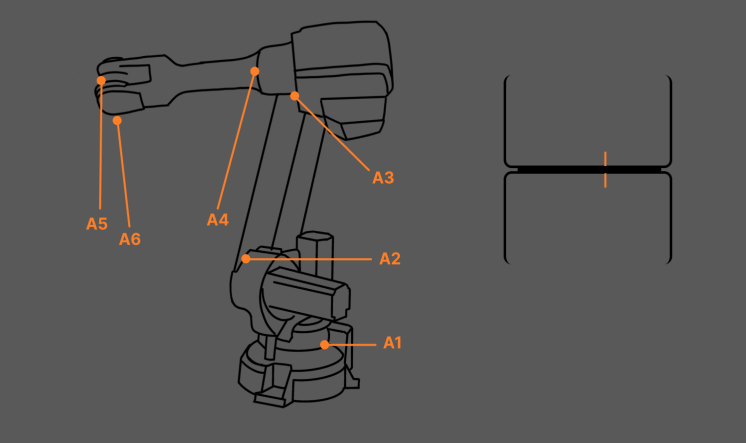
Check criteria:
-
When the zero-position graduation lines do not have significant deviations, you can further check the consistency between the value in the teach pendant and the factory value.
-
If the graduation lines are significantly misaligned, it indicates a loss of robot zero positions, and re-calibration is required.
Calibrate zero positions:
Refer to the robot’s user manual for instructions on calibrating zero positions or contact the robot manufacturer for support.
Check Whether Movement Distance Error Becomes Larger
Use the teach pendant to control the robot to move a certain distance along a fixed direction (e.g., X or Y-direction) in the workspace. After the movement, compare the theoretical distance with the actual distance the robot moved and measure the difference.
Check method:
-
Select two points on the X/Y/Z axis and the diagonals respectively. Record the robot’s movement distance (D) on the teach pendant and measure the actual distance (D') with a ruler. Then compare the differences.
-
It is recommended to measure in all three directions (XYZ) and at different positions.
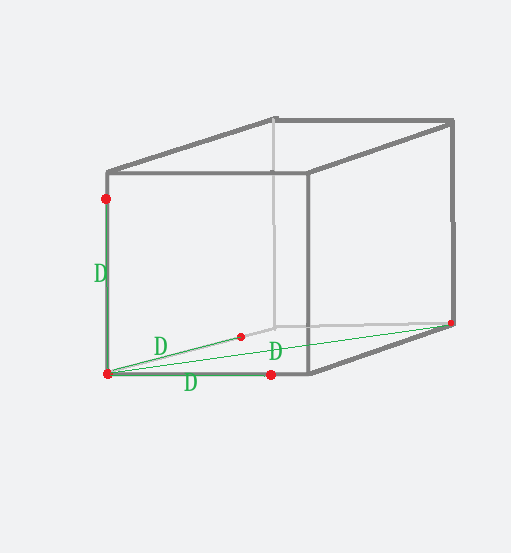
Check criteria:
The smaller the overall difference, the smaller the error in movement distance, and the higher the robot absolute accuracy.
Compare the movement distance error with the error recorded in the application deployment phase.
-
If the error does not increase significantly, the robot absolute accuracy can be used. Continue troubleshooting according to the Approach to Troubleshooting Picking Errors.
-
If the error increases, the robot absolute accuracy declines. The robot accuracy error is one of the main sources of error leading to the picking inaccuracy issue. Contact the robot manufacturer to calibrate the robot absolute accuracy.
Confirm Robot TCP Accuracy
Check method:
Use the error analysis tool to evaluate the TCP accuracy.
Check criteria:
-
If the tip mounted to the robot flange coincides with another tip, the TCP accuracy is good.
-
If there is a large deviation, the TCP accuracy is poor. Contact the robot manufacturer to calibrate the TCP.