Profile Mode
This topic provides descriptions of the parameters in the profile mode.
Brightness Settings
Parameters in this category affect the brightness of the laser lines in the raw image, thus affecting the quality of the profile, intensity image, and depth map.
-
The grayscale values of the pixels at the center of the laser lines should be between 200 and 255.
-
The recommended order of adjusting parameters is: Exposure Time > Analog Gain > Digital Gain or Laser Power
Exposure Mode
Description |
Select the exposure mode for acquiring the raw image based on the color and texture of the target object. |
|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
Values |
|
Instruction |
After selecting different options, different parameters are displayed in the Brightness Settings category for adjustment:
|
Exposure Time
Description |
Set the exposure time for acquiring the raw image. Exposure time affects the brightness and width of the laser lines in the raw image, as well as the max scan rate of the laser profiler. Longer exposure time results in brighter and wider laser lines and lower max scan rate. Shorter exposure time results in darker and narrower laser lines and higher max scan rate. |
||
|---|---|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
||
Values |
|
||
Instruction |
|
| You can check the current max scan rate of the laser profiler in the upper right of the data display area. |
Raw images obtained with different Exposure Time values (all other conditions identical):
Exposure time: 40 μs |
|
|---|---|
Exposure time: 200 μs |
|
Exposure time: 1500 μs |
|
HDR Exposure Settings
Description |
Set the exposure time for acquiring the raw image. Exposure time affects the brightness and width of the laser lines in the raw image, as well as the max scan rate of the laser profiler. Longer exposure time results in brighter and wider laser lines and lower max scan rate. Shorter exposure time results in darker and narrower laser lines and higher max scan rate. |
||
|---|---|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
||
Values |
|
||
Instruction |
For detailed instructions, refer to Adjust HDR Exposure Settings below.
|
| You can check the current max scan rate of the laser profiler in the upper right of the data display area. |
Adjust HDR Exposure Settings
In the HDR exposure mode, each exposure is divided into three phases to ensure that, in the raw image, laser lines reflected by regions of different textures or colors can all achieve appropriate brightness.
When using the HDR exposure mode, you need to adjust the total exposure time and the proportions of the three exposure phases. Among these, the total exposure time is determined by using the timed exposure mode.
Follow these steps to adjust the HDR exposure settings:
-
In the profile mode, find the region with the most complex textures or colors on the target object surface and acquire data.
-
Set Exposure Mode to Timed and adjust Exposure Time, until the brightness of the laser line reflected by the region least likely to overexpose on the target object meets the requirement. The value of Exposure Time when the brightness of this laser line meets the requirement is the value that should be set for Total exposure time in HDR Exposure Settings.
-
Set Exposure Mode to HDR and double-click Edit to the right of HDR Exposure Settings to open the HDR Exposure Settings window.
-
In Total exposure time, enter the exposure time determined in step 2.
-
Click Apply to close the current window. In the profile mode, acquire data again and check the brightness of the laser lines in the raw image.
-
If the brightness of the laser lines meets the requirement, the process is completed.
-
If the brightness of the laser line reflected by the region most likely to overexpose on the target object does not meet the requirement, proceed to step 6.
-
-
Set Exposure Mode to Timed and adjust Exposure Time, until the laser line reflected by the region most likely to overexpose on the target object is just visible in the raw image. The current value of Exposure Time is the value that should be set for Exposure time 3 in HDR Exposure Settings.
-
Set Exposure Mode to HDR and double-click Edit to the right of HDR Exposure Settings to open the HDR Exposure Settings window.
-
Adjust Expected proportions until the value of Exposure time 3 roughly matches the exposure time determined in step 6.
The exposure times of the three exposure phases should satisfy: Exposure time 1 > Exposure time 2 > Exposure time 3.
If after step 8, the above relationship is not satisfied, please adjust Expected proportions again.
-
Click Apply to close the current window. In the profile mode, acquire data again and check the brightness of the laser lines in the raw image.
-
If the brightness of the laser lines meets the requirement, the process is completed.
-
If the laser lines still have overexposed parts, please try the following solutions:
-
Increase the proportion of Exposure time 1 slightly or decrease the proportion of Exposure time 3 slightly.
-
Decrease First threshold or Second threshold (available in the Administrator account).
