Error Control¶
During project implementation, one of the most commonly encountered problems is the picking error. The picking error refers to the situation where the robot does not reach the ideal position when picking the workpiece. Picking errors can be caused by various reasons, and can be analyzed from the three aspects, namely the extrinsic parameter error, vision error, and robot error. The detailed structure is shown in the figure below.
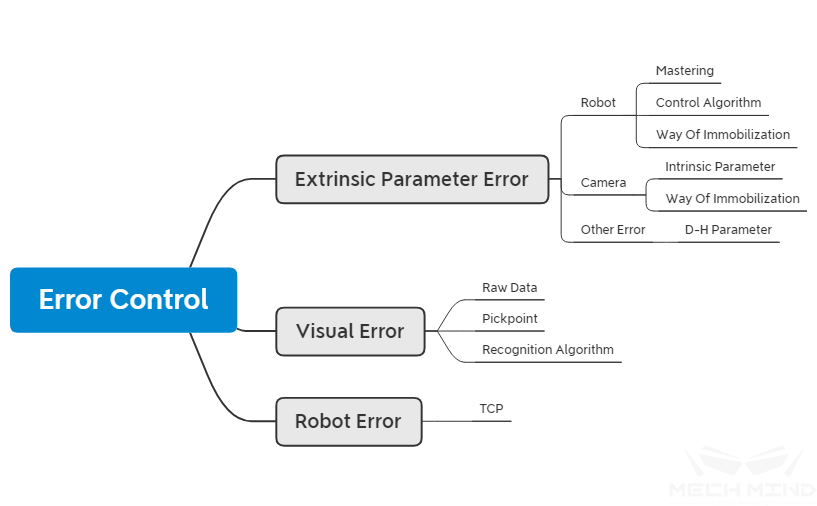
Extrinsic Parameter Error¶
Robot¶
Zero Position¶
- Zero position
The robot controls the movement of each axis for the robot motor via a closed-loop servo system, and controls each motor by the instructions of the controller. The pulse encoder installed on the motor can feedback the signal of the motor to the robot. During the robot’s movement, the controller continuously receives and analyzes the signal returned by the encoder, so as to achieve the correct control of the robot during the entire movement. The controller accurately analyzes the information returned by the encoder based on the zero position (also called home position) of each axis, so that the position of the robot can remain unchanged during the operation. During the normal operation of the robot, the zero position and the joint position of the robot will be saved, and the internal battery will be used to maintain power when the controller is normally powered off. This data will be saved every time the robot is shut down normally. Each time the robot is powered on, it will directly read the data in the backup for identification to ensure the same state as when the power was off. The zero position of the robot may be shifted or lost under conditions such as impact, battery power loss, or unused for a long time.
If the zero position of the robot is missing, it may be caused by the following reasons:
The robot’s joint axes work beyond the soft limits (this is very dangerous);
The robot cannot reach the specified position , because a different zero position results in different robot tool positions under the same joint angle;
The robot cannot move the specified length along the specified direction (such as unable to walk 1 meter correctly).
When Mech-Vision is used to calibrate extrinsic parameters, it calculates the multiple waypoints that the robot should reach based on the calibration parameters. When the zero position of the robot is lost, the robot is often impossible to reach these waypoint accurately, finally causing errors in the calculation results of the extrinsic parameters.
Tip
There are many ways to detect whether the robot zero position is missing. Here are two of the most commonly used detection methods:
Adjust the angle of all robot axes to 0° by using the teach pendant, and then observe whether the nameplates on the axes of the robot are aligned. If they are not aligned, it indicates that the robot zero position is lost;
Control the robot to move a certain distance along the specified direction and observe whether the robot’s walking distance is consistent with the theoretical distance.
When confirming that the zero position of the robot is lost by the above methods, you can calibrate the zero position according to the zero-position calibration method of different robots.
Control Algorithm¶
Some newly developed robots have problems with the control algorithm at a low probability, that is, the robot cannot move to a specified position, and there is a deviation. In the case that the robot cannot accurately move to an accurate position, the robot thus cannot perform the tasks of calibrating the extrinsic parameters.
Mounting Method¶
The mounting method of the robot directly determines whether the robot can maintain stability during the long-term operation. If the robot is mounted insecurely, for example, it is mounted using expansion bolts or large bases with fixing, it cannot guarantee that the robot will remain stable or keep the running at high speed during the long-term operation. If the robot moves, the position relationship between the robot and the camera is destroyed, and the robot will not pick accurately. This situation is not common and is hard to detect once it happens. Therefore, you need to confirm the mounting method when mounting the robot.
Tip
If the long-term operation is required, it is best to use chemical bolts for fixing. Do not operate the robot until the chemical bolts are firmly fixed; otherwise it will cause the bolts to loose;
If the short-term operation is required, such as exhibitions, the robot can be fixed on a relatively stable surface. However, the speed of the robot should not be adjusted to a particularly high value; otherwise it will cause the robot to move.
