Introduction to 3D Vision-Guided Robotics Solution
What Is the 3D Vision-Guided Robotics Solution?
The 3D vision-guided robotics solution integrates Mech-Mind’s sensing, perception, robot programming/planning technologies into a comprehensive solution, aiming to address the challenges that robots face in complex, unknown, or dynamic environments.
This solution offers a wide range of applications such as 3D vision guided workpiece loading, depalletizing and palletizing, locating and assembly, and piece picking. It is widely used in various industries such as automotive, logistics, supermarkets, and heavy industry.
By integrating the Mech-Mind Vision System into the robot system, a complete vision-guided robotic application can be built to guide the robot to perform intelligent tasks.
Components of a Typical 3D Vision-Guided Robotic Application
A typical vision-guided robotic application usually consists of the robot, camera(s), industrial personal computer (IPC), and Mech-Mind’s software products.
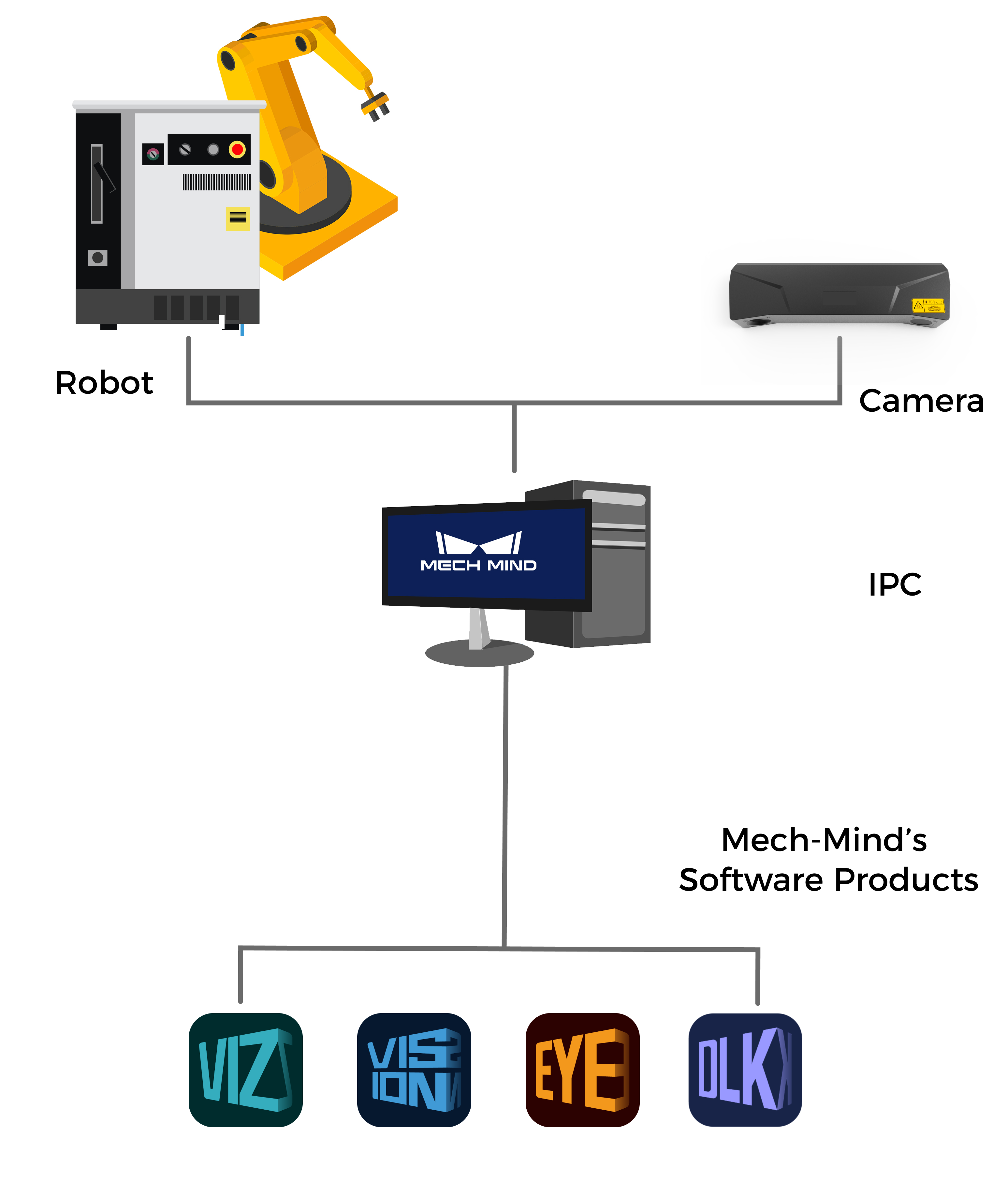
- Robot
-
A robot is a programmable multi-purpose handling device with some autonomy that can perform tasks such as movement, manipulation, or positioning. In the Mech-Mind Vision System, it performs intelligent tasks based on the results output by the vision system.
