Introduction to Image Classification¶
What Image Classification Does¶
Image classification solves the problem of what an object is.
In industrial scenarios, image classification means recognizing workpieces’ types, models, front and back faces, and correctness of placing, etc.
In the example below, the target objects are almonds, walnuts, and cashews. Given an image, the image classification model determines whether it is an almond, walnut, or cashew in the image and assigns the corresponding label to the image.
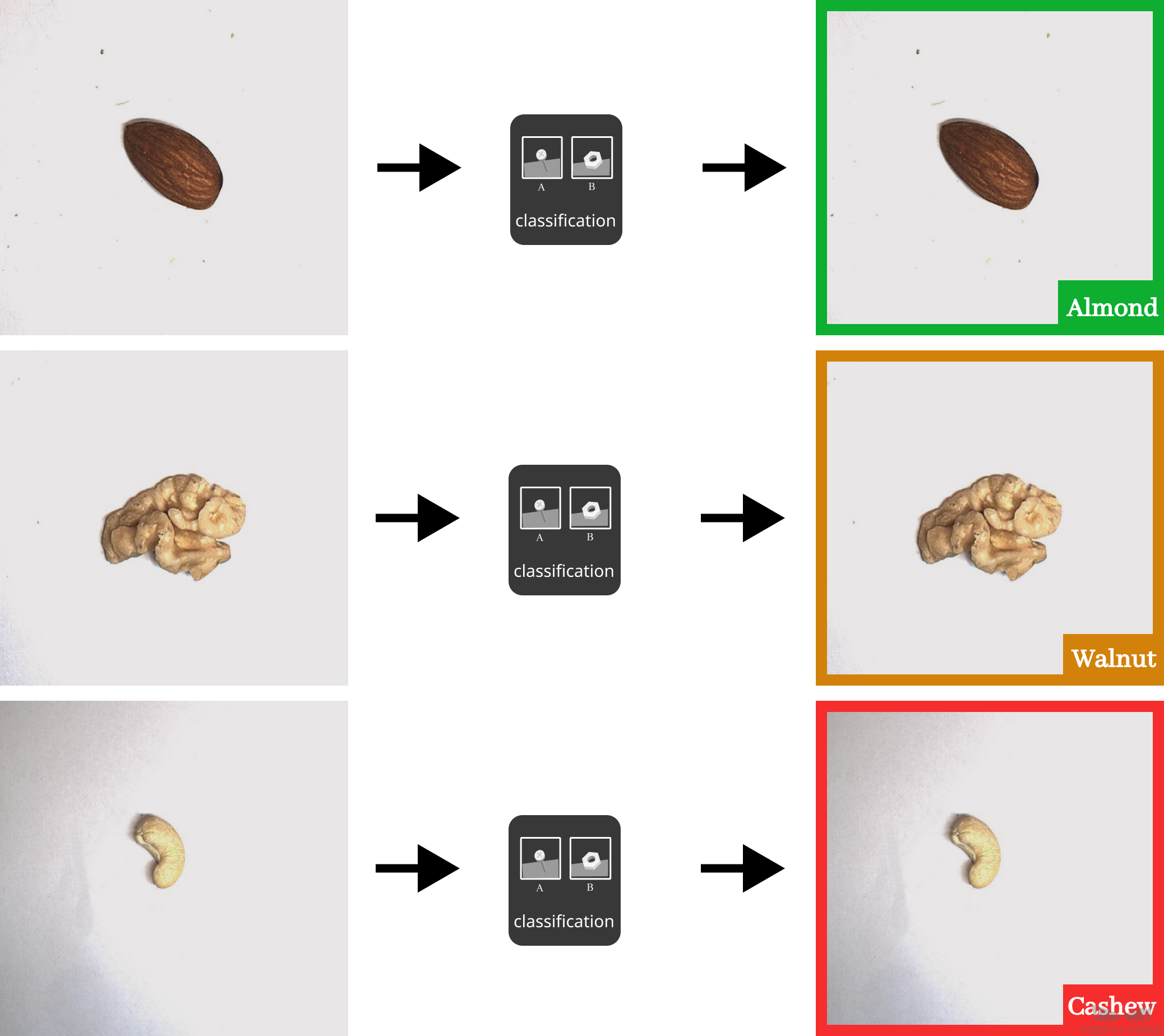
Figure 1. Classifying and assigning labels to images¶
Attention
A label assigned by an image classification model is for the entire image. If an image contains multiple objects of different classes, classification of such an image requires the image to be segmented first so that each segment contains only one object. Alternatively, instance segmentation or object detection can be used based on actual needs.
Typical Industrial Application Scenarios of Image Classification¶
The image classification model can be used for projects that involve classifying different images. The following are some typical application scenarios:
Distinguishing the type, orientation, front and back faces of workpieces for machine tending projects.
