Morphological Transformations¶
Usage Scenario¶
This Step is usually used for image pre-processing when the quality of images is not ideal and further adjustment is needed.
Apply operations such as dilation, erosion, and opening and closing to denoise, fill, etc. based on actual requirements.
Input and Output¶
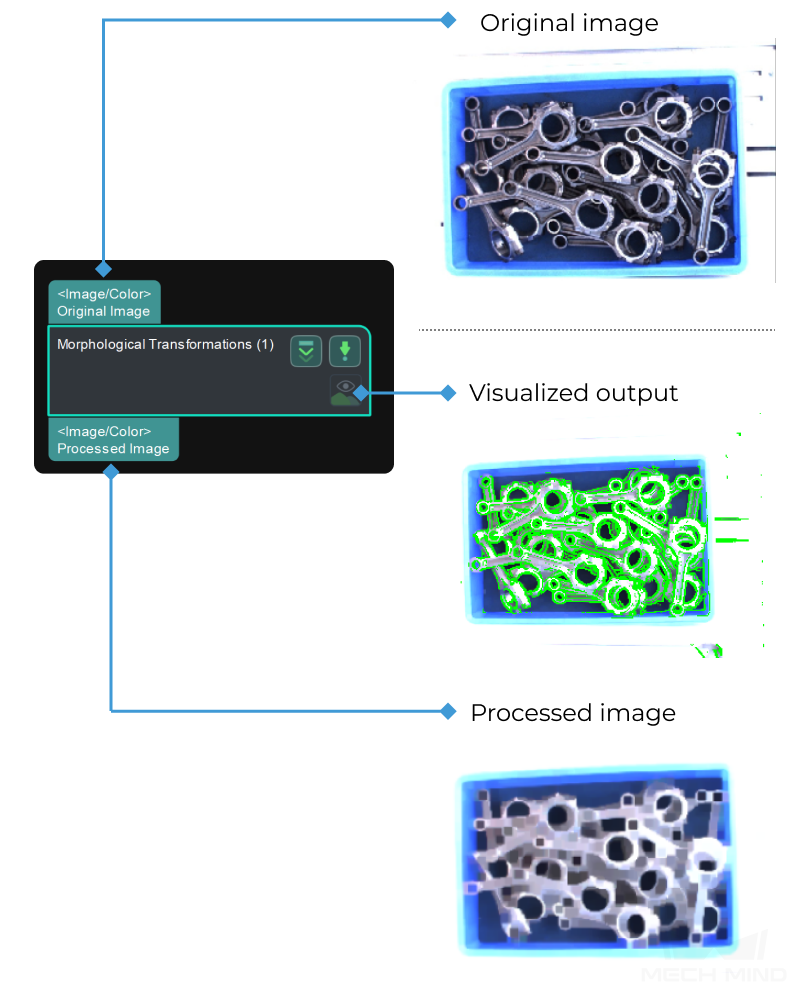
When ClosingOperator is selected, the input and output are as shown in the figure below.
Parameter Description¶
Morphological Transformations
Description: This parameter is used to choose the type of morphological transformation.Default setting: DilateOperatorList of options: ClosingOperator, DilateOperator, ErodeOperator, OpeningOperator, SkeletonInstruction:
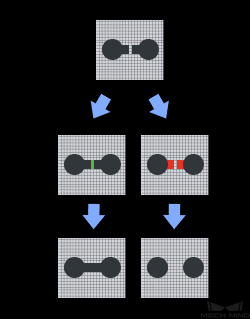
ClosingOperator: Closing is reverse of Opening, Dilation followed by Erosion. It is useful in closing small holes inside the foreground objects, or small black points on the object.
- Kernel Size
- Kernel Shape
Performance on image detail restoration: MORPH_RECT < MORPH_CROSS < MORPH_ELLIPSE
Time required for operation: MORPH_RECT < MORPH_CROSS < MORPH_ELLIPSE
DilateOperator: Dilation. It is mainly used to increase the object area and join broken parts of an object.
- Kernel Size
- Kernel Shape
Performance on image detail restoration: MORPH_RECT < MORPH_CROSS < MORPH_ELLIPSE
Time required for operation: MORPH_RECT < MORPH_CROSS < MORPH_ELLIPSE
ErodeOperator: Erosion. It is mainly used to remove small noises and detach two connected objects.
