set_guidepost & branch_by_guidepost¶
The scene for this combination is: when there is a common part in multiple logical branches, the common part is not required to be copied by multiple times, use set_guidepost to mark the current branch, merge it into the common part, and then use branch_by_guidepost Task to restore the program running logic to the original branch.
The following figure is an example:
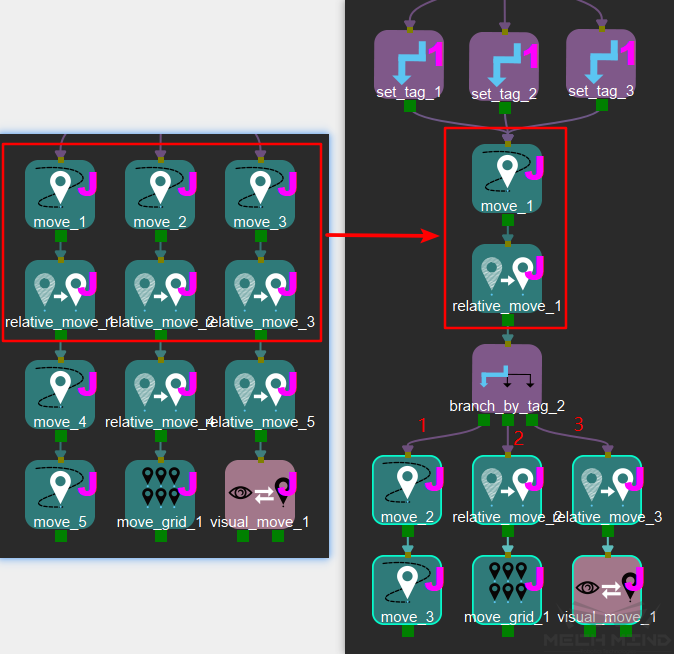
The three branches have common Tasks: move and relative_move. No matter which branch, they will proceed to the same position when completing the previous process. At this time, the same Task can be selected, and set_guidepost Tasks are added to the branches to mark the current branch number. When the program finishes move and relative_move Tasks, branch_by_guidepost will restore the program running logic to the previously running branch according to the current identification.
Parameter settings
set_guidepost
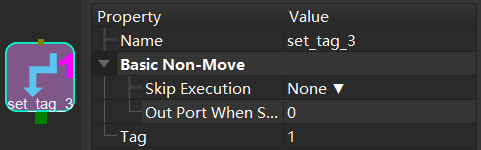
Basic parameters for non-movement, see General Parameters of Non-Move Tasks
routePort: the ID of the current branch, used to restore the branch of the branch_by_guidepost Task
branch_by_guidepost

Basic parameters for non-movement, see General Parameters of Non-Move Tasks
size: output ports of the branch_by_guidepost Task, based on the total number of routePort