-
-
Analog Gain
Description |
Increasing this parameter can enhance the brightness of the raw image. However, noise will also be introduced. |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
|||
Values |
LNX-8030:
|
LNX-8080 and LNX-8300:
|
||
Instruction |
|
|||
Raw images acquired with different Analog Gain values (all other conditions identical):
Analog Gain: 1.0 |
|
|---|---|
Analog Gain: 2.8 |
|
Digital Gain
Description |
Increasing this parameter can enhance the brightness of the raw image. However, a relatively large amount of noise will also be introduced.
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
Visibility |
Expert, Guru |
||
Values |
|
||
Instruction |
If Analog Gain has reached its maximum value, but the laser lines are still too dark, you can increase Digital Gain. |
|
The value of Digital Gain affects the minimum value of Min Grayscale Value:
|
Raw images acquired with different Digital Gain values (all other conditions identical):
Digital Gain: 0 |
|
|---|---|
Digital Gain: 5 |
|
Laser Power
Description |
Set the power of the emitted laser light, which affects the brightness of the laser lines in the raw image. |
||
|---|---|---|---|
Visibility |
Expert, Guru |
||
Values |
|
||
Instruction |
If the object is reflective or light-colored, you can decrease this parameter to reduce the brightness of the laser lines. If the object is unreflective or dark-colored, you can increase this parameter to enhance the brightness of the laser lines.
|
Raw images obtained with different Laser Power values (all other conditions identical):
Laser Power: 50 |
|
|---|---|
Laser Power: 100 |
|
ROI
Set ROI.
Z-Direction ROI
Description |
A Z-direction ROI retains only the middle part of the raw image and trims the top and bottom parts off. Setting a Z-direction ROI can reduce the amount of data to be processed and enhance the max scan rate. |
|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
Values |
The options are the ratio of the height of the trimmed image to the height of the untrimmed image.
|
Instruction |
The Z-direction ROI reduces the height of the raw image without altering its width. Please adjust this parameter based on the region where the laser lines are, ensuring that the needed laser lines are not trimmed off. |
Raw images obtained with different Z-Direction ROI values (all other conditions identical):
| Z-Direction ROI: 1 | Z-Direction ROI: 1/2 | Z-Direction ROI:1/4 |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Profile Extraction
The parameters in this category affect the extraction of the profile.
The profile extraction process is as follows:
-
Valid pixels are selected based on the value of Min Grayscale Value. In each laser line, the spot of each pixel column is calculated.
-
In each pixel column, the spots that meet the requirements of Min/Max Spot Intensity and Min/Max Laser Line Width are retained.
-
From pixel columns that contain multiple spots, the final spot is selected based on the value of Spot Selection, and the profile is formed.
Min Grayscale Value
Description |
Set the minimum grayscale value of the valid pixels in the raw image. Pixels with grayscale values smaller than this value will not participate in profile extraction.
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
||
Values |
|
||
Instruction |
|
|
The influence between Min Grayscale Value and other parameters are as follows.
|
Profile extraction results with different Min Grayscale Value values (all other conditions identical):
Min Grayscale Value: 20 |
|
|---|---|
Min Grayscale Value: 50 |
|
Min Grayscale Value: 70 |
|
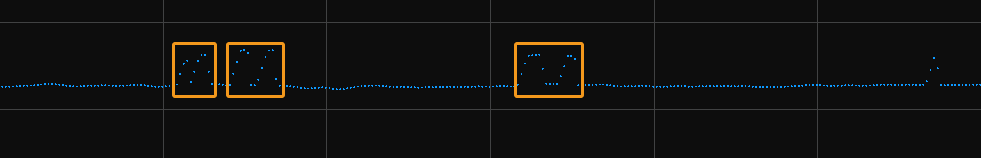
Min Spot Intensity
A spot is calculated from each pixel column of each laser line. The intensity of a spot is the average grayscale value of all the valid pixels in the pixel column of the laser line.
In the figure below, this column of this laser line has 4 valid pixels, so the intensity of the spot in this column is the average of the grayscale values of these 4 valid pixels.

Description |
Set the minimum intensity for the spots. Spots with intensity values smaller than this value will be excluded. |
|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
Values |
|
Instruction |
The spots of laser lines produced by stray light or interreflection usually have low intensities. Setting an appropriate minimum intensity can remove these spots. |
|
The influence between Min Spot Intensity and other parameters are as follows.
|
Max Spot Intensity
A spot is calculated from each pixel column of each laser line. The intensity of a spot is the average grayscale value of all the valid pixels in the pixel column of the laser line.
