Point Cloud Clustering¶
Function¶
Perform point cloud clustering according to specified rules; often used for segmentation of target objects.

Usage Scenario¶
This Step is usually used for point cloud pre-processing to eliminate interference from unwanted point clouds.
It supports two point cloud clustering methods: clustering using Euclidean distance (EuclideanCluster) and clustering using region growing segmentation (RegionGrowingSeg).
When the point cloud has obvious spatial separation, it is recommended to use Euclidean clustering (EuclideanCluster); when the point cloud is spatially continuous, but the curvatures of the connection parts change greatly, it is recommended to use region growing segmentation (RegionGrowingSeg).
Input and Output¶
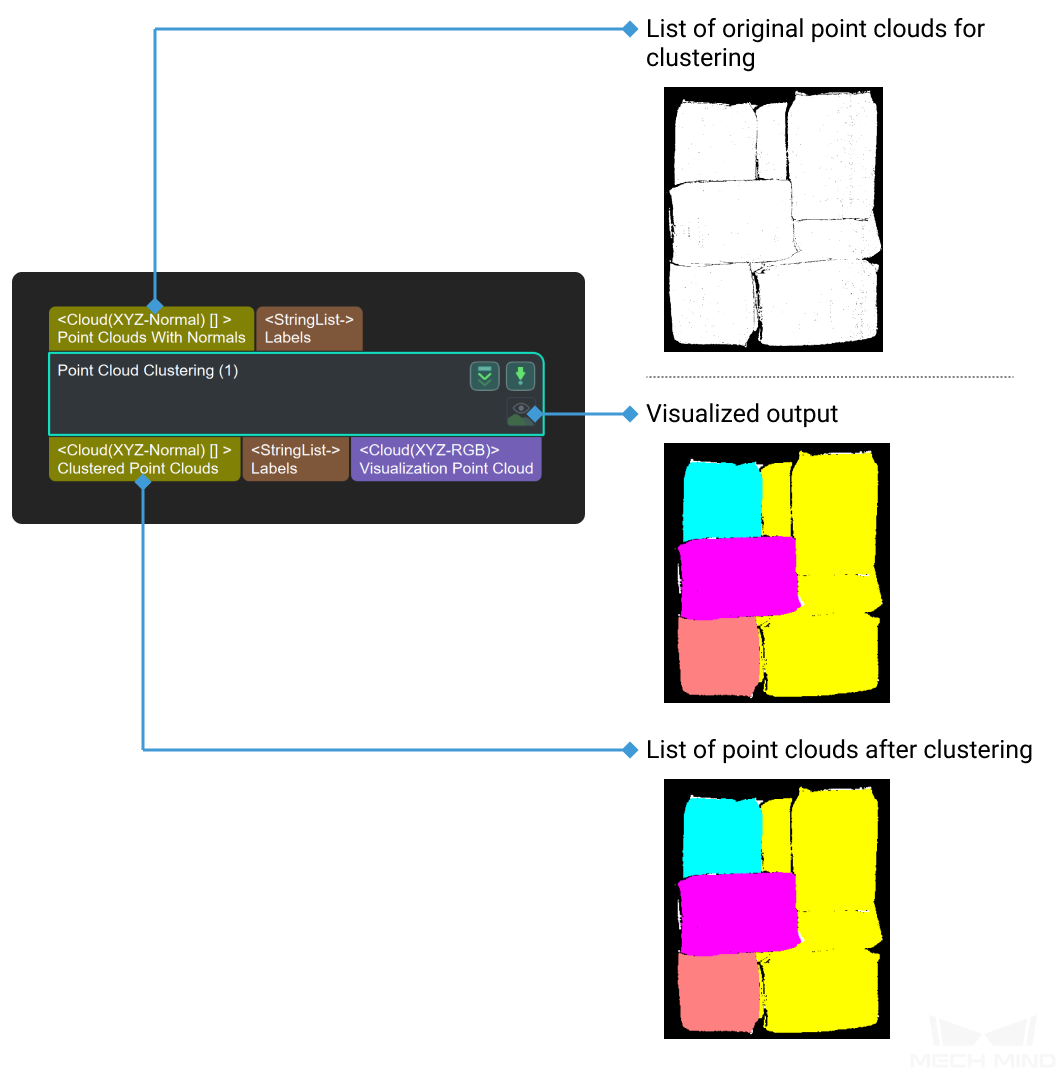
Parameters¶
Cluster Algorithm
Default Value: EuclideanClusterList of Values: EuclideanCluster, RegionGrowingSegInstruction: This parameter is used to select the clustering method, and there are two clustering methods in total. In practical engineering, it is recommended to use the EuclideanCluster algorithm, and this algorithm parameter is introduced first.
