Kawasaki Example Program¶
This section introduces the example program provided with Mech-Center and the operations required to perform an actual pick-and-place task.
The example program mm_sample.as can be found in Mech-Center/mech_interface/kawasaki. It contains two parts: vision_sample_1 obtains vision results from Mech-Vision; vision_sample_2 obtains planned path from Mech-Viz.
Check the section corresponding to your own application setup:
Before running the program, please make sure that:
You have loaded the Standard Interface program onto the robot and can establish communcation with Mech-Center.
You have completed the extrinsic parameter calibration with the calibration program or by manually adding calibration points.
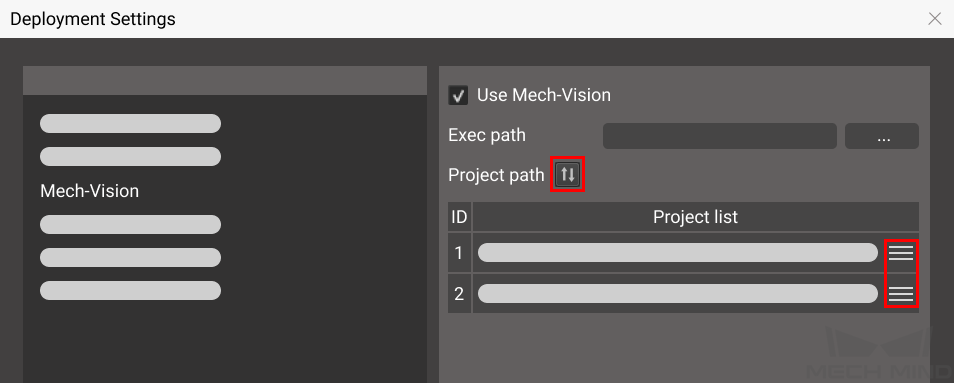
Mech-Vision and Mech-Viz projects are created and set to autoload.
The Project list in is synced by clicking on
 , and the order of Mech-Vision projects have been adjusted according to actual needs.
, and the order of Mech-Vision projects have been adjusted according to actual needs.The TCP has been correctly specified.
The robot speed is set to a low value, so that the operator can notice any unexpected behavior before accidents occur.
Obtain Vision Results from Mech-Vision¶
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | .PROGRAM vision_sample_1()
;**********************************************************
;* FUNCTION:simple pick and place with Mech-Vision
;* mechmind, 2022-5-1
;**********************************************************
accuracy 1 always
speed 30 always
TOOL gripper ;set TCP
Home ;move robot home position
lmove camera_capture ;move to camera capture position
break
pos_num = 0
;Set ip address of IPC
call mm_init_skt(127,0,0,1,50000,60)
twait 0.1
;Set vision recipe
;call mm_switch_model(1,1)
;Run vision project
call mm_start_vis(1,1,2)
twait 1
call mm_get_visdata(1,pos_num,ret2)
if ret2 <> 1100
halt
end
call mm_get_pose(1,&pick[1],label[l],speed[1])
LAPPRO pick[1],100
LMOVE pick[1]
break
;Add object grasping logic here.
ldepart 100
lmove waypoint[1]
lappro drop[1],100
lmove drop[1]
;Add object releasing logic here.
ldepart 100
HOME
.END
|
Program Logic¶
Move the robot to HOME position.
Move the robot to the image capturing pose.
Initialize communication with mm_init_skit.
If parameter recipes are used in the Mech-Vision project, the recipe to be used is set with mm_switch_model.
Run the Mech-Vision project with mm_start_vis.
Wait for 1 second. Under Eye-In-Hand, this TWAIT instruction is required to make sure the robot stays still until image acquisition is completed. Under Eye-To-Hand, this TWAIT instruction can be replaced with LMOVE or JMOVE.
Obtain the vision results from Mech-Vision.
Check if the returned status code indicates any error. If an error code is returned, the program is halted.
Move the robot to the picking pose and perform picking.
Move the robot to a waypoint between the picking pose and placing pose.
Move the robot to the set placing pose and perform placing.
Return the robot to HOME position.
The following parts should be modified according to your actual needs.
Define the TCP¶
Change the value of gripper in line 8 to the actual TCP values.
