Use Only Mech-Vision to Send Vision Points¶
This section elaborates an Adapter example program that used only Mech-Vision to sent vision points. This section includes the following contents:
Background Introduction¶
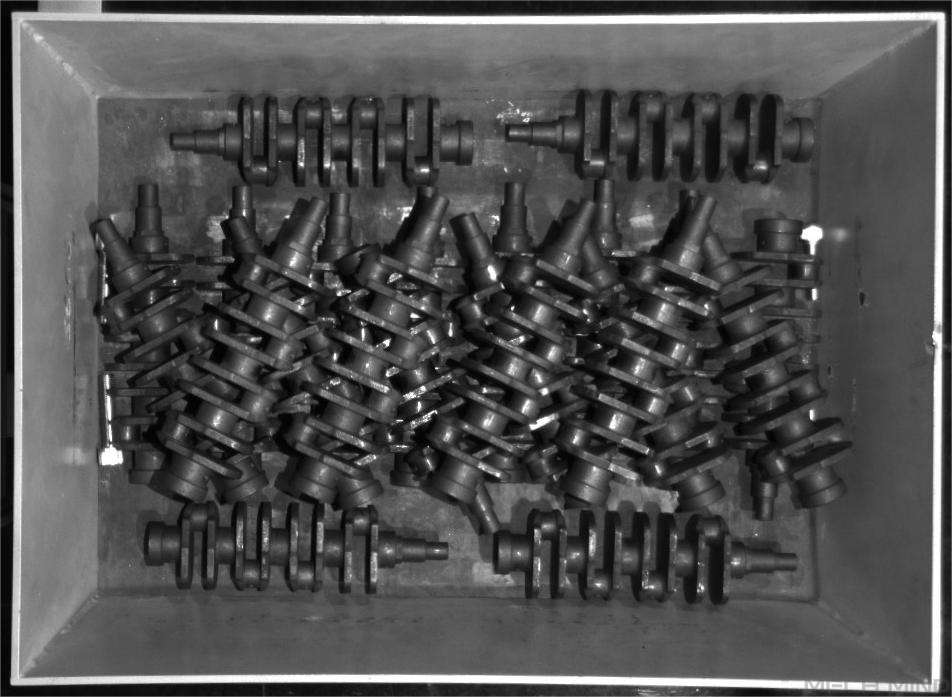
This section introduces an Adapter example program written for a crankshaft feeding scenario, in which the camera was mounted on a bracket above the bin and Mech-Vision output the pose of the workobject to pick after capturing the image.
This Adapter example program worked with the Mech-Vision example project “Large Non-Planar Workpieces” ().
This Mech-Vision example project adopted 3D model matching algorithms, and set different model files and pick points for different workobjects. Therefore, the parameter recipe needed to be set when the recipe ID (workobject ID) was sent together with the image capturing command from the robot side. For details on how to configure a parameter recipe and obtain its ID, please refer to the Parameter Recipe section.
Communication Solution¶
The robot and the industrial PC (IPC) installing Mech-Mind vision-series software communicated with each other through the TCP/IP Socket protocol. Data were exchanged in ASCII string format with the comma (,) as the separator.
During the communication, Mech-Mind vision-series software acted as the server while the robot as the client.