In the figure below, this column of this laser line has 4 valid pixels, so the intensity of the spot in this column is the average of the grayscale values of these 4 valid pixels.

Description |
Set the maximum intensity for the spots. Spots with intensity values greater than this value will be excluded. |
|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
Values |
|
Instruction |
Setting an appropriate maximum intensity can remove abnormally bright spots produced by specular reflection. |
|
The value of Min Spot Intensity determines the minimum value of Max Spot Intensity: Minimum value of Max Spot Intensity = Min Spot Intensity + 1
|
Min Laser Line Width
Laser line width is a property of each pixel column in a laser line. It is equal to the number of valid pixels in such a pixel column.
In the figure below, this column of this laser line has 4 valid pixels, so the laser line width of this pixel column is 4.

Description |
Set the minimum width for the laser lines. If the width of a pixel column in a laser line is smaller than this value, the spot of this pixel column in this laser line is excluded. |
|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
Values |
|
Instruction |
Setting appropriate minimum and maximum widths can exclude the laser lines produced by stray light or interreflection, which are usually too wide or too narrow. |
Max Laser Line Width
Laser line width is a property of each pixel column in a laser line. It is equal to the number of valid pixels in such a pixel column.
In the figure below, this column of this laser line has 4 valid pixels, so the laser line width of this pixel column is 4.

Description |
Set the maximum width for the laser lines. If the width of a pixel column in a laser line is greater than this value, the spot of this pixel column in this laser line is excluded. |
|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
Values |
|
Instruction |
Setting appropriate minimum and maximum widths can exclude the laser lines produced by stray light or interreflection, which are usually too wide or too narrow. |
Spot Selection
Description |
If a pixel column contains multiple spots, the final spot is selected according to the value of this parameter. |
|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
Values |
|
Instruction |
Adjust based on the actual needs. |
Profile Processing
The parameters in this category process the extracted profile, improving the quality of the profile.
Filter
Description |
Set the type of filters. Filtering the profile can reduce noise and smooth the profile. |
|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
Values |
|
Instruction |
Adjust based on the actual needs. |
Mean Filter Window Size
Description |
Set the window size of the mean filter. This parameter should be set when Filter is set to Mean. |
|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
Values |
|
Instruction |
Larger window size results in higher intensity of smoothing but may also distort object features. |
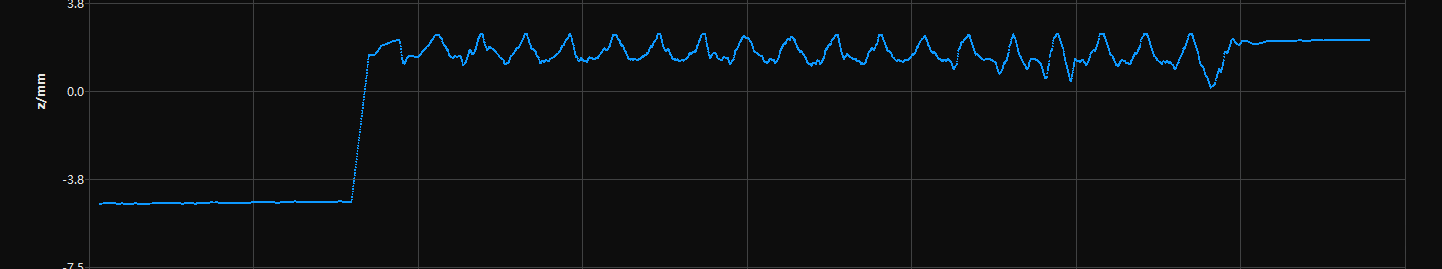
Profile extraction results with different Mean Filter Window Size values (all other conditions identical):
No filter used |
|
|---|---|
Mean Filter Window Size: 2 |
|
Mean Filter Window Size: 8 |
|
Mean Filter Window Size: 32 |
|
Median Filter Window Size
Description |
Set the window size of the median filter. This parameter should be set when Filter is set to Median. |
|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
Values |
|
Instruction |
Larger window size removes more noise. |
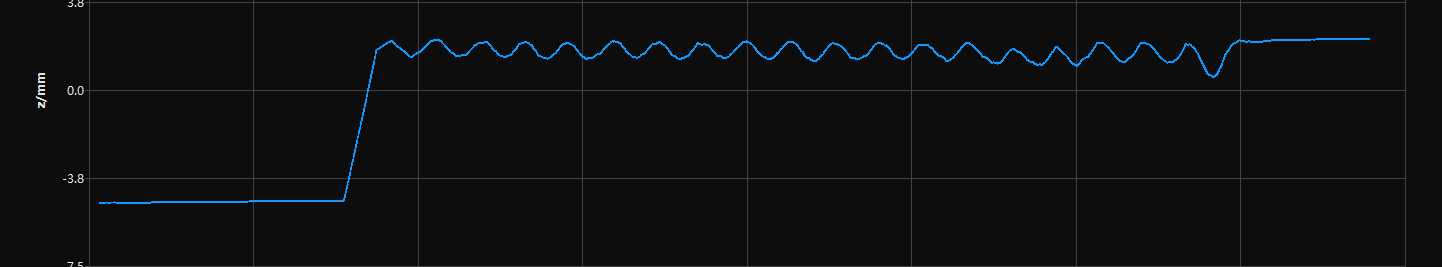
