Other Interfaces¶
This section introduces other interfaces of Adapter, as listed below.
Notify Service¶
When a Mech-Viz project proceeds to a particular branch or Step, and a corresponding function in Adapter program needs to be called, you can add a Notify Step in the project.
Example
For example, a function is written to increase the number of depalletized parts in the Adapter program. Then we can add a Notify Step after the last Step of the depalletizing process. When the project executes to the Notify Step, the Adapter can be triggered to call the function. The example function is shown below.
Create a class that inherits the parent class NotifyService.
from interface.services import NotifyService, register_service class NotifyService(NotifyService): service_type = "notify" service_name = "FANUC_M410IC_185_COMPACT" def __init__(self, update_success_num, update_fail_num): self.update_success_num = update_success_num self.update_fail_num = update_fail_num def handle_message(self, msg): if msg == "Success": self.update_success_num() elif msg == "Fail": self.update_fail_num()
When Mech-Viz executes to the Notify Step and a message “Success” is sent, the Adapter will call the update_success_num() function, while a message “Fail” will trigger the Adapter to call the update_fail_num() function.
Instantiate the NotifyService class and register the service in the class that controls the main program of Mech-Viz.
class MyClient(TcpClientAdapter): def __init__(self, host_address): super().__init__(host_address) self._register_service() def _register_service(self): self.robot_service = NotifyService(self.update_success_num, self.update_fail_num) self.server, port = register_service(self.hub_caller, self.robot_service) def update_success_num(self): # the num of unstack successfully plus 1 self.success_num += 1 def update_fail_num(self): # the num of unstack fiplus 1 self.fail_num += 1
Add Notify Step in a proper position in the workflow of Mech-Viz.
Please note that the Adapter Name and Message in the Notify Step correspond to service_name and msg set in the NotifyService class, and therefore the parameters set in Mech-Viz should be configured accordingly.
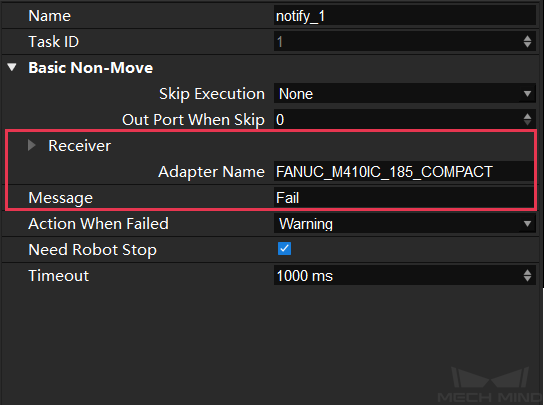
After the project is executed, if the notify service is successfully registered, the service_type and service_name will be displayed in the interface of Mech-Center.
VisionWatcher Service¶
After Mech-Vision finished running, some results will be output, such as vision result:{‘noCloudInRoi’: False, ‘function’: ‘posesFound’, ‘vision_name’: ‘TJTvision-3’}. If some problems occur, Adapter can send out error messages via VisionWatcher service.
Example
Create a class that inherits the class VisionResultSelectedAtService.
from interface.services import VisionResultSelectedAtService, register_service class VisionWatcher(VisionResultSelectedAtService): def __init__(self, send_err_no_cloud): super().__init__() self.send_err_no_cloud = send_err_no_cloud def poses_found(self,result): has_cloud_in_roi = not result.get("noCloudInRoi", False) if not has_cloud_in_roi: time.sleep(2) self.send_err_no_cloud()
The child class VisionWatcher needs to override the poses_found() function of the parent class, so the logic of calling the function send_err_no_cloud() that sends error messages in Adapter will be changed in poses_found(). During operation, the value of vision result will be passed to the parameter result in poses_found().
Instantiate the VisionWatcher in the class that controls the main program of Mech-Viz.
class MyClient(TcpClientAdapter): def __init__(self, host_address): super().__init__(host_address) self._register_service() def _register_service(self): self.robot_service = VisionWatcher(self.send_err_no_cloud) self.server, port = register_service(self.hub_caller, self.robot_service) def send_err_no_cloud(self): # send no cloud error message self.send("12,NoCloudErr,done".encode())
In the instantiation of VisionWatcher class, the send_err_no_cloud() function is passed to VisionWatcher() as a parameter. When there are no point clouds, according to the logic in poses_found(), the function that sends error messages will be called.
In running of the project, if the VisionWatcher service is successfully registered, it will be displayed in the interface of Mech-Center.