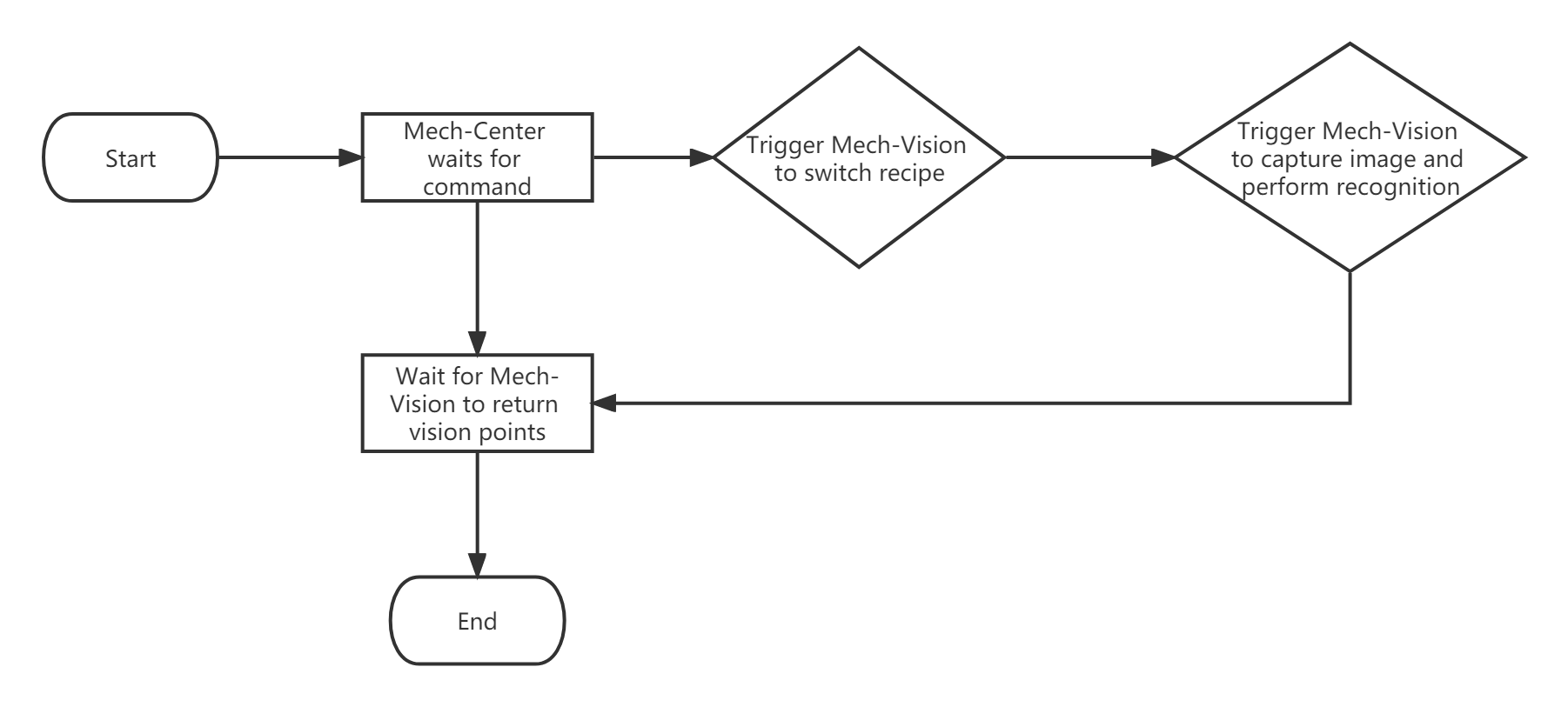
The following figure shows the communication process.
The communication process is detailed as follows:
Mech-Center waited for the robot to send the image capturing command
Pand the recipe ID.Mech-Center triggered Mech-Vision to switch the parameter recipe.
Mech-Center triggered Mech-Vision to capture the image and perform recognition.
Mech-Vision returned the status code and the pose of the workobject to pick after successful image capturing and recognition.
Mech-Center returned the status code and the robot Tool Center Point (TCP) pose to the robot.
Note
To facilitate the robot’s picking, Mech-Center converted the pose of the workobject to pick to the robot TCP.
Packet Format¶
The following table shows the packet format used for communication.
Request Command
Workobject ID
Sending (Robot -> IPC)
PAn integer, value range: 1–100
Status Code
Vision Point (TCP)
Receiving (IPC -> Robot)
An integer, value range: 0–4; 0-Normal recognition; 1-Illegal command; 2-Vision project not registered; 3-No vision points; 4-No point clouds
6 floating-point values separated by comma (,) in the format of x,y,z,a,b,c
Note
The length of the response packet is fixed. If the status code in a response packet is a value from 1 to 4, the vision point data will be filled in with zeros (0).
Packet Example
Request
P,1Normal response
0,1994.9217,-192.198,506.4646,-23.5336,-0.2311,173.6517Note
This example indicates that Mech-Vision successfully recognized the workobject and returned the TCP: 1994.9217,-192.198,506.4646,-23.5336,-0.2311,173.6517.
Abnormal response: illegal command
1,0,0,0,0,0,0Abnormal response: Vision project not registered
2,0,0,0,0,0,0Abnormal response: No vision points
3,0,0,0,0,0,0Abnormal response: No point clouds
4,0,0,0,0,0,0
Programming Guidelines¶
To fulfill project objectives, the Adapter example program has been written according to the following guidelines.