-
A robot cell usually consists of a robot body, a controller, and a teach pendant.
-
In industrial applications that require a high level of automation, a programmable logic controller (PLC) can be used to control the motion and operation of the robot. If a higher level of control and monitoring is required, a host computer can also be used to perform more complex programming and control of the robot, such as path planning, task planning, and motion control. The Mech-Mind Vision System supports collaboration with the PLC and host computer.
-
In this article, “robot side” is used as a generic term for the robot, PLC, or host computer.
-
- Camera
-
It is the Mech-Eye industrial 3D camera developed by Mech-Mind, which is used to capture image and location information of the objects.
- IPC
-
It refers to the computer that provides the operating environment for the Mech-Mind’s software products.
- Mech-Mind’s software products
-
Mech-Mind’s software products perform vision processing based on image and location information captured by the camera, and output the location and orientation of the objects and the planned motion path of the robot, thus guiding the robots to complete intelligent tasks, such as picking, depalletizing and palletizing, gluing, sorting, etc. The functions provided by different Mech-Mind software vary. For details, refer to Introduction to Mech-Mind’s Software Products.
-
In this article, the cameras and IPC provided by Mech-Mind, and Mech-Mind’s software products constitute the Mech-Mind Vision System.
-
Introduction to Mech-Mind’s Software Products
The Mech-Mind Vision System mainly involves the following software:
-
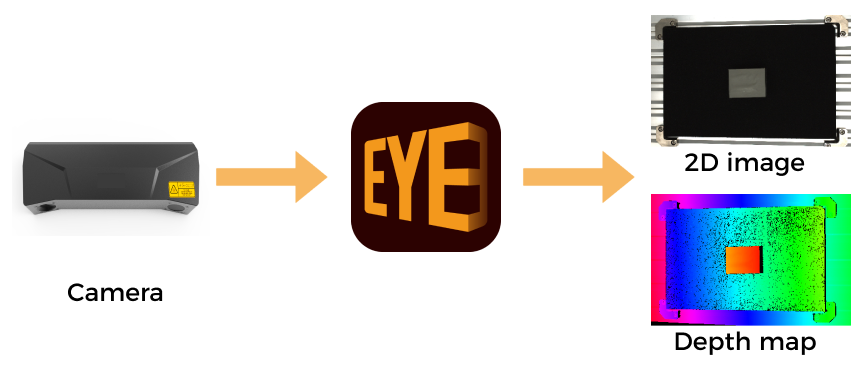
Mech-Eye Viewer
Mech-Eye Viewer allows users to adjust the parameters of the Mech-Eye industrial 3D camera according to the characteristics of the target object, and obtain high-quality 2D images, depth maps, and point clouds.
-
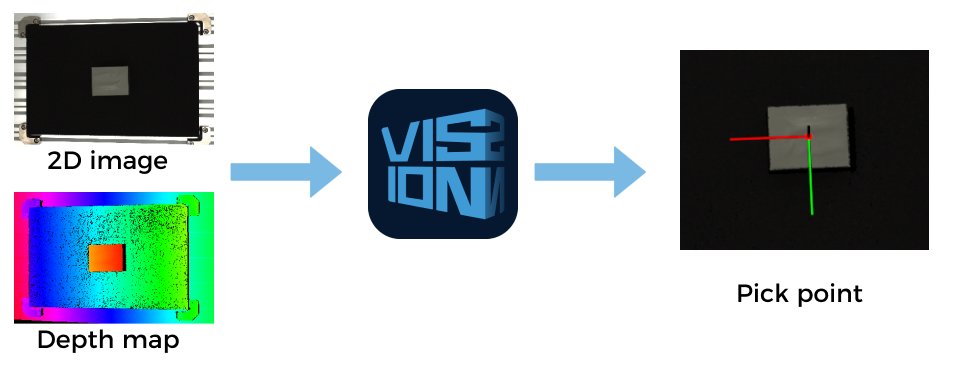
Mech-Vision
Mech-Vision is a state-of-the-art machine vision software. With its fully graphical interface, advanced machine vision applications such as piece picking, high-precision positioning, assembly, industrial inspection/measurement, and automatic path planning can be completed without writing codes.