- Kernel Size
- Kernel Shape
Performance on image detail restoration: MORPH_RECT < MORPH_CROSS < MORPH_ELLIPSE
Time required for operation: MORPH_RECT < MORPH_CROSS < MORPH_ELLIPSE
OpeningOperator: Opening is another name of erosion followed by dilation. It is useful in removing noise.
- Kernel Size
- Kernel Shape
Performance on image detail restoration: MORPH_RECT < MORPH_CROSS < MORPH_ELLIPSE
Time required for operation: MORPH_RECT < MORPH_CROSS < MORPH_ELLIPSE
Skeleton: Extract the contour of the object.
Configuration Example¶
ClosingOperator¶
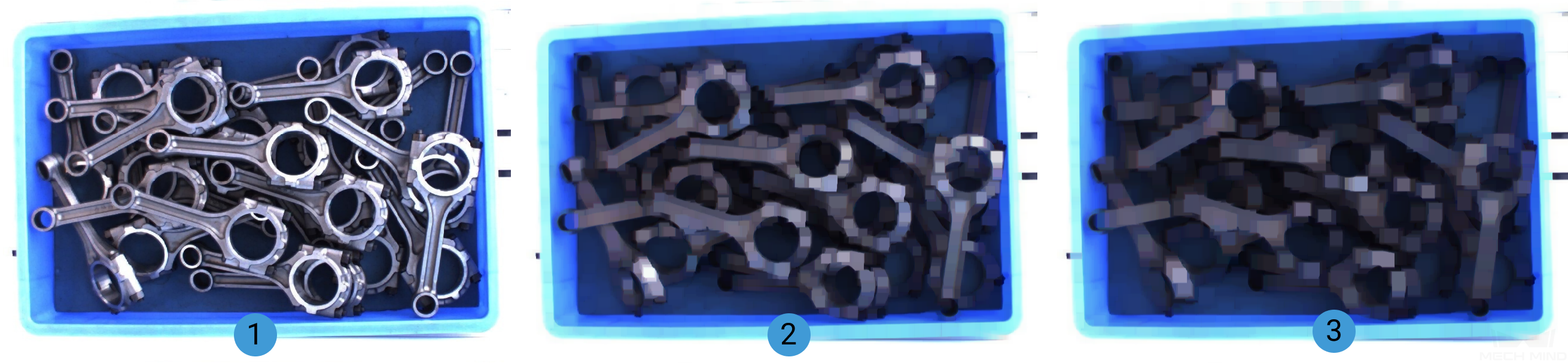
When ClosingOperator is selected, the size increase of the kernel is shown in the images below (The kernel size grows by degrees and from image 1 to 3):
