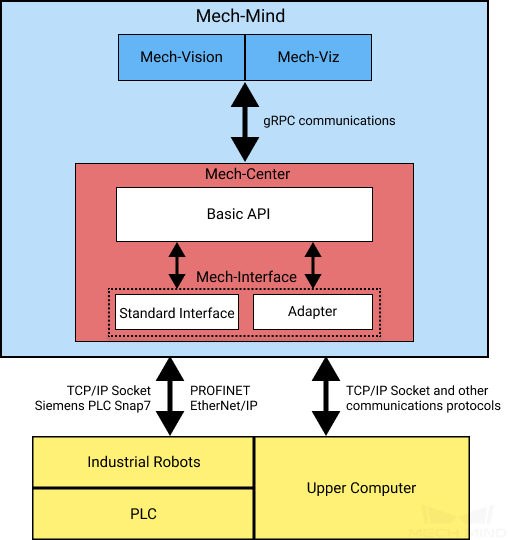
Mech-Interface Overview¶
This section covers the mechanism, differences between the two types of communication, and their application scenarios.
Communication Mechanism¶
The two types of communication mechanism are as shown in the figure below.
Adapter is a Python program that is used to establish communication between external communication devices (e.g., industrial robots, upper computers, PLC) and Mech-Vision and Mech-Viz. It cannot only communicate with Mech-Vision and Mech-Viz, but also communicate with external devices over any communication protocol supported by Python.
Standard Interface can be viewed as a complete set of Adapter programs provided by Mech-Mind. It supports a number of communication protocols and provides a powerful control command set and an error monitoring system. With these powerful functions, it can meet the requirements of most users.
Differences between Standard Interface and Adapter¶
Adapter and Standard Interface are both used to establish communication between external devices and Mech-Vision and Mech-Viz. Standard interface is a set of standardized Adapter programs, which does not support customized development.
For internal communication with Mech-Vision and Mech-Viz, both types of communication utilize Basic API, while specific communication protocols are used to communicate with external devices.
The differences between Standard Interface and Adapter are as shown in the table below.
Differences or Similarity |
Standard Interface |
Adapter |
Internal Communication |
Utilize Basic API to communicate with Mech-Vision and Mech-Viz |
|
External Communication |
Support the following communication protocols only: - TCP/IP Socket - UDP - Siemens PLC Snap7 - PROFINET - EtherNet/IP - Mitsubishi MELSEC - Modbus TCP |
Support any type of communication protocol supported by Python |
Function |
Provide vision results only |
|
Deployment Difficulty |
Easy to use, and can be deployed rapidly |
Require programming with high time and labor costs |
Extensibility |
Do not support extension |
Can be extended to support more communication protocols and functions |
Application Scenarios¶
In real application scenarios, the selection of a specific type of Mech-Interface is based on external communication devices, the communication protocol in use, the required communication functions, etc.
The common communication devices and protocols supported by Standard Interface and Adapter are as shown in the table below.
External Device |
Protocol |
Type of Mech-Interface |
Description |
Robot |
TCP/IP Socket |
Standard Interface |
Mech-Interface acts as the server |
UDP |
Mech-Interface acts as the server |
||
PROFINET |
Mech-Interface acts as the slave device |
||
EtherNet/IP |
Mech-Interface acts as the slave device |
||
Modbus TCP |
Mech-Interface acts as the slave device |
||
Upper Computer |
HTTP |
Adapter |
Applicable to integrated project where the robots are master-controlled by Mech-Mind |
WebSocket |
|||
TCP/IP Socket |
Standard Interface |
Mech-Interface acts as the server |
|
PLC |
TCP/IP Socket |
Standard Interface |
Mech-Interface acts as the server |
Siemens PLC Snap7 |
Mech-Interface acts as the client |
||
PROFINET |
Mech-Interface acts as the slave device |
||
EtherNet/IP |
Mech-Interface acts as the slave device |
||
Modbus TCP |
Mech-Interface acts as the slave device |
||
Mitsubishi MC |
Mech-Interface acts as the client |
Hint
When Mech-Interface is used to communicate with external devices, it is recommended to use Standard Interface if the project requirements can be met; when Standard Interface cannot meet all the requirements (for example, the communication protocol used by external devices is not supported, or other functions that are not supported by Standard Interface is required), Adapter should be used.
Please refer to Standard Interface Development Manual for functions of Standard Interface.
Please refer to Functions for functions of Adapter.
Please refer to the following sections for more detailed information about Standard Interface and Adapter.