Based on the image data captured on-site, this software performs a series of vision processing and outputs the vision results (such as the position and orientation of the target object). In addition, based on the vision results, this software can perform collision-free path planning for the robot, and output the planned picking path.
-
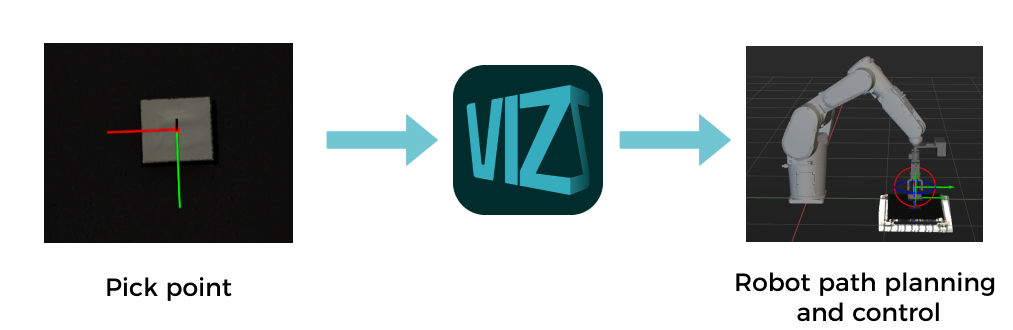
Mech-Viz
Mech-Viz is a robot path planning software. It uses the information provided by Mech-Vision, including the point clouds and workpiece positions, to intelligently plan the robot path for picking, carrying, palletizing and depalletizing, and other complex application scenarios.
This software allows users to build a workflow for the robot in a visualized manner and provides a 3D simulation function for validation before using the real robot. It has already been adapted to most major robot brands around the world.
-
Mech-DLK
Mech-DLK is machine vision deep learning software. With a variety of built-in industry-leading deep learning algorithms, it can solve many problems that traditional machine vision cannot handle, such as highly difficult segmentation, positioning, and classification.
Through intuitive and simple UI interactions, even without programming or specialized deep learning knowledge, users can quickly implement model training and validation with this software.
-
Communication Component for the Vision System
The communication component for the vision system (runs in the background) enables data exchange among software within the vision system and provides standardized and customized communication with external devices, such as robots, PLCs, and host computers, which makes vision-guided intelligent robotic applications possible.
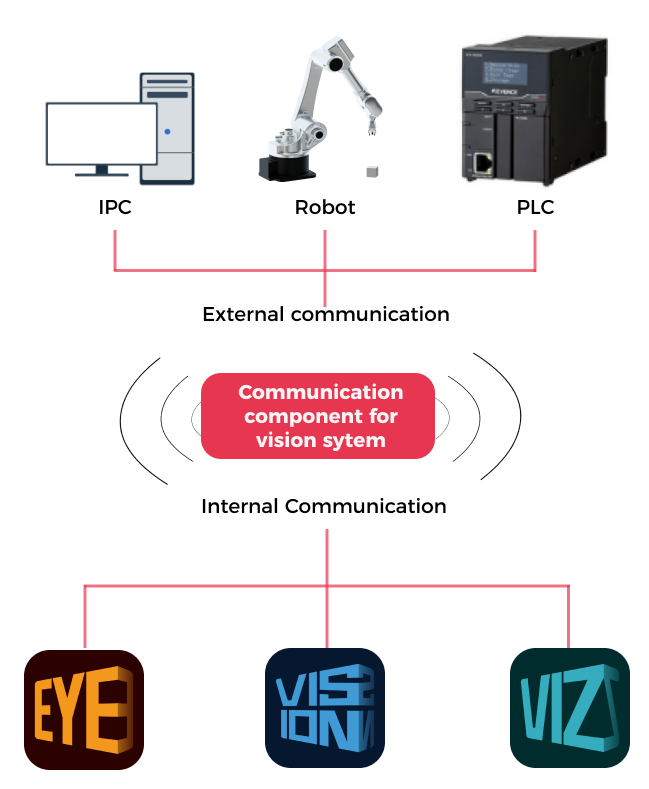
The relationship between Mech-Mind’s software products is shown in the following figure.