EuclideanCluster : determine whether a class belongs to based on proximity
RegionGrowingSeg : determine whether a class belongs based on normality and curvature
EuclideanCluster
- Max Distance of Neighboring Points in Output Clusters
- Default value: 0.0030Instruction: This parameter is the clustering tolerance. When this parameter is adjusted up, points that are farther apart will be grouped into the same class; When this value is adjusted down, points that are closer together will be grouped into different categories.Example of adjustment: As shown below, the left panel shows the result of this parameter at the default value of
0.003and the right panel shows the result of this parameter adjusted to0.005. The user can see that after the adjustment, the green point cloud in the middle is divided into different categories.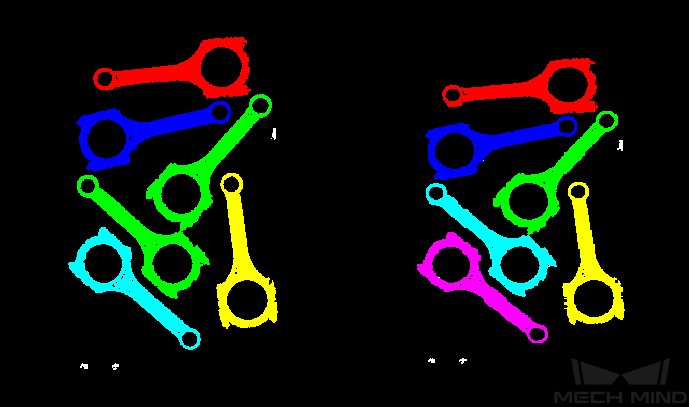
- Cores
- Default value: 4Instruction: This parameter is used to adjust the normal angle difference threshold of adjacent points during region growth. When this value is adjusted to a larger value, the tolerance for normal angle difference of adjacent image points becomes larger and points with larger angle difference will still be grouped together.
RegionGrowingSeg
- Number of Neighbours
- Default value: 30Instruction: This parameter is used to adjust the number of pixels searched during the region growing process. When the value is adjusted to a higher value, the number of searched pixel points becomes larger and the region grows faster, resulting in a smaller number of classes obtained by clustering.
- Smoothness Threshold
- Default value: 4Instruction: This parameter is used to adjust the threshold for the difference in normal angle between neighbouring points during region growth. When this value is adjusted upwards, the tolerance for the normal phase angle difference of adjacent image points becomes larger and points with larger angle differences will still be grouped together.
- Curvature Threshold
- Default value: 1Instruction: This parameter is used to adjust the upper threshold value for the curvature of points in the region growth process.
Min Points Num in Cluster
Default value: 800 | Instructions: This parameter is for filtering the results after clustering. Only the classes with number of points greater than the minimum number of points can be output. When this parameter is large, the number of final output classes will decrease; when the parameter is small, the number of final output classes will increase.
Max Points Num in Cluster
Default Value: 3,000,000 | Instructions: This parameter is for filtering the results after clustering. Only the classes with number of points lower than the minimum number of points can be output. When this parameter is small, the number of final output classes will decrease; when the parameter is large, the number of final output classes will increase. | Example: Suppose that the point cloud is clustered into 5 classes, and their numbers of points are10,000,20,000,30,000,40,000, and50,000respectively. If the maximum number of points of the class is set to45,000and the minimum number of points is set to15,000, then the classes with10,000and50,000points will be filtered out, and only the classes with20,000,30,000, and40,000points will be output.
Use GPU
Default value: UnselectedList of values: Selected, UnselectedInstruction: This paramater decides whether to accelerate calculation with GPU.