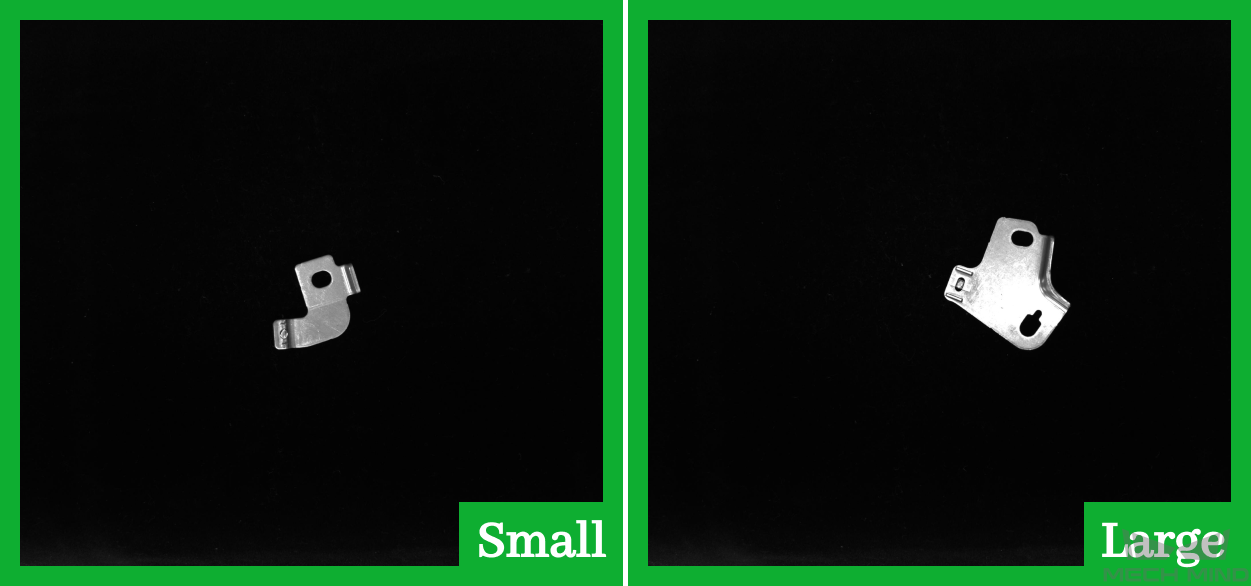

Figure 2. Recognizing different types of workpieces for machine tending¶
Judging whether the objects are placed correctly for assembly or picking.
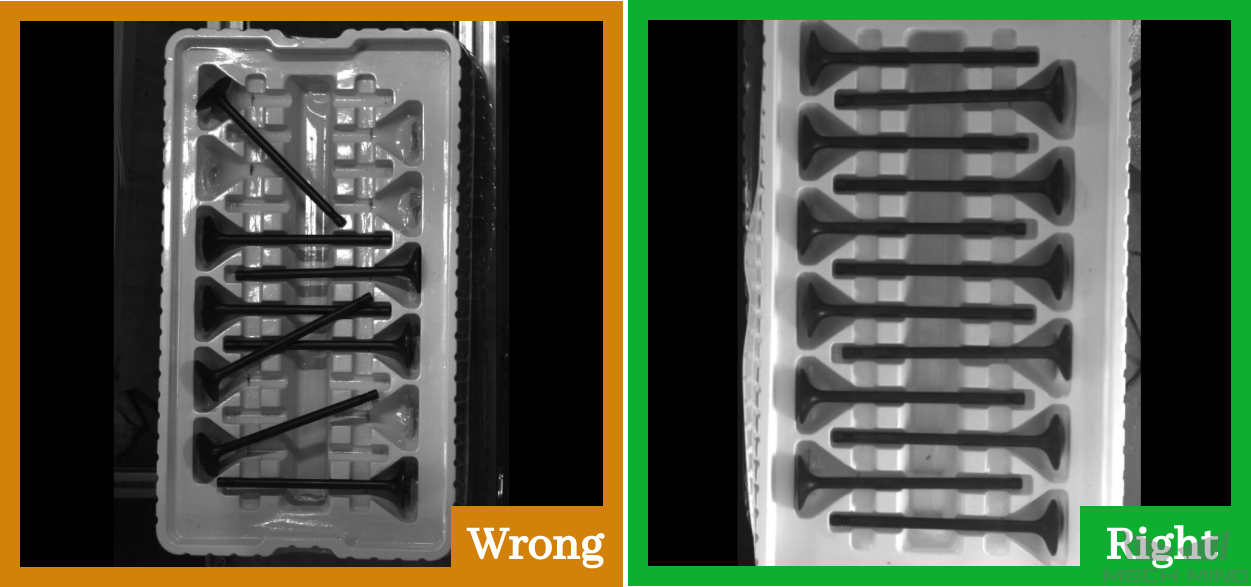
Figure 3. Determining whether objects are placed correctly¶
Application Process of Image Classification¶
Given a sufficient quantity of correctly labeled training image data obtained from actual application scenarios, an image classification model can be properly trained to correctly classify target objects. The application process of image classification is as follows:
Collect the Training Data: take enough pictures of target objects in each class with the camera.
Label the Training Data: assign a label corresponding to the object to each picture.
Train the Model: feed the labeled data to the image classification model for training.
Use the Model: apply the trained model in an actual project.