Profile extraction results with different Median Filter Window Size values (all other conditions identical):
No filter used |
|
|---|---|
Median Filter Window Size: 5 |
|
Median Filter Window Size: 9 |
|
Gap Filling
Description |
Set the size of the gaps that can be filled in the profile. When the number of consecutive data points in a gap in the profile is no greater than this value, this gap will be filled. The data used for filling is calculated based on the difference between the two neighboring points (that is, based on linear interpolation). |
||
|---|---|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
||
Values |
|
||
Instruction |
Adjust based on the size of the gaps to be filled.
|
Raw images obtained with different Gap Filling values (all other conditions identical):
Gap Filling: 0 |
|
|---|---|
Gap Filling: 5 |
|
Gap Filling Edge Preservation
Description |
Set the degree of preservation of object edges when filling gaps. |
|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
Values |
|
Instruction |
If you need to preserve features with abrupt depth variations, such as object edges, you can increase this parameter, but the amount of gaps being filled will decrease. |
Mask
Description |
Use masks to exclude unneeded data, such as noise and laser lines produced by interreflection. |
|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
Values |
Enable Mask:
|
Instruction |
Double-click Edit to open the Mask Tool window. For detailed instructions, refer to Use Mask Tool below. |
Use Mask Tool
Through the mask tool, you can add, edit, and delete masks.
Add Masks
Follow these steps to add masks:
-
Select the appropriate tool in the toolbar on the left:
-
 : used to add a rectangle mask.
: used to add a rectangle mask. -
 : used to add a polygon mask.
: used to add a polygon mask.
-
-
Determine the location of the unneeded data in the raw image and draw a mask:
-
Rectangle mask: Hold and drag.
-
Polygon mask: Click to add a vertex of the polygon mask. After all needed vertices are added, press the Enter key or right-click to finish drawing the polygon mask.
In a polygon mask, the overlapped regions are not effective:

-
Click Acquire again at the top to acquire the raw image after the masks are added to check the effect of the masks.
-
If the position, shape, or size of the masks are not satisfactory, you can edit the masks or delete the masks.
-
-
-
After all masks are added, click Apply to close the current window.
After Apply is clicked, the value of the Enable Mask parameter is automatically changed to True. If you do not need to apply the masks, change the value of this parameter to False.
Edit Masks
If the position, shape, or size of the masks are not satisfactory, follow these steps to edit the masks:
-
Click
 in the toolbar on the left.
in the toolbar on the left. -
Select the mask that needs to be edited and conduct the needed adjustment:
-
Move a mask: Select the mask and drag.
-
Adjust the size of a rectangle mask: Select a vertex of the rectangle mask and drag.
-
Adjust the shape of a polygon mask:
-
Move an existing vertex: Select a vertex of the polygon mask and drag.
-
Add a new vertex: Left-click on an edge of the polygon mask.
-
Delete an existing vertex: Select a vertex of the polygon mask and right-click.
Click Acquire again at the top to acquire the raw image after the masks are edited to check the effect of the masks.
-
-
-
After all editing is completed, click Apply to close the current window.
After Apply is clicked, the value of the Enable Mask parameter is automatically changed to True. If you do not need to apply the masks, change the value of this parameter to False.