The preceding figure lists only the core packet processing logic. The next section will explain the Adapter example program in detail.
Explanations to Example Program¶
Note
You can download the Adapter example program here .
Import Python packages
Import all modules depended by the Adapter program.
import json import logging import math import sys from time import sleep import os sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "..", ".."))) from transforms3d import euler from interface.adapter import TcpServerAdapter, TcpClientAdapter from util.transforms import object2tcp
Define class
Define the sub-class “TestAdapter” that inherits the parent class “TcpServerAdapter”.
class TestAdapter(TcpServerAdapter): vision_project_name = "Large_Non_Planar_Workpieces" # vision_project_name = 'Vis-2StationR7-WorkobjectRecognition-L1' is_force_real_run = True service_name = "test Adapter" def __init__(self, address): super().__init__(address) self.robot_service = None self.set_recv_size(1024)Note
This example defined the Adapter program as the TCP/IP Socket server.
Set how to receive command and the packet processing logic
Set the processing logic of the received request, including the image capturing command and parameter recipe ID.
# Receive command _create_received_section def handle_command(self, cmds): photo_cmd, *extra_cmds = cmds.decode().split(',') recipe = extra_cmds[0] # Check command validity _check_cmd_validity_section if photo_cmd != 'P': self.msg_signal.emit(logging.ERROR, 'Illegal command: {}'.format(photo_cmd)) self.send(('1' + '' + '').encode()) return # Check whether vision is registered _check_vision_service_section if not self.is_vision_started(): self.msg_signal.emit(logging.ERROR, 'Vision project not registered: {}'.format(self.vision_project_name)) self.send(('2' + '' + '').encode()) return # Change TODO parameter "extra_cmds" according to actual conditions sleep(0.1) # wait for a cycle of getting in Vision # _check_vision_result_function_section try: result = self.select_parameter_group(self.vision_project_name, int(recipe) - 1) if result: result = result.decode() if result.startswith("CV-E0401"): self.send(('5' + '' + '').encode()) return elif result.startswith("CV-E0403"): self.send(('5' + '' + '').encode()) return raise RuntimeError(result) except Exception as e: logging.exception('Exception happened when switching model: {}'.format(e)) self.send(('5' + '' + '').encode()) return self.show_custom_message(logging.INFO, "Switched model for project successfully") self.msg_signal.emit(logging.WARNING, 'Started capturing image') try: self.check_vision_result(json.loads(self.find_vision_pose().decode())) except Exception as e: self.msg_signal.emit(logging.ERROR, 'Calling project timed out. Please check whether the project is correct: {}'.format(e)) self.send(('2' + '' + '').encode())Note
“handle_command” function the start point for the TCP/IP Socket server to process received packets.
Define the check of Mech-Vision vision results
Set the Adapter to check Mech-Vision vision results.
# Check vision results def check_vision_result(self, vision_result, at=None): noCloudInRoi = vision_result.get('noCloudInRoi', True) if noCloudInRoi: self.msg_signal.emit(logging.ERROR, 'No point clouds') self.send(('4' + '' + '').encode()) return poses = vision_result.get('poses') labels = vision_result.get('labels') if not poses or not poses[0]: self.msg_signal.emit(logging.ERROR, 'No vision points') self.send(('3' + '' + '').encode()) return self.send(self.pack_pose(poses, labels).encode()) self.msg_signal.emit(logging.INFO, 'Sent TCP successfully')
Set the output format of vision points
Set the output format of the vision points.
# Pack pose _pack_pose_section def pack_pose(self, poses, labels, at=None): pack_count = min(len(poses), 1) msg_body = '' for i in range(pack_count): pose = poses[i] object2tcp(pose) t = [p * 1000 for p in pose[:3]] r = [math.degrees(p) for p in euler.quat2euler(pose[3:], 'rzyx')] p = t + r self.msg_signal.emit(logging.INFO, 'Sent pose: {}'.format(p)) msg_body += ('{:.4f},' * (len(p) - 1) + '{:.4f}').format(*p) if i != (pack_count - 1): msg_body += ',' return '{},'.format(0) + msg_body + ''
Define the close operation of Adapter
Define how to close Adapter.
def close(self): super().close()