Teach the Image Capturing Pose¶
Record the image capturing pose in camera_capture in line 10.
Teach the Waypoint(s)¶
Waypoints are intermediate poses between the picking pose and placing pose. They are used to ensure that the robot doesn’t collide with the surrounding when moving between the picking and placing poses.
You can add one or more waypoints to waypoint[] in line 31.
Teach the Placing Pose¶
Record the placing pose in drop[1] in line 33.
Define Z-Offset from Picking/Placing Pose¶
Z-offset distances relative to the tool frame from the picking/placing pose are used to ensure collision doesn’t occur when the robot is approching or departing the picking/placing pose.
Adjust the following commands according to your actual needs.
LAPPRO pick[1],100 in line 26: the Z-offset when approching the picking pose is set to 100. Robot will move to 100 mm above the picking pose.
ldepart 100 in line 30: the Z-offset when departing the picking pose is set to 100. Robot will move to 100 mm above the picking pose.
lappro drop[1],100 in line 32: the Z-offset when approching placing pose is set to 100. Robot will move to 100 mm above the placing pose.
ldepart 100 in line 35: the Z-offset when departing the placing pose is set to 100. Robot will move to 100 mm above the placing pose.
Add Object Grasping and Releasing Logics¶
Add logic for controlling the tool action when picking the object to line 29.
Add logic for controlling the tool action when placing the object to line 34.
Define HOME position¶
The HOME position need to be set on the teach pendant in beforehand.
Obtain Planned Path from Mech-Viz¶
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 | .PROGRAM vision_sample_2()
;**********************************************************
;* FUNCTION:simple pick and place with Mech-Viz
;* mechmind, 2022-5-1
;**********************************************************
accuracy 1 always
speed 30 always
TOOL gripper ;set TCP
Home ;move robot home position
LMOVE camera_capture ;move to camera_capture position
break
pos_num = 0
;Set ip address of IPC
call mm_init_skt(127,0,0,1,50000,60)
twait 0.1
;Set vision recipe
;call mm_switch_model(1,1)
;Run Viz project
call mm_start_viz(1)
twait 0.1
;set branch exitport
;call mm_set_branch(1,1)
;get planned path
call mm_get_vizdata(2,pos_num,vispos_num,ret1)
if ret1 <> 2100
halt
end
for count=1 to pos_num
call mm_get_pose(count,&movepoint[count],label[count],speed[count])
end
;follow the planned path to pick
for count =1 to pos_num
speed speed[count]
LMOVE movepoint[count]
if count == vispos_num then
;add object grasping logic here
end
end
;go to drop location
ldepart 100
lmove waypoint[1]
lappro drop[1],100
lmove drop[1] ;drop point
;add object releasing logic here
ldepart 100
HOME
.END
|
Program Logic¶
Move the robot to HOME position.
Move the robot to the image capturing pose.
Initialize communication with mm_init_skit.
If parameter recipes are used in the Mech-Vision project, the recipe to be used is set with mm_switch_model.
Run the Mech-Viz project with mm_start_viz.
Obtain the planned path from Mech-Viz.
Check if the returned status code indicates any error. If an error code is returned, the program is halted.
Store obtained target points in the planned path to &movepoint[] with a FOR loop.
Move the robot along the planned path with a FOR loop and perform picking.
Move the robot to a waypoint between the picking pose and placing pose.
Move the robot to the set placing pose and perform placing.
Return the robot to HOME position.
The following parts should be modified according to your actual needs.
Define the TCP¶
Change the value of gripper in line 8 to the actual TCP values.
Teach the Image Capturing Pose¶
Record the image capturing pose in camera_capture in line 10.
Teach the Waypoint(s)¶
Waypoints are intermediate poses between the picking pose and placing pose. They are used to ensure that the robot doesn’t collide with the surrounding when moving between the picking and placing poses.
You can add one or more waypoints to waypoint[] in line 41.
Teach the Placing Pose¶
Record the placing pose in drop[1] in line 43.
Add Object Grasping and Releasing Logics¶
Add logic for controlling the tool action when picking the object to line 29.
Add logic for controlling the tool action when placing the object to line 34.
Define HOME position¶
The HOME position need to be set on the teach pendant in beforehand.