Delete Masks
Follow these steps to delete unsatisfactory masks:
-
In the right panel, select the mask that needs to be deleted in Mask list, and click
 .
.If you need to delete all the masks, click Clear to the right of Mask list. -
In the pop-up window, click Confirm to delete the mask.
Click Acquire again at the top to acquire the raw image after the mask is deleted to check the effect of the remaining masks. -
After all deletion is completed, click Apply to close the current window.
After Apply is clicked, the value of the Enable Mask parameter is automatically changed to True. If you do not need to apply the masks, change the value of this parameter to False.
Correction
The parameters in this category are used to correct the tilt of and height error in the profile.
Tilt Correction
Description |
Correct the tilt of the profile, which is caused by the rotation of the laser profiler around the Y-axis. |
|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
Values |
Enable Tilt Correction:
Tilt Correction Angle:
|
Instruction |
For detailed instructions, refer to Perform Tilt Correction below. |
Perform Tilt Correction
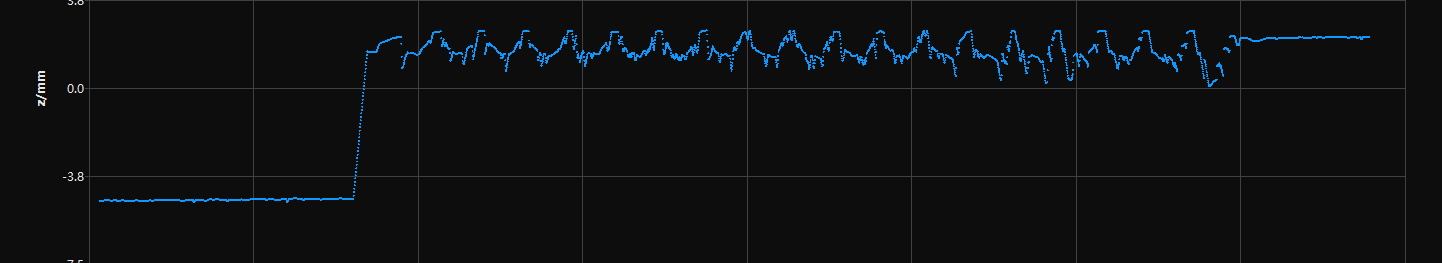
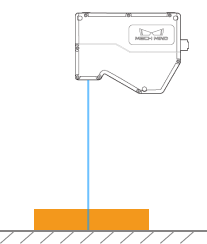
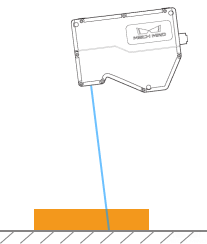
This tool is used to correct the tilt of the profile, which is caused by the rotation of the laser profiler around the Y-axis.
As shown below, the rotation of the laser profiler around the Y-axis make the tilt of the acquired profile differ from the tilt of the actual object.
Not rotated |
Rotated around the Y-axis |
||
Laser profiler |
|
|
|
Acquired profile |
|
|
|
Prerequisites
In order to perform tilt correction, the following prerequisites must be satisfied:
-
It is recommended to use a target object whose surface includes flat regions.
-
A relatively complete profile of the flat regions can be acquired. If the profile is incomplete, please refer to Profile Mode and adjust the other parameters first.
-
Keep the target object still relative to the laser profiler, and acquire the profile of the flat regions on the target object.
Instructions
Follow these steps to perform tilt correction:
-
Double-click Edit to the right of Tilt Correction to open the Tilt Correction window.
-
Select the detection areas and drag to adjust their positions. Make sure to satisfy the following criterion while adjusting:
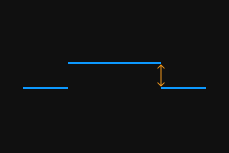
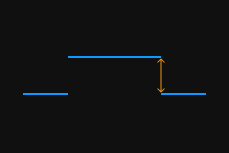
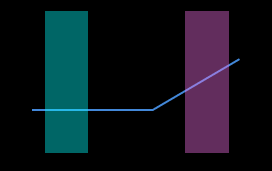
The profile selected by the two detection areas should correspond to two locations on the same flat region of the target object. Please refer to the following example:
Target object 
Detection areas
Correct
Incorrect
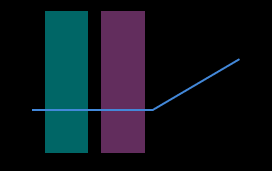

The detection areas can overlap. -
Select the detection areas and drag the handles on them to adjust their widths. Refer to the following criterion while adjusting:
With the above criterion satisfied, the detection area can be as wide as possible to include more data for tilt correction.