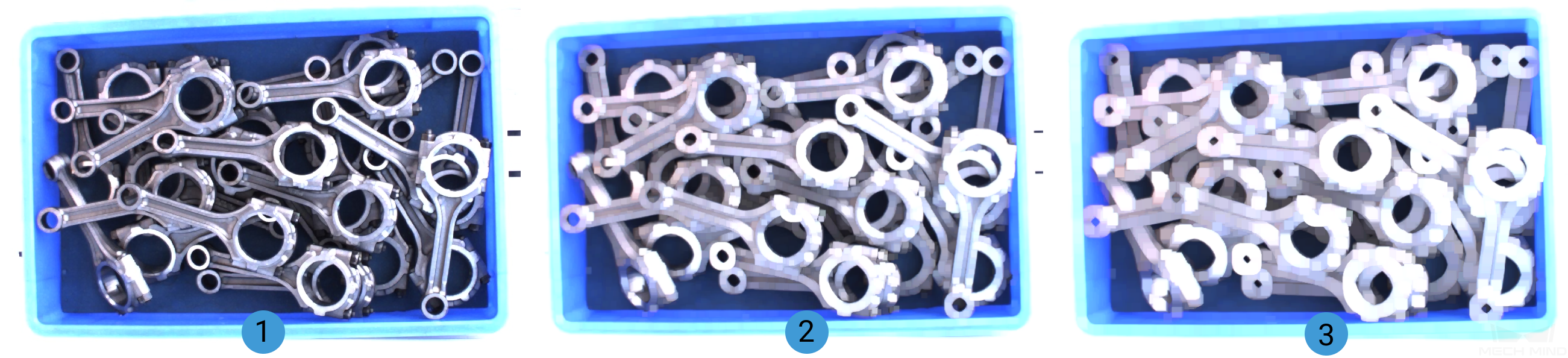
DilateOperator¶
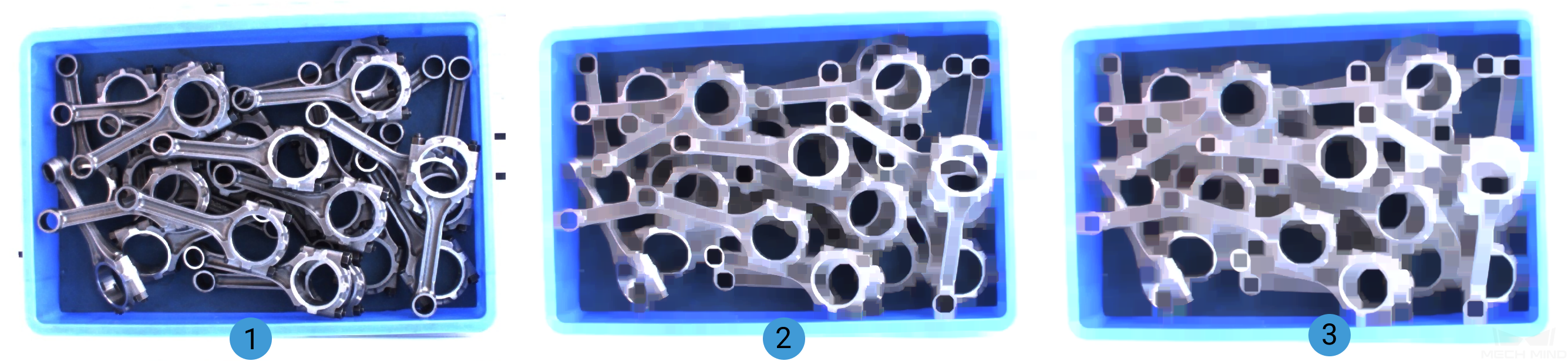
When DilateOperator is selected, the size increase of the kernel is shown in the images below (The kernel size grows by degrees and from image 1 to 3):

ErodeOperator¶
When ErodeOperator is selected, the size increase of the kernel is shown in the images below (The kernel size grows by degrees and from image 1 to 3):
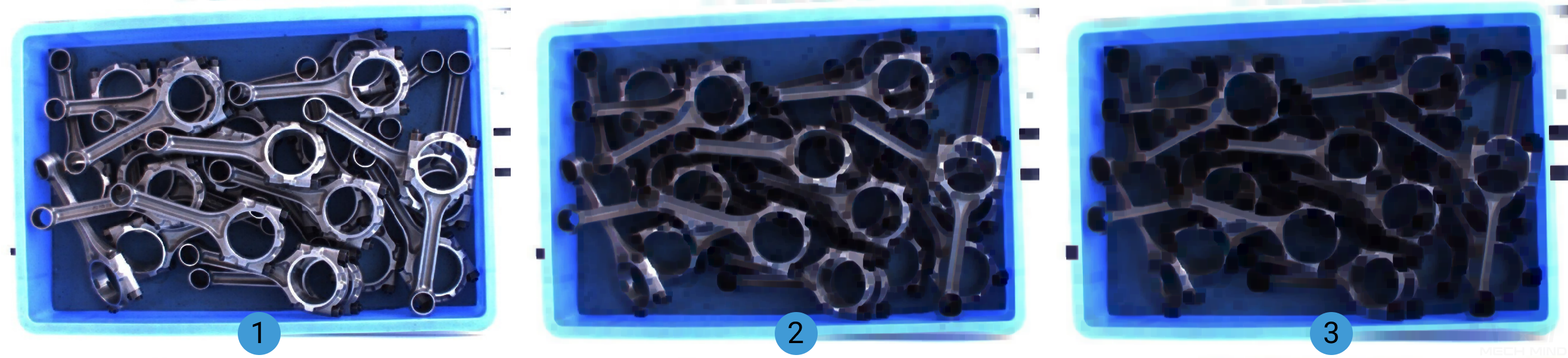
OpeningOperator¶
When OpeningOperator is selected, the size increase of the kernel is shown in the images below (The kernel size grows by degrees and from image 1 to 3):