JPs Constraints¶
Definition of Terms
Shoulder: The relative positional relationship between the center of the wrist and Axis1. Axis1 refers to the rotation center axis of the robot axis 1.
Elbow: Relative positional relationship between wrist and LowerArm. LowerArm refers to the line connecting the rotation centers of the robot axis 2 and axis 3.
Wrist: Robot axis 5 is the wrist. Whether the wrist JPs can be negative means whether the robot’s wrist can rotate in the negative direction.
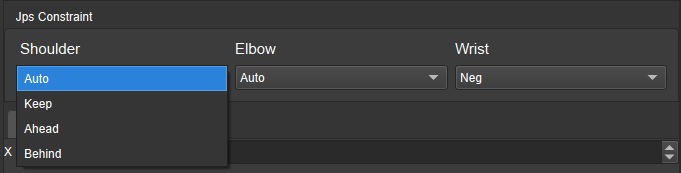
Figure 1. JPs constraint settings¶
List of Values
Auto: This joint’s motion is under completely zero constraints. The optimal solution is the one in which each axis undergoes the minimum amount of rotation.
Keep: Record the current JPs status of the robot as the constraints for getting the next JPs solution. Taking axis 3 as an example, if axis 3 is positive when getting the next JPs solution, only solutions in which axis 3 is positive will be considered.
Ahead: The wrist center is ahead of Axis1.
Behind: The wrist center is behind Axis1.
After clicking , a window showing all the JPs solutions to the current target point will pop up. After clicking one of the solutions, the corresponding pose of the solution will be displayed in the simulation, thus showing the possible solutions under different constraints, as shown in Figure 2
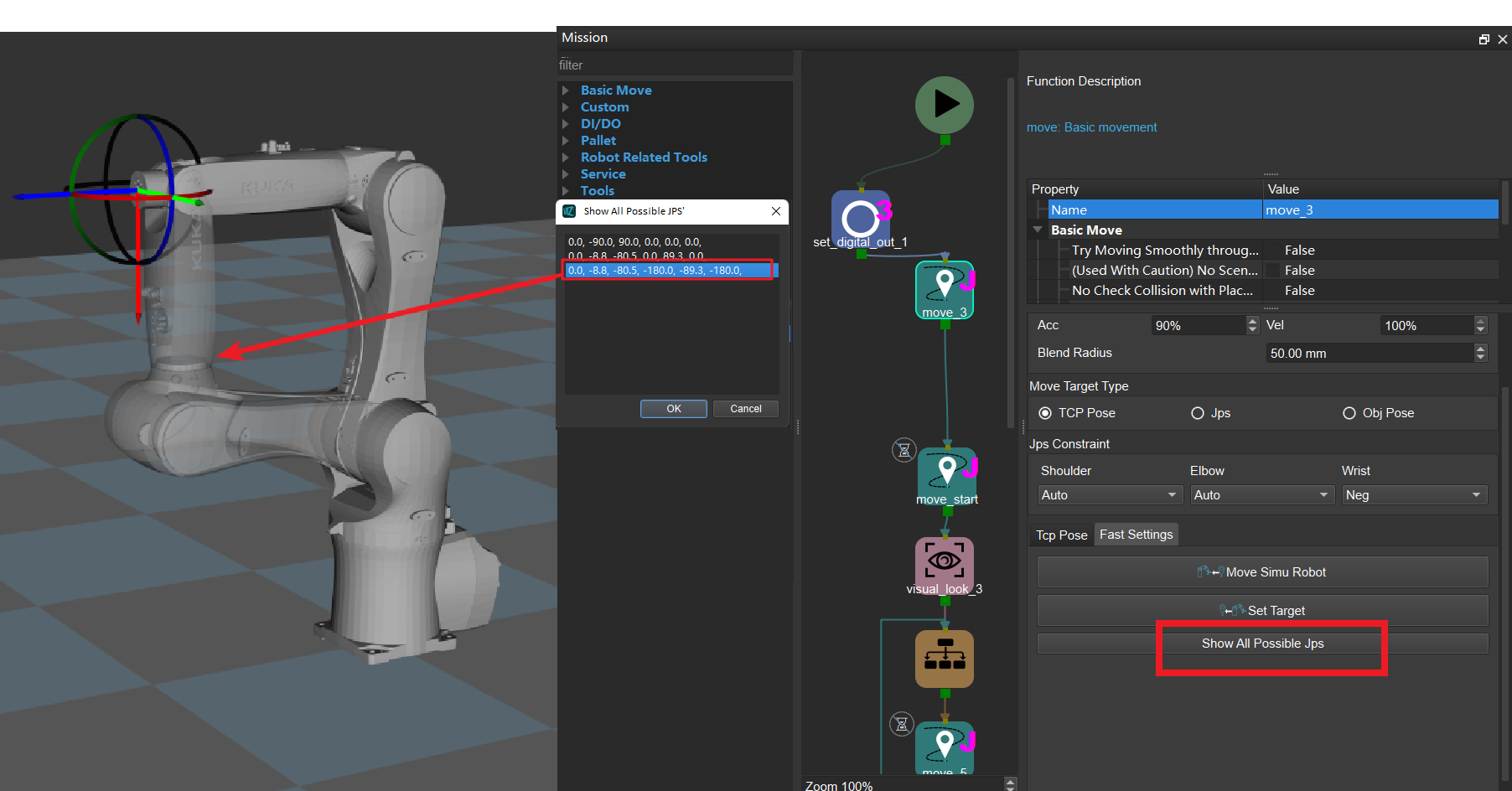
Figure 2. Viewing possible JPs solutions¶
Attention
JPs constraint settings only apply to 6-axis robots. 4-axis robots are considered as not having abnormal shoulder, elbow, and wrist positions.
relative_move, smart_pallet_pattern, and mixed_pallet do not support JPs constraint settings and have default JPs constraints, that is, the statuses of the shoulder, elbow, and wrist do not change, the robot’s motion does not cross solution systems (does not go through singularities).