-
In Expected tilt angle under Tilt angles, enter the angle that the profile in the detection areas should reach after the correction.
Positive values rotate the profile counterclockwise; negative values rotate the profile clockwise. The range of possible values is -45° to 45°. Example of expected tilt angle
A target object as shown below is placed on a horizontal surface:
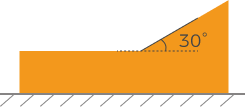
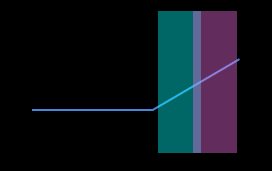
The value that should be entered for Expected tilt angle depends on the positions of the detection areas:
Detection areas Expected tilt angle 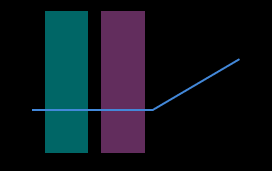
0°

30°
-
Click Correct. The green line in the image area on the left represents the profile that has been rotated to Expected tilt angle after tilt correction. Check if this profile satisfies your requirements:
-
If yes, click Apply to apply the tilt correction result and close the window.
-
If no, repeat steps 2 to 5.
-
-
Acquire data again in the profile mode and switch to Profile to check the effect of correction.
Height Correction
Description |
Correct the height error in the profile, which is caused by the rotation of the laser profiler around the X-axis. |
|---|---|
Visibility |
Beginner, Expert, Guru |
Values |
Enable Height Correction:
Height Correction Ratio:
|
Instruction |
For detailed instructions, refer to Perform Height Correction below. |
Perform Height Correction
This tool is used to correct the height error in the profile, which is caused by the rotation of the laser profiler around the X-axis.
As shown below, the rotation of the laser profiler around the X-axis make the height difference between two locations in the acquired profile differ from the actual difference.
| Not rotated | Rotated around the X-axis | |
|---|---|---|
Laser profiler |
|
|
Acquired profile |
|
|
Prerequisites
In order to perform height correction, the following prerequisites must be satisfied:
-
It is recommended to use a target object with known dimensions and flat surfaces, such as a gauge block, and place the target object on a horizontal surface.
-
A relatively complete profile of the target object can be acquired. If the profile is incomplete, please refer to Profile Mode and adjust the other parameters first.
-
Keep the target object still relative to the laser profiler.
-
Select two surfaces (such as the top surface of the gauge block and the horizontal surface on which the gauge block is placed) for calculating the height difference, and determine the actual height difference of the two surfaces.
Instructions
Follow these steps to perform height correction:
-
Double-click Edit to the right of Height Correction to open the Height Correction window.
-
Select the detection areas and drag to adjust their positions. Make sure to satisfy the following criterion while adjusting:
The profile segments selected by the two detection areas should correspond respectively two the two surfaces used for calculating the height difference.
Two surfaces used for calculating the height difference

Detection areas
Correct
Incorrect
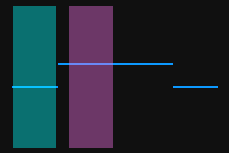
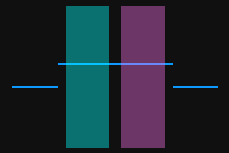
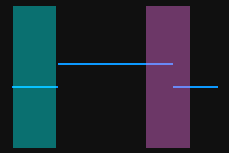
-
Select the detection areas and drag the handles on them to adjust their widths. Refer to the following criterion while adjusting:
With the above criterion satisfied, the detection areas can be as wide as possible to include more data for height correction.
-
In Actual height difference under Height differences, enter the actual height difference between the two surfaces.
The minimum value of Actual height difference is 0.01 mm, and the maximum value is the Z-axis measurement range of the laser profiler. -
Click Correct. The green line in the image area on the left represents the profile after height correction. Check if this profile satisfies your requirements:
-
If yes, click Apply to apply the height correction result and close the window.
-
If no, repeat steps 2 to 5.
-
-
Acquire data again in the profile mode and switch to Profile to check the effect of correction.