Camera¶
Intrinsic Parameter¶
The extrinsic parameter problems are caused by the camera’s intrinsic parameters when the camera’s field of view or working distance is exceeded. When the camera is delivered, a reasonable working distance of the camera has been determined based on the hardware. When the camera is working beyond its working distance or field of view, it will cause deviations in the generated point cloud because the camera is not accurately calibrated at these positions, which finally causes deviations in the calculated extrinsic parameters.
Tip
It is recommended that when using the camera, you should determine the working distance of the camera, check whether the intrinsic parameters of the camera are accurate, and finally calibrate extrinsic parameters within the working distance of the camera.
Mounting Method¶
The mounting method of the camera may cause the change of the extrinsic parameters. The stability of the mounting directly determines whether the station can be used for a long time and the extrinsic parameters are kept stable. For details on how to mount the camera, please see Mounting the Camera.
Tip
The severe collisions on the camera stand or large vibrations may also cause the camera stand to become loose. Take special care when mounting the camera and prevent the camera stand from being bumped and leaned against.
Other Errors¶
In the process of initial adaptation of the robot, in order to obtain the kinematic relationship of the robot, it is necessary to find the operation parameters of the corresponding robot (hereinafter referred to as D-H parameters) in the robot’s websites or user manuals. The relationship between the joint axes of the robot can be established by obtaining the operation parameters of the robot. In the actual process, the D-H parameters in the software may be inconsistent with those of the real robot. There are two possible causes:
Robot sub-models of the obtained D-H parameters are incorrect or the obtained D-H parameters have a certain error with the real robot;
There is a difference in D-H parameters between the user manual and the real robot.
If the D-H parameters are inconsistent, the TCP of the robot in the software may be different from that in the teach pendant, which will cause the extrinsic parameter deviation during the calculation.
Tip
To check whether D-H parameters are consistent, connect to the robot by Mech-Viz, observe whether the posture of the 6 axes of the robot is consistent with the TCP in Mech-Viz under the condition that joint angles on two sides are consistent. If they are inconsistent, deviant D-H parameters may be the reason.
Vision Error¶
Raw Data¶
- Raw data:
Raw refers to the raw data input to Mech-Vision for processing. The data mainly includes RGB images and depth maps.
When the light is changed (such as from day to night) on the site, if the configuration parameters on the camera are not updated in time, the follow issues may occur:
The collected point cloud has too much noise or the details are not obvious, making subsequent matching algorithm unable to continue or identify errors;
The quality of the collected RGB images changes, and the brightness of the images collected in a dark environment is not enough, resulting in no results in deep learning or poor recognition results.
Tip
If the above issues occur, you can adjust the 2D and 3D exposure parameters respectively in Mech-Eye Viewer, so that the RGB images and the depth maps meet requriements. Alternatively, during project deployment, apply Illumination Control.
Pick Point¶
Pick point error is one of the common errors. There are two methods to set the pick point in Mech-Vision: one is dragging the pick point, and the other is teaching the pick point. The pick point added by teaching has a small error under the condition that the robot is accurate, so this situation is not considered here, and the situation of dragging a pick point will be analyzed here.
Dragging a pick point is required to be performed in Mech-Vision. You can adjust the position of the pick points based on the matching model. Dragging a pick point is relatively inaccurate, because it does not provide the position that the robot should reach. In real situations, ideal positions may not be able to reach by the robot. If a more accurate pick point is required, please use the teaching method to obtain the pick points.
Tip
If there are errors in the pick points, you can directly find them from the coordinates on the point cloud in the Mech-Viz software and check whether the pick points of each workpiece are in the ideal position.
Algorithm¶
Deviations due to the output by Mech-Vision are collectively referred to as algorithm errors here. The deployment of vision algorithms is often set based on the original images collected on site. If the changes in lighting and working environment occur, the original parameters may not be applicable. It can be found in Mech-Vision and adjusted according to the instructions of the software user manual. Meanwhile, the recognition of some special workpiece may lead to sporadic errors, that is, no problems occur during the long-term operation, and occasional recognition errors occur due to the environmental changes, especially for the axisymmetric objects, the local optimal solution will occur, which leads to recognition error.
Attention
Errors may occur due to template errors on some sites, that is, the template obtained via the STL file is inaccurate with the actual object to be captured, which will cause that the best results cannot be obtained when performing the template matching. The possible causes for this are
The STL file is the file for the finished product, but the file to be grasped is the file for the rough material. In the production process, a machining allowance is left to ensure subsequent processes, which results in the workpiece that needs to be identified is larger than the template file.
At this time, you can adjust the scaling of the template appropriately.
Robot Error¶
TCP¶
The TCP error of the robot refers to the inconsistency between the actual tool center and the theoretical tool center of the robot. It is mainly caused by inaccurate robot TCP calibration. For example, the fixed point is moved, the robot’s posture change is not large enough, and the TCP does not match with the fixed point. During the use of the software, it is required to create a tool in Mech-Viz and enter the correct TCP value.
Tip
To calculate TCP, a better method is to use a robot to calibrate TCP, and enter the calibrated value into Mech-Viz, and save a backup on the robot side.
Tip
For a project that does not require high accuracy, directly adjust the TCP value in the software to improve the accuracy of the picking.