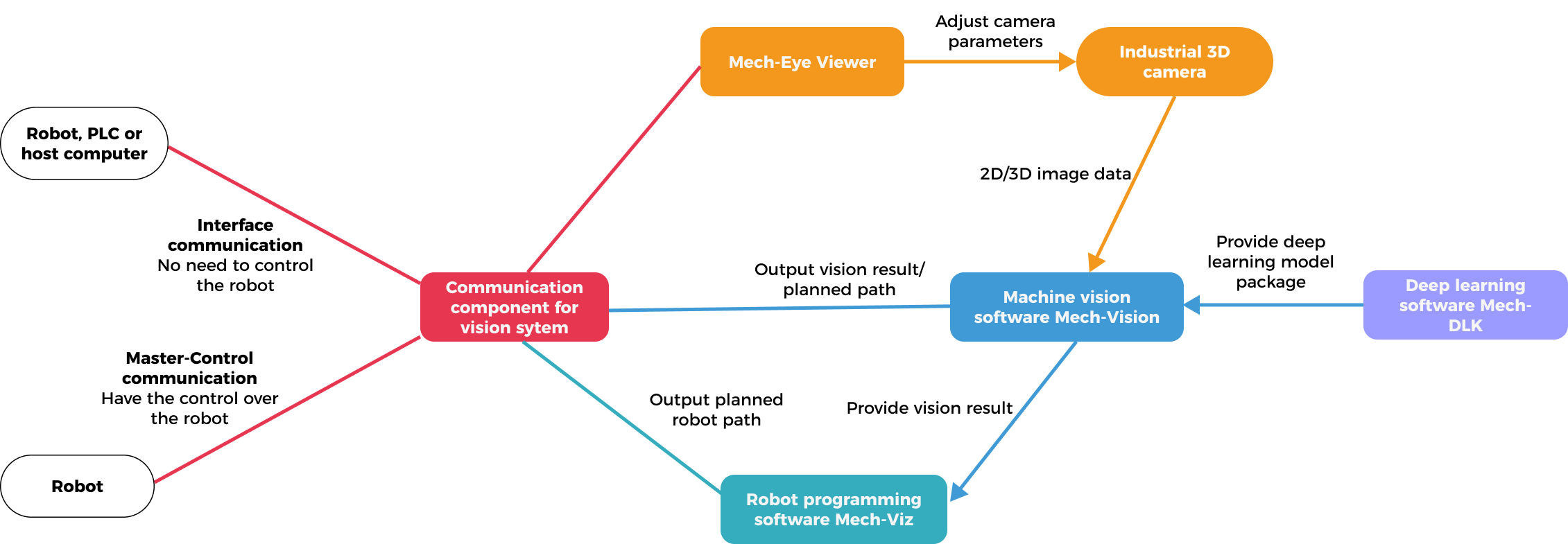
Integration with the Robot System
The Mech-Mind Vision System provides external communication interfaces, which allow it to communicate and integrate with the robot, PLC or host computer within the robot system. This enables the vision system to return the vision results or planned robot path (by Mech-Vision or Mech-Viz) to the robot side for use.
The Mech-Mind Vision System supports the following communication modes:
-
Master-Control communication
In this mode, the vision side has control over the robot, i.e., the vision system acts as the master device, while the robot as the slave device. The vision system sends motion or IO commands to the robot, and the robot continuously listens to and executes these commands. The vision system controls the robot to perform tasks based on the planned path, such as loading or depalletizing/palletizing.
When this mode is used, the robot can be controlled by loading a master-control program to the robot or by using the robot’s SDK (Software Development Kit). This mode supports communication between the vision system and the robot.
-
Interface communication
In this mode, the vision system does not need to take control of the robot. Typically, the robot side acts as the master device, while the vision system is the slave device. The robot side and the vision system use the same standard communication protocol to communicate (such as TCP socket). The robot side sends requests while the vision system processes them and sends responses (poses and labels of the target objects) back. Depending on the request, the vision system returns either the vision result or the planned picking path. The robot makes further decisions or performs the appropriate tasks according to the responses returned from the vision system.
When this mode is used, you should write the robot interface program (for communicating with the vision system) and the robot application program (for receiving the data returned from the vision system and controlling the robot to perform tasks), and load them to the robot. This mode supports communication between the vision system and the robot, the PLC, or the host computer.
For more information about the communication modes, refer